Nucleic acid aptamer eta01 of Pseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin a and its application
A technology of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and nucleic acid aptamers, applied in the field of biomedicine, can solve problems that have not yet been seen, and achieve the effects of wide application value, low preparation cost, and broad market prospects.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0040] Example 1: Detection of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Exotoxin A by Colorimetric Biosensor Using Nucleic Acid Aptamer ETA01 as Recognition Element
[0041] (1) Synthesize the nucleic acid aptamer ETA01 (synthesized by Shanghai Sangong Co., Ltd.), the sequence is: 5'-GAGCGGCACGAACCAGTAAAGTCTTCCCGACCGC-3'.
[0042](2) The nucleic acid aptamer ETA01 was dissolved in a suitable volume of selection buffer (50 mM Tris-HCl, 100 mM NaCl, 1 mM MgCl 2 , 5 mM KCl, pH 7.4); then heat-activated. The method of heat activation treatment is as follows: after denaturation at 95°C for 5 min, immediately placed in an ice-water bath for 10 min, and then placed at room temperature for 10 min.
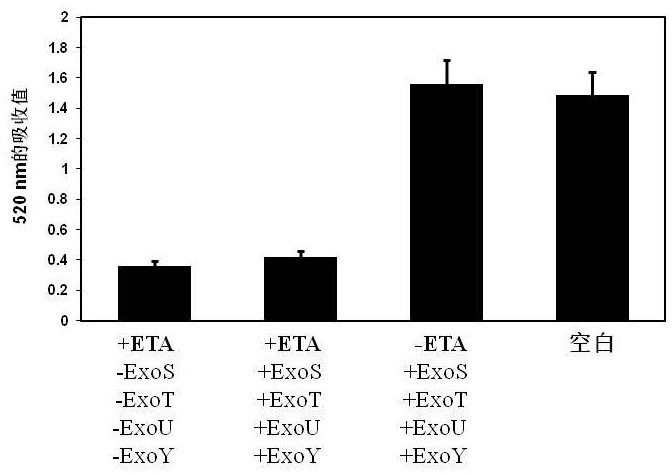
[0043] (3) The heat-activated nucleic acid aptamer ETA01 (final concentration of 2 μM) was treated with exotoxin A (ETA), extracellular enzyme S (ExoS), and extracellular enzyme T (ExoT) of Pseudomonas aeruginosa, respectively. , one or more of extracellular enzyme Y (ExoY), and extracellular enzyme U (Exo...
Embodiment 2
[0049] Example 2 Using the nucleic acid aptamer ETA01 as the recognition element, the gel migration retardation experiment was used to detect the ETA of Pseudomonas aeruginosa
[0050] (1) Synthesize the ETA01 sequence, and label the fluorophore FITC at its 5' end (synthesized by Shanghai Sangong Co., Ltd.), the sequence is: 5'-TGCAACTCCAACTAACCATGTGTTCATCTGAGGGTGGTCTTCGCA-3'.
[0051] (2) Dissolve the FITC-labeled nucleic acid aptamer ETA01 in an appropriate volume of selection buffer (50 mM Tris-HCl, 100 mM NaCl, 1 mM MgCl) 2 , 5 mM KCl, pH 7.4); then thermally activated. The method of heat activation treatment is as follows: after denaturation at 95°C for 5 min, immediately placed in an ice-water bath for 10 min, and then placed at room temperature for 10 min.
[0052] (3) Incubate the heat-activated FITC-labeled ETA01 with two mixtures of Pseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin containing and not containing ETA for 1 h at room temperature in a dark box, respectively, and the exot...
Embodiment 3
[0056] Example 3: Using the biotin-labeled nucleic acid aptamer ETA01 as the recognition element, the enzyme-linked aptamer adsorption method was used to detect the ETA of Pseudomonas aeruginosa
[0057] (1) Synthesize the sequence of nucleic acid aptamer ETA01, label the 5' end with biotin (synthesized by Shanghai Sangong Company), and the sequence is: 5'-TGCAACTCCAACTAACCATGTGTTCATCTGAGGGTGGTCTTCGCA-3'.
[0058] (2) Dissolve Pseudomonas aeruginosa ETA, ExoS, ExoT, ExoY, and ExoU expressed in E. coli in carbonate buffer at pH 9.6, the molar concentration is 100 mM, and add 100 μL / well to the enzyme-linked strip. in a humidified chamber overnight at 4°C.
[0059] (3) Discard the coating solution, add 100 μL of maleic acid blocking solution containing 1% casein to each well, and block at room temperature for 1 hour.
[0060] (4) Dissolve biotin-labeled ETA01 in an appropriate volume of selection buffer (50 mM Tris-HCl, 100 mM NaCl, 1 mM MgCl) 2 , 5 mM KCl, pH 7.4), followed b...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com