doped a 5 b 19 Gadolinium-containing hydrogen storage alloy, electrode, battery and preparation method thereof
A technology of A5B19 and hydrogen storage alloy, which is applied in the direction of negative electrode, nickel battery, battery electrode, etc., can solve the problems of metal magnesium being volatile, dust explosion, safety hazards, etc., and achieves good rate discharge performance, high capacity retention rate, The effect of high discharge capacity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0078] According to one embodiment of the present invention, the doped A of the present invention 5 B 19 The preparation method of type gadolinium-containing hydrogen storage alloy comprises the steps:
[0079] (1) will be based on the doped A 5 B 19 The raw materials obtained from the composition of the gadolinium-containing hydrogen storage alloy are melted to a melt under the conditions of a pressure of -0.08 to -0.02 MPa and a temperature of 1000 to 2000 °C in an inert atmosphere;
[0080] (2) When the temperature of the melt reaches 1100-1600°C, it is made into a solid alloy;
[0081] (3) Heat-treating the solid alloy in an inert atmosphere for 10-70 hours under the conditions of a vacuum of 0.001-0.5 Pa and a temperature of 700-1500°C.
[0082] The doped A obtained by the present invention 5 B 19 type gadolinium-containing hydrogen storage alloys have the composition shown below: Re x Gd y Ni z mn a Al b m c Zr d Ti e , as described above.
[0083] In step...
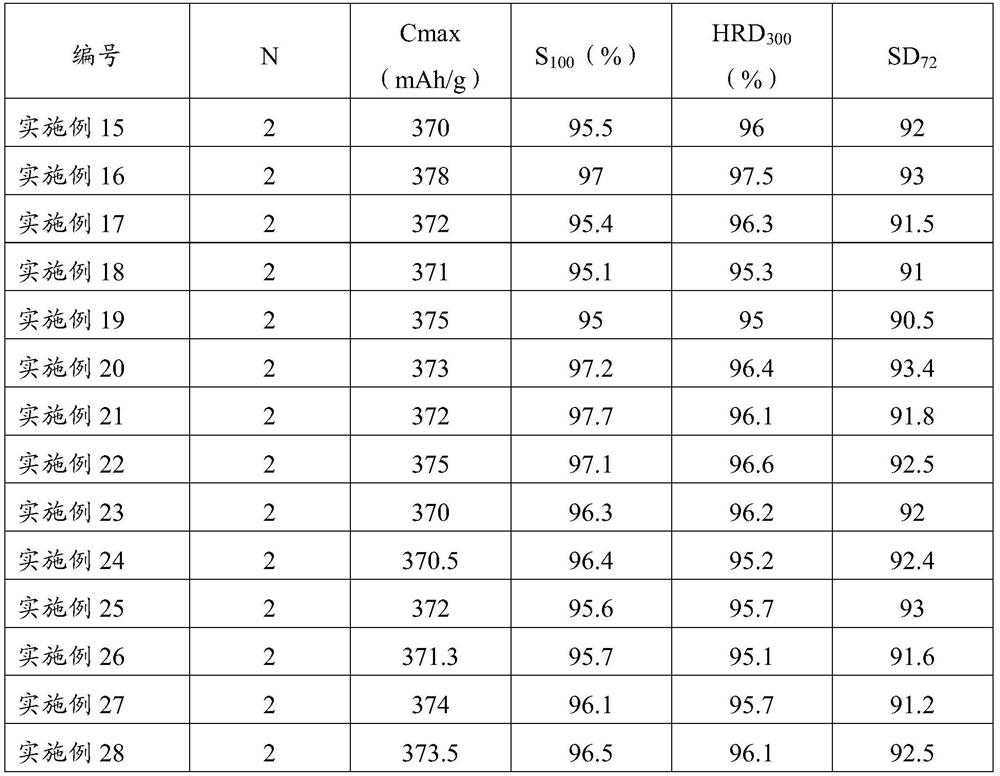
Embodiment 1~14
[0099] Select and weigh raw materials according to the composition of the hydrogen storage alloy in Table 1. The raw materials are put into the vacuum induction melting furnace, and the furnace is washed with inert gas, which is repeated 4 times. Vacuumize the vacuum induction melting furnace to 3Pa, continue to fill inert gas into the vacuum induction melting furnace, so that the pressure in the vacuum induction melting furnace is -0.055MPa. The raw material was melted to a melt at 1500°C, and the heating was stopped. When the temperature of the melt reaches 1430° C., the melt is cast to a cooling copper roll, and the flakes are flung into alloy flakes with a thickness of 0.3 mm.
[0100] Put the alloy sheet in a vacuum treatment furnace, under the protection of inert gas, heat treatment at a vacuum degree of 0.01Pa and a temperature of 950°C for 25 hours to obtain doped A 5 B 19 type gadolinium-containing hydrogen storage alloy.
Embodiment 15~28
[0102] The hydrogen storage alloys of Examples 1 to 14 were mechanically crushed into hydrogen storage alloy powders of 200 to 300 meshes, and the hydrogen storage alloy powders with a mass ratio of 1:4 were mixed with carbonyl nickel powder, and the diameters of 15mm were made under a pressure of 11MPa. The MH electrode sheet (negative electrode material). The MH electrode sheet (negative electrode material) was placed between two sheets of nickel foam, and a nickel strip as a tab was sandwiched at the same time, and then pressed under a pressure of 11 MPa to obtain a hydrogen storage alloy electrode. Spot welding around the electrode sheet ensures close contact between the electrode sheet and the nickel foam.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com