Polyurethane foams for comfort applications
A polyurethane and foam technology, applied in the field of flexible polyurethane foam, can solve the problems of low compression set, heat dissipation, low foam density, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1-2
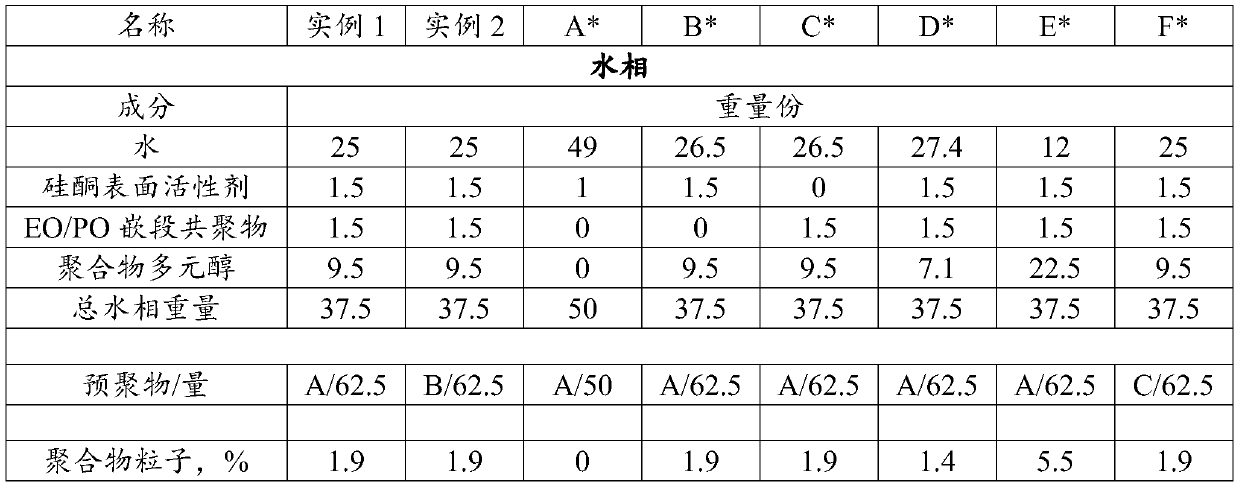
[0095] Examples 1-2 and Comparative Samples A-F
[0096] A. Quasi-prepolymer formation
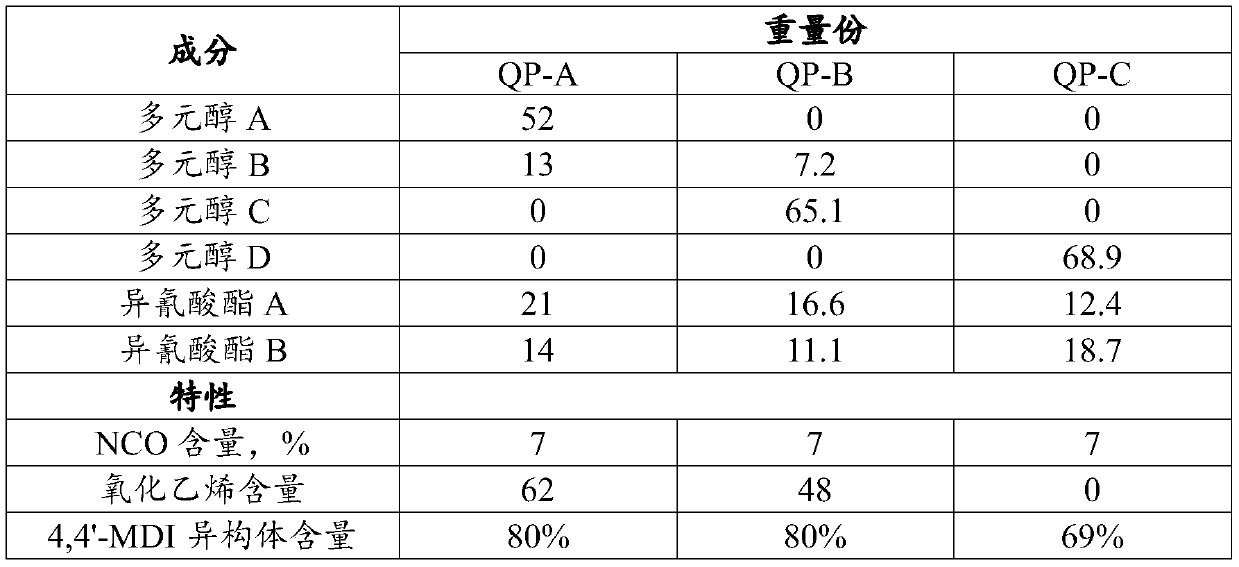
[0097] Quasi-prepolymers A-C were prepared from the ingredients as indicated in Table 1 in the following general manner. One or more polyols were dried to a moisture content of less than 250 ppm by heating the polyol to 100° C. overnight with stirring under nitrogen. A trace amount of benzoyl chloride was added to the dry polyol and stirred. Separately, one or more polyisocyanates are heated to 50°C and combined with one or more polyols. No urethane catalyst is added to the resulting reaction mixture, which contains not more than 1 part per million by weight of metal and not more than 100 parts per million of amine compound. The reaction mixture was heated at 75°C under nitrogen until a constant isocyanate content was obtained. The quasi-prepolymer was then cooled to room temperature and stored under nitrogen.
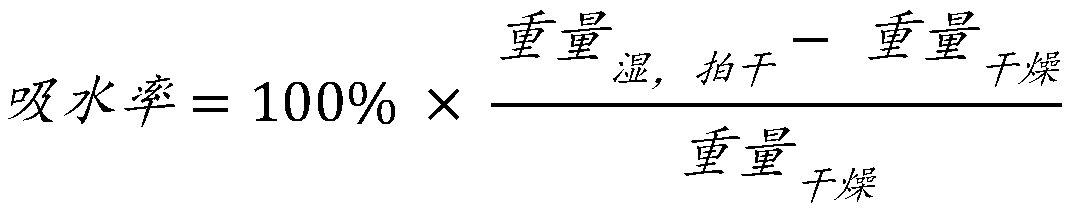
[0098] NCO content was measured according to ASTM D5155. The ethylene o...
example 2
[0122] Example 2 is the same as Comparative Sample B and Comparative Sample C except that both the silicone surfactant and the ethylene oxide / propylene oxide block copolymer are present in the aqueous phase. Density reduced to less than 60kg / m 3 , and the compression set was significantly reduced to 10%. At the same time, good moisture absorption is retained and a high air flow rate is obtained.
example 1
[0123] Example 1 shows the effect of using a quasi-prepolymer with a slightly lower ethylene oxide content. The density is significantly lower than any of Comparative Samples A-C, and the compression set is significantly lower. Moisture is retained. Example 1 represents a significant improvement over Comparative Samples A-C.
[0124] Comparative Sample D and Comparative Sample E demonstrate the effect of varying the amount of polymer polyol. Too little polymer polyol (D) or too much polymer polyol (E) can result in a significant and undesirable increase in compression set. Too little polymer polyol also results in a significant increase in density.
[0125] Comparative Sample F demonstrates the need for the quasi-prepolymer to contain oxyethylene groups. Quasi-prepolymers are not even capable of forming stable foams without the hydrophilic properties imparted by the oxyethylene groups.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Granularity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Average molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Average molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com