Multi-task relationship learning method for centrum positioning, identification and segmentation in nuclear magnetic resonance imaging
A technology of nuclear magnetic resonance image and learning method, applied in the field of medical image processing, can solve the problem of ignoring the close connection between tasks
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
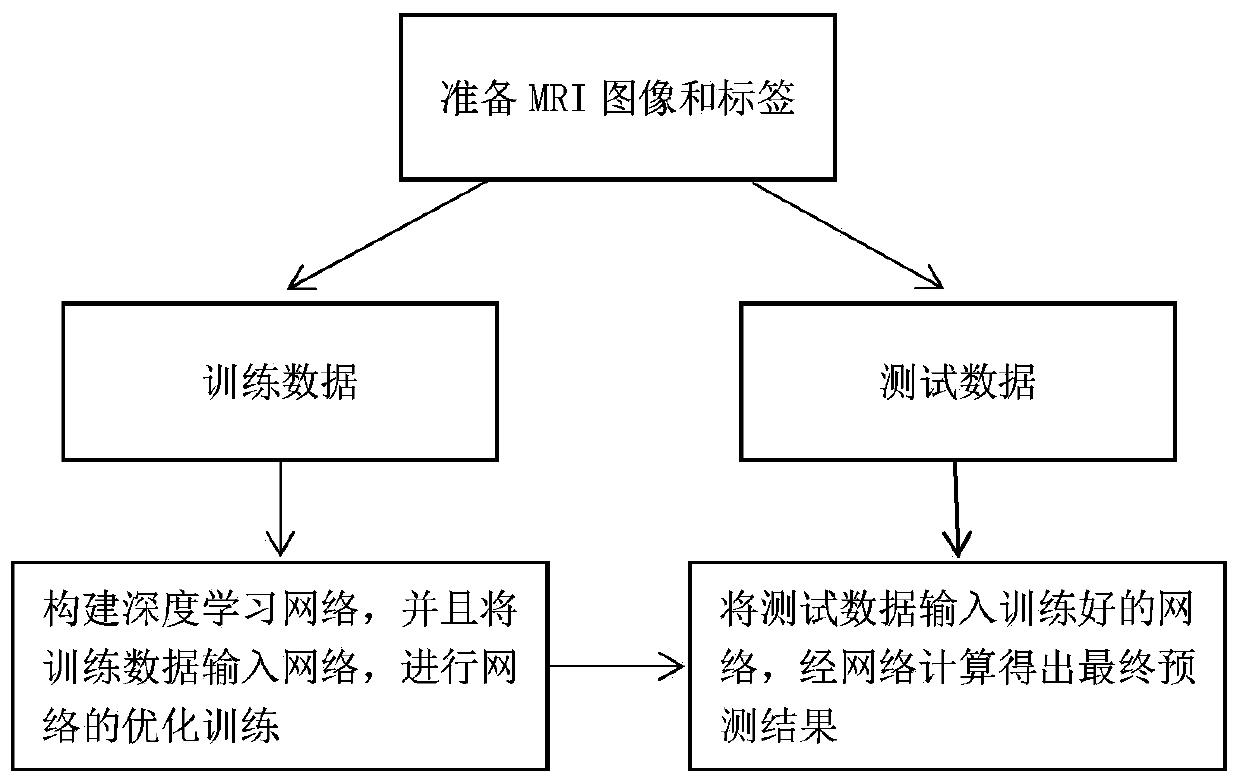
[0107] A multi-task relational learning method for vertebral body localization, recognition and segmentation in MRI images, such as figure 1 shown, including the following steps:
[0108] (1) Image preprocessing
[0109] By preprocessing the NMR images and semantic segmentation labels, the final data structure meets the requirements for input and loss function calculation of the multi-task relational learning network model; in this embodiment, the NMR images refer to MR lumbar spine images ;
[0110] (2) Build a multi-task relational learning network model
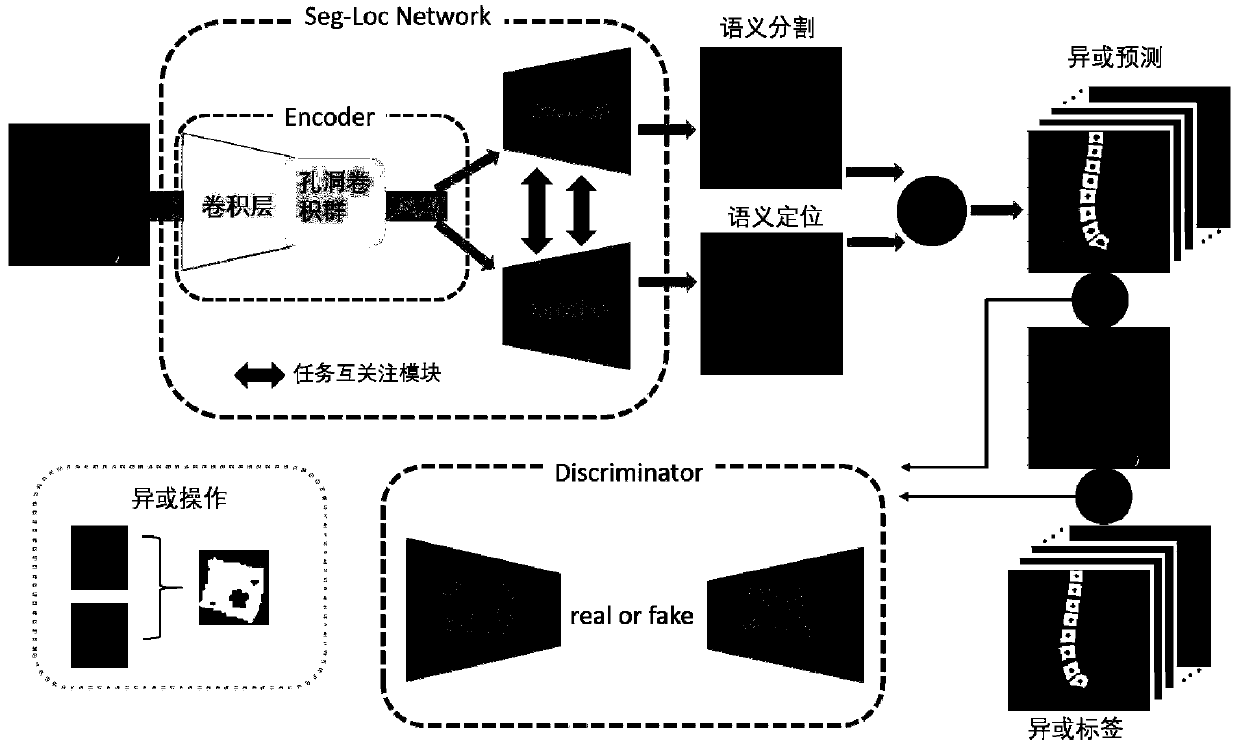
[0111] like figure 2 As shown, the multi-task relational learning network model includes Seg-Loc network, XOR operation and discriminant network;
[0112] As a generator for adversarial training, the Seg-Loc network uses the task mutual attention module to learn the relationship between semantic localization and semantic segmentation end-to-end through network parameter learning, and outputs semantic localization resu...
Embodiment 2
[0127] According to a kind of multi-task relational learning method that is used for the vertebral body location, identification and segmentation in the magnetic resonance image described in embodiment 1, its difference is:
[0128] In step (1), comprise steps as follows:
[0129] The original MRI image faces some challenges, such as the weak edge information of the vertebral body; the strong noise leads to uneven gray scale of the vertebral body imaging; the diversity of resolution leads to different sizes of vertebrae in the data set; and the generated MRI spine image contains With different degrees of lesions, each image contains different numbers of vertebral bodies. After statistics, the number of MRI images containing 6 vertebral bodies (S1-L5), 7 vertebral bodies (S1-T12), and 8 vertebral bodies (S1-T11) are nearly equal.
[0130] A. First adjust all MRI images to 512*512;
[0131] B. Use ITK-SNAP software to label all MRI images with vertebral body segmentation label...
Embodiment 3
[0141] According to a kind of multi-task relational learning method that is used for the vertebra body location, identification and segmentation in the nuclear magnetic resonance image described in embodiment 2, its difference is:
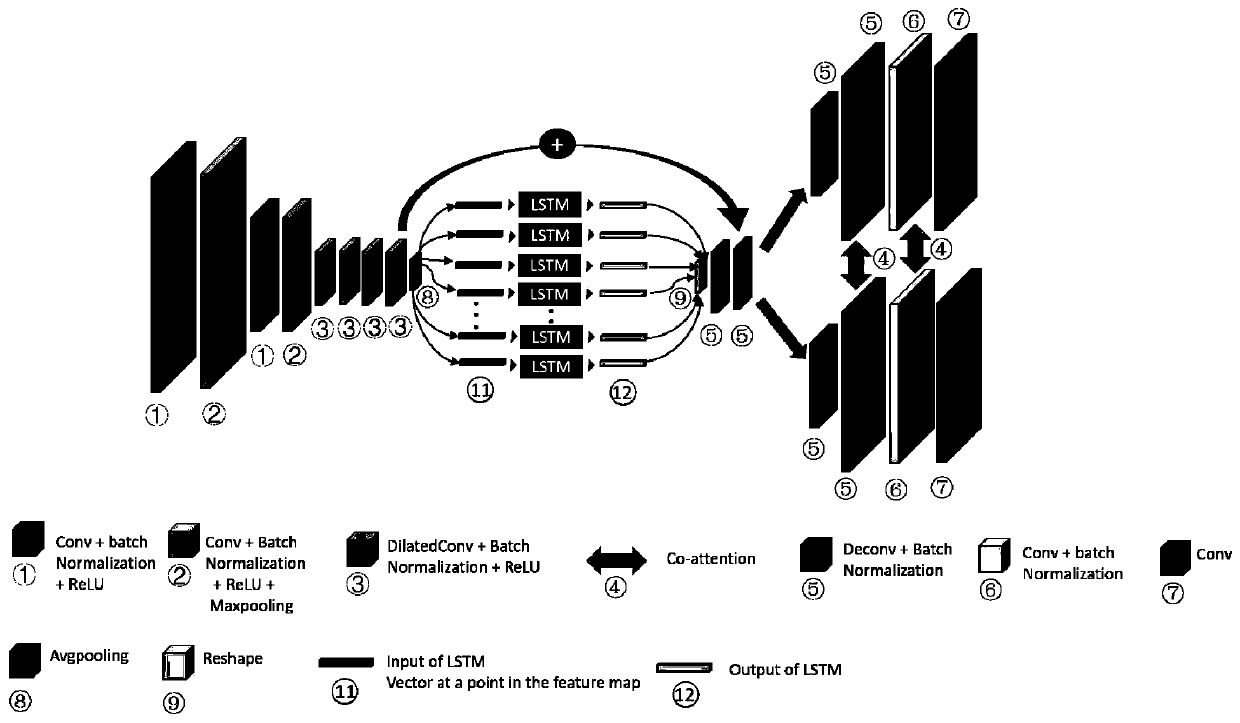
[0142] In step (2), the Seg-Loc network is the generative network of the proposed multi-task relational learning network. like image 3 As shown, the structure of the Seg-Loc network is an encoder-decoder network. The encoder-decoder network includes an encoder, two decoders, and two task mutual attention modules. The two decoders share an encoder. There are two encoders between the two decoders. A task mutual attention module;
[0143] The two decoders output semantic positioning results and semantic segmentation results respectively; the task mutual attention module is used to learn the relationship between semantic positioning and semantic segmentation;
[0144] The encoder includes convolutional layer, LSTM, hole convolution group, batch norm...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com