Power grid weak link identification method based on Bayesian reasoning
A weak link and identification method technology, applied in the direction of power network operating system integration, electrical components, circuit devices, etc., can solve the problems of identifying the actual power grid, computing power and network adaptability constraints, identification and evaluation objects not covered, etc. , to achieve the effect of reducing the modeling error
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
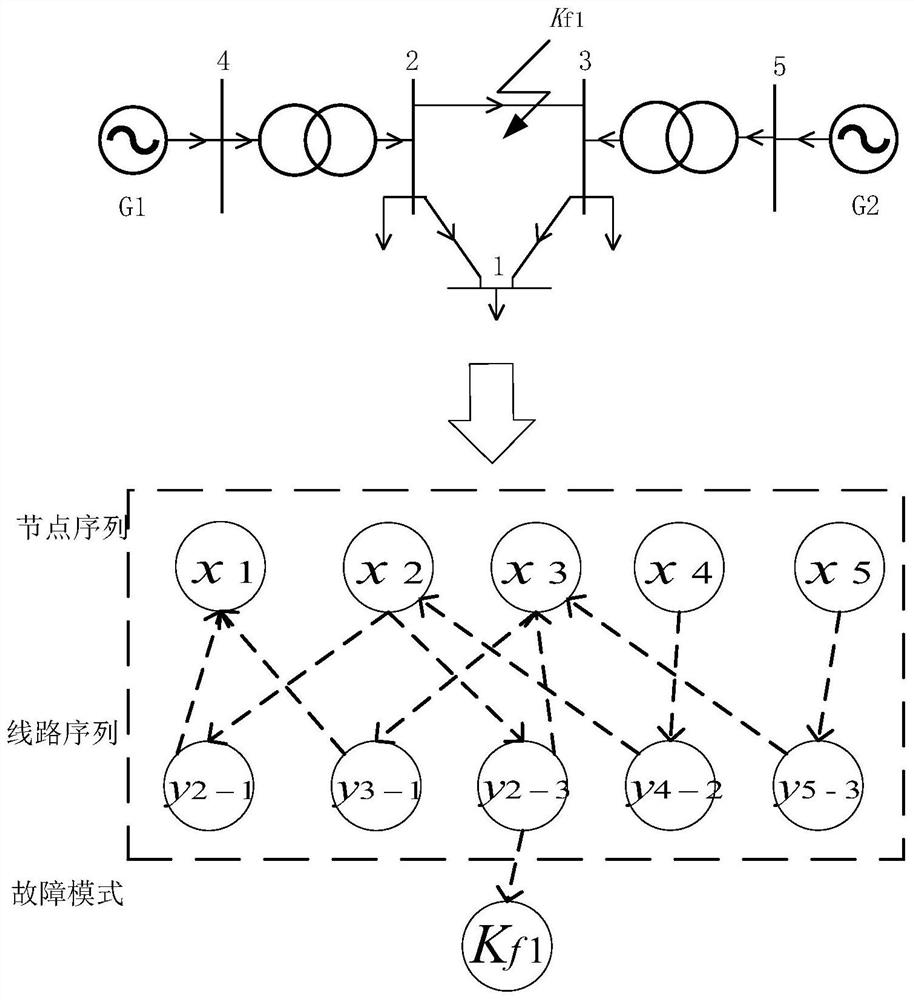
[0037] The embodiment of the present invention provides a comparison diagram of the power flow topology of a simple power grid and the Bayesian network model proposed by the present invention for auxiliary analysis, such as figure 1 Shown:
[0038] according to figure 1 According to the topological structure of the power grid, the nodes and branches in the network are separated, and the nodes and branches are connected one by one by topological knot lines. According to the real-time running power flow results, the direction of the branch-nodes in the model is determined according to the flow direction. The node points to the end node and obeys the node conditional probability distribution and the joint probability distribution
[0039] figure 1 Middle current slave node X 5 Flow X 3 through the middle node y 5-3 , then the corresponding parent node X in the Bayesian network 5 point to the middle node y 5-3 , satisfying the conditional probability distribution P(y 5-3...
Embodiment 2
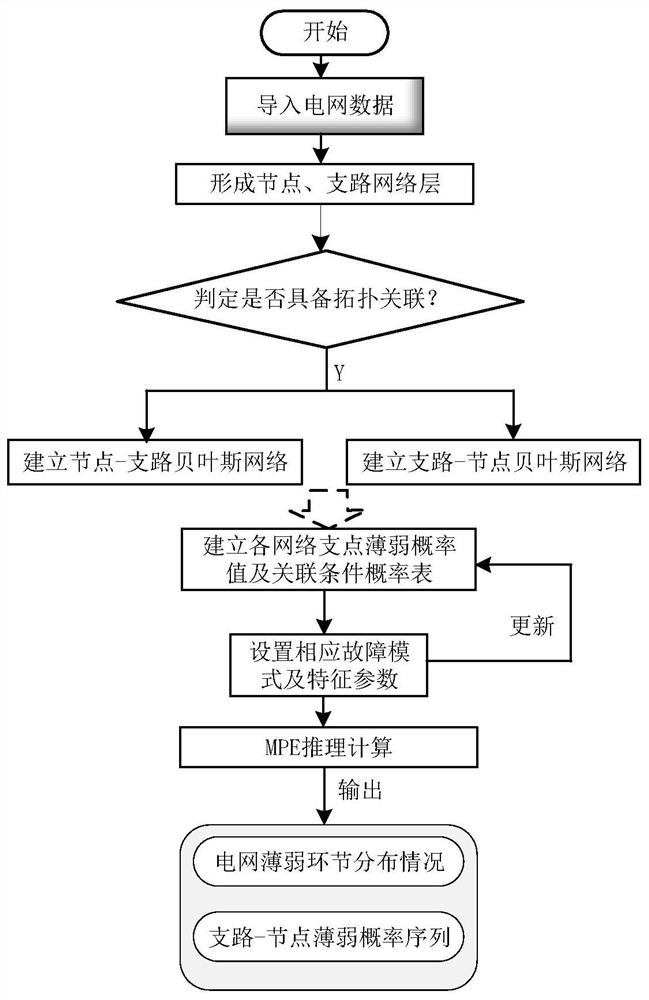
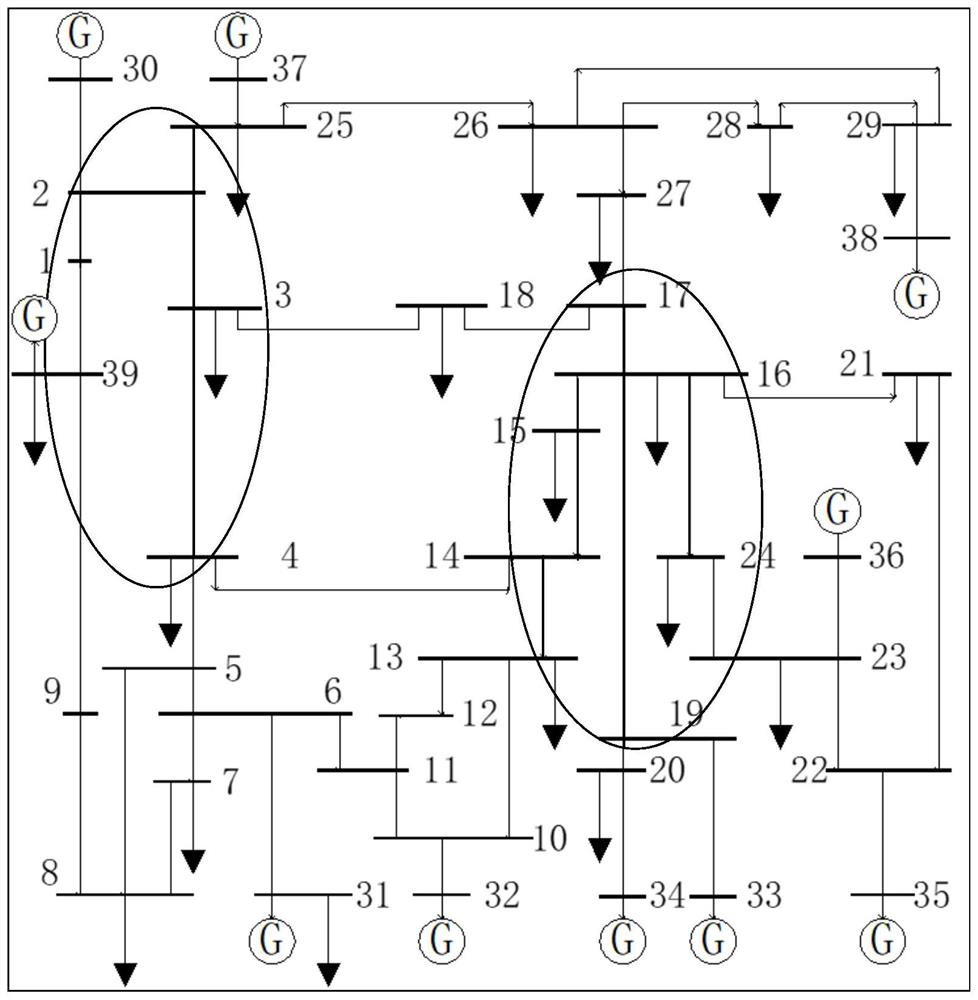
[0073] This embodiment takes the IEEE New England 39-node system as an example, and uses MATLAB programming to implement a method for identifying weak links in a power grid based on Bayesian reasoning.
[0074] Table 1 Line Weakness under Multiple Fault Modes
[0075]
[0076] Taking the three lines 13-14, 14-15, and 16-17 in the same power flow direction as an example, in Table 1, π y13-14 , π y14-15 , π y16-17 Respectively represent the weakness of lines 13-14, 14-15, 16-17, the failure mode includes single component failure and multiple failures in the N-1 criterion, O y13 , O y14 , O y16 Indicates that faults occur at nodes 13, 14, and 16 and cause network power flow changes. When multiple faults occur, the vulnerability of the same branch is greatly affected by the electrical distance of the attack point. When the fault range affects the branch, the branch vulnerability The value is relatively high, and the difference between its value and the weak degree under th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com