Quantum secret communication system and method based on secret sharing and asymmetric cryptography
A quantum secure communication and asymmetric cryptography technology, applied in key distribution, can solve problems such as key pool theft, vulnerability, loss of key security, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
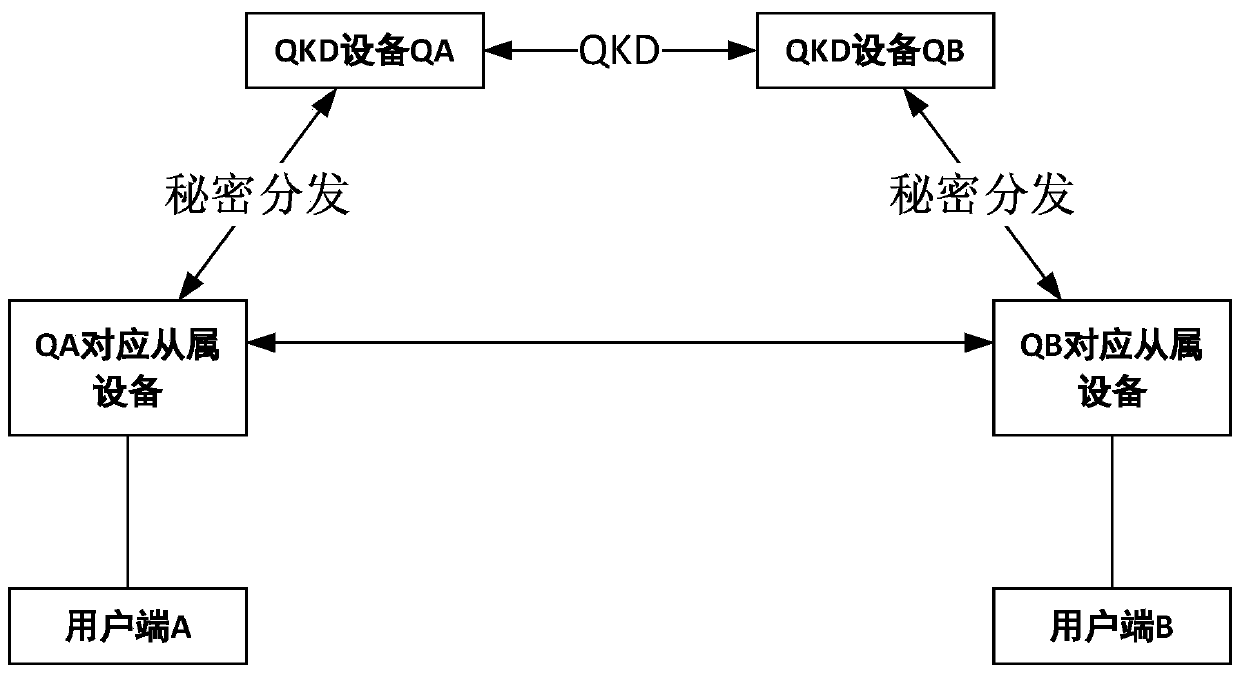
[0060] Such as figure 1 As shown, the quantum secure communication system based on secret sharing and asymmetric cryptography of the present invention is used for secure communication between clients through QKD devices, including key fobs, multiple clients, QKD devices and QKD slave devices.
[0061] The client goes to the QKD slave device in the area to register, and gets the key card after being approved. The key card has built-in identity authentication protocol and user registration information;
[0062] There are QKD channels between different QKD devices, which can form a symmetric key pool through QKD. QKD channels are built between QKD devices and their corresponding QKD slave devices, and a symmetric key pool can be formed through QKD, or the corresponding QKD slave devices can bring There is a key card and a symmetric key pool pre-issued by QKD equipment.
[0063]The user terminal can be a mobile terminal or a fixed terminal. When it is a mobile terminal, the key c...
Embodiment 2
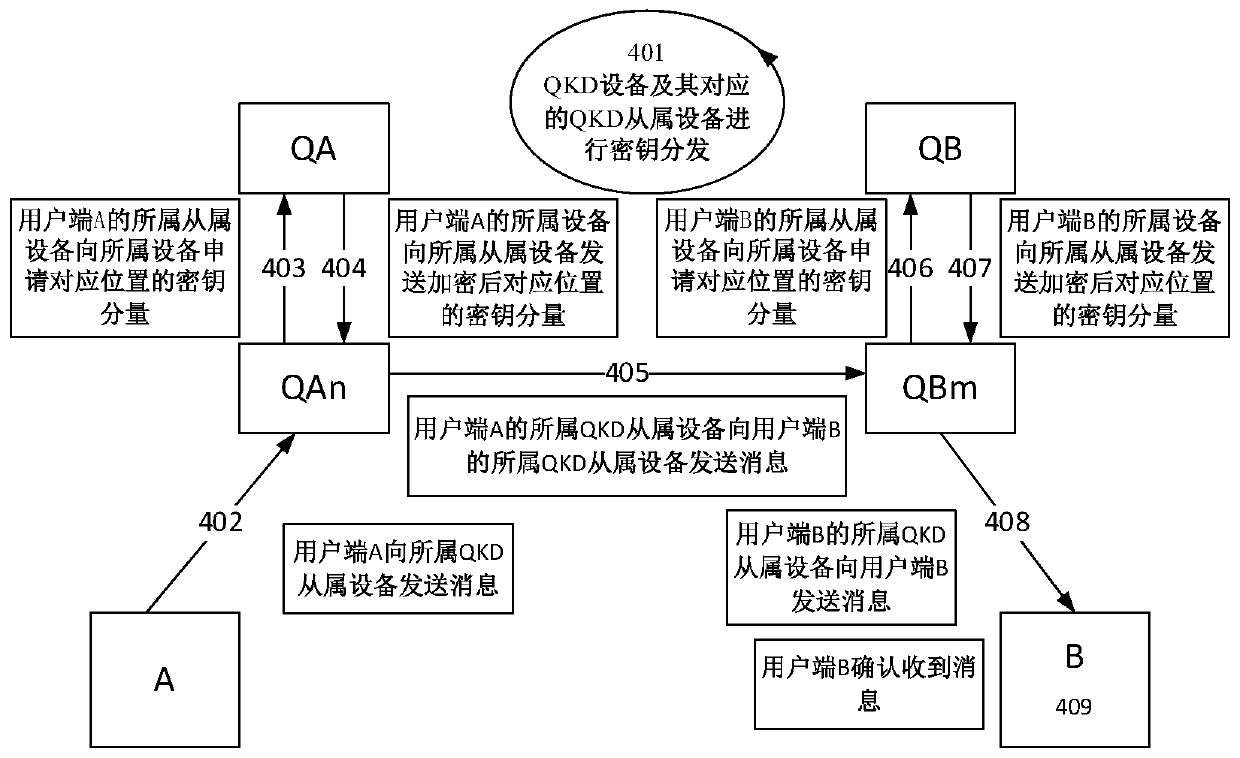
[0068] This embodiment provides a key distribution method of a quantum secure communication system based on secret sharing and asymmetric cryptography. Clients belong to different QKD devices, here it is assumed that there is a pair of QKD devices Q A and QKD device Q B , Q A There are N slaves Q An (n ∈ [0, N-1]), Q B There are M slave devices Q Bm (m ∈ [0, M-1]). The key distribution method is as follows:
[0069] Step 101, generate a QKD key K between different QKD devices, and K corresponds to the location of the local QKD key pool as K P ;
[0070] Step 102, QKD device Q A Calculate n=H(K)%N, choose Q An as a key distribution object. H is a hash operation, and % is a modulo operation.
[0071] Step 103, QKD device Q A Perform (2, 2) secret sharing on K.
[0072] Step 104, QKD device Q A After encrypting the secret, send it to its corresponding multiple QKD slave devices Q An .
[0073] Step 105, each corresponding QKD slave device Q An Received from QKD...
Embodiment 3
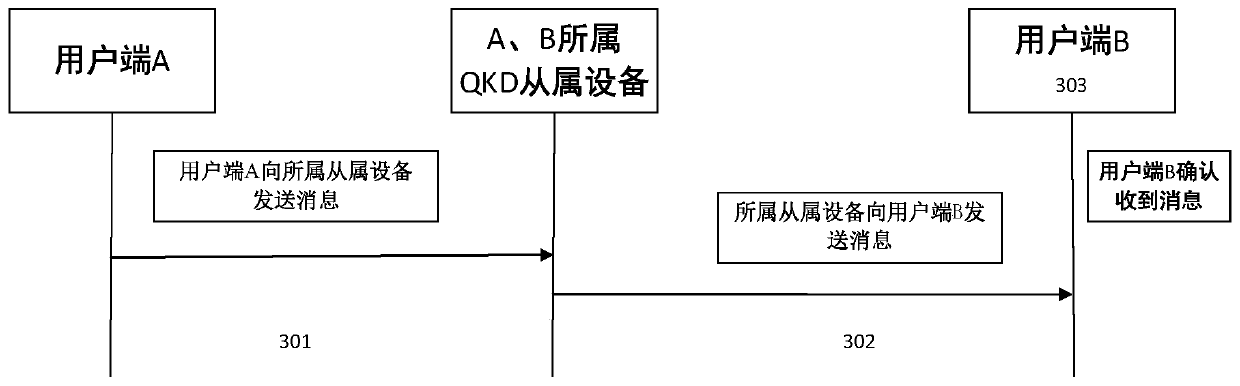
[0087] When the client belongs to the same QKD device, the key distribution method is as follows:.
[0088] Step 201, Q A Generate a random number key K, and form a large number of random arrays into the local key pool, K corresponds to the position of the local key pool as K P ;
[0089] Step 202, QKD device Q A Calculate n=H(K)%N, select Q An as a key distribution object. H is a hash operation, and % is a modulo operation. Q A Also calculate c=H(H(K))%N, select Q Ac As the key distribution object, the M xP Simultaneously sent to Q Ac .
[0090] Step 203, QKD device Q A Perform (2, 2) secret sharing on K.
[0091] Step 204, QKD device Q A After encrypting the secret, send it to its corresponding multiple QKD slave devices Q An .
[0092] Step 205, each corresponding QKD slave device Q An Received from QKD device Q A The ciphertext, decrypt to get the message, and multiple sets of key entries Q A ||Q B ||K P ||H(K)||x 1 ||(X 2 , K 2 ) are distributed an...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com