Preparation method of animal decellularized lung biological scaffold material
A decellularization and bio-scaffold technology, applied in tissue regeneration, medical science, prosthesis, etc., can solve problems such as unstable effect, low decellularization efficiency, and large damage to extracellular matrix components, and achieve enhanced tolerance , weaken the effect of contradiction
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0042] Example 1 Preparation of decellularized porcine lung bioscaffold material
[0043]Animals were anesthetized with Zytex, and after systemic heparinization, the lungs were removed. Insert and secure catheters from the pulmonary artery and trachea. Perfuse 2L of PBS solution containing heparin (enough dose is sufficient for anticoagulation) from the cannula of the pulmonary artery (it can also be other isotonic solutions containing anticoagulant substances, such as: aqueous solution containing calcium ion chelating agent, low molecular weight heparin , heparin analogs, etc.), the perfusion time is 0.5 hours, and then placed in a -20°C refrigerator for at least 24 hours. After the pig lungs were fully thawed, 0.9% m / v normal saline and 0.2% m / v dextrose solution (osmotic pressure 10mOsm / L) were perfused successively from the trachea at a flow rate of 100 mL / min, and the perfusion time was 1 hour and 3 hours, respectively. Hour. Afterwards, 1% v / v SLES (or other ionic det...
experiment example 1
[0052] Experimental Example 1 Comparison of pig lung bio-scaffold materials with and without dextrose solution perfusion
[0053] In this experimental example, on the basis of Example 1, the step of treating the ECM protective agent dextrose was selectively omitted, and as a control, the difference between it and the biological scaffold material obtained in Example 1 was compared.
[0054] The result is as Figure 4-Figure 9 Shown:
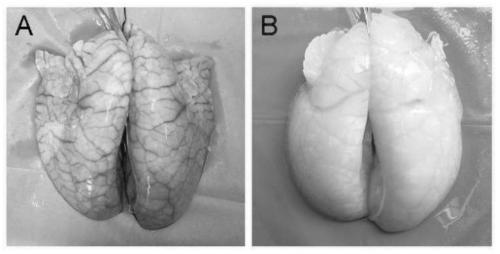
[0055] Figure 4 Decellularized porcine lung bioscaffold material treated with dextrose solution perfusion ( Figure 4 A) and pig lung bioscaffold material without dextrose solution perfusion treatment ( Figure 4 B), the results show that the texture of the decellularized porcine lung bioscaffold treated with dextrose solution perfusion is firmer and better maintains the shape of the original organ.
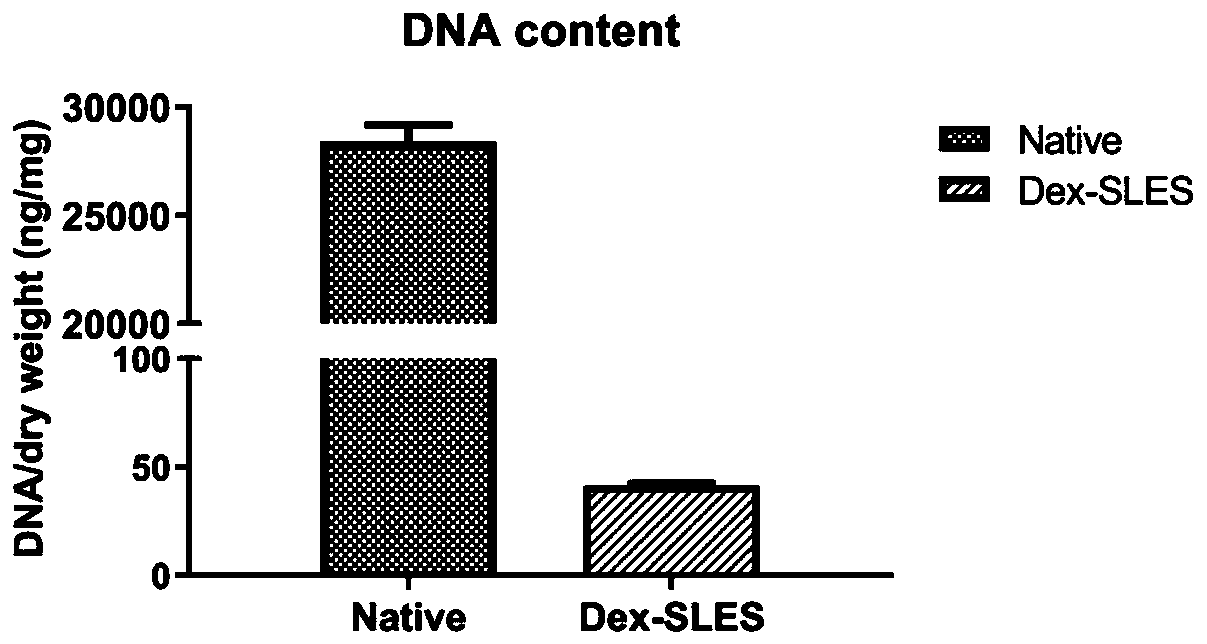
[0056] Figure 5 with Image 6 It is the results of the collagen and glycosaminoglycan GAG content of the porcine lung bioscaffold treated wi...
experiment example 2
[0059] Comparison of Experimental Example 2 Degradability and Immunogenicity
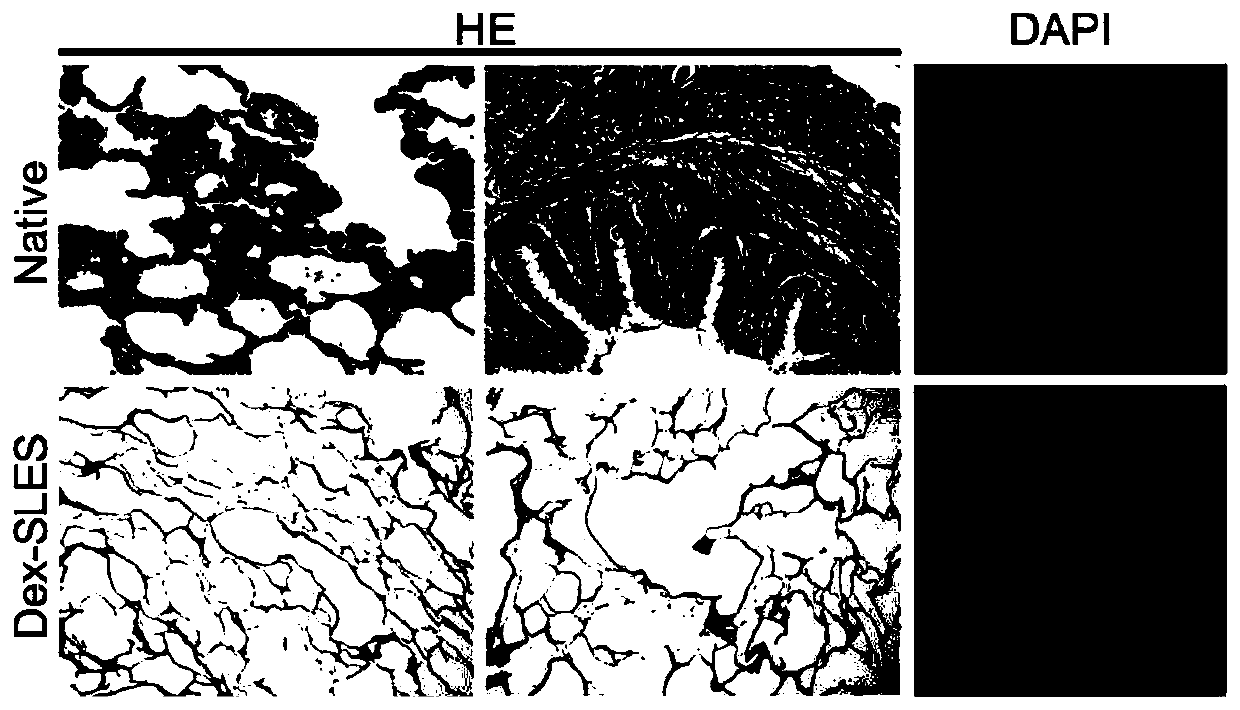
[0060] In order to test the biodegradability and immunogenicity of bioscaffolds, pig lung bioscaffolds treated with and without dextrose solution perfusion were implanted into the omentum of rats. At the 1st and 4th week of implantation, the material was removed and fixed with 4% formalin, and stained after sectioning.
[0061] The result is as Figure 9 Shown: the extracellular matrix components of the decellularized porcine lung bioscaffold treated with dextrose solution perfusion degrade more slowly, the number of neutrophils and lymphocytes infiltrated around the scaffold material is less, and the immunogen caused by Sex is lower.
[0062] Conclusion: The decellularized porcine lung bioscaffold treated with dextrose solution perfusion degrades slowly in animals, and can provide a more stable and long-lasting scaffold for stem cell attachment, propagation, and differentiation in tissue engineer...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com