Carbon nano fluorescent material suitable for seawater medium, preparation method and applications thereof
A technology of fluorescent materials and carbon nanometers, applied in luminescent materials, material analysis through optical means, nano-carbon, etc., can solve problems such as complex preparation and synthesis routes, complex components, and difficult degradation, and achieve good economic and social benefits. Preparation Simple method and stable fluorescence performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0053] The present invention also provides the preparation method of above-mentioned carbon nanometer fluorescent material, wherein, comprise the following steps:
[0054] Step 1: Mix carbon source A and nitrogen source B into a solution;
[0055] Step 2: adding passivating agent to the mixture obtained in step 1;
[0056] Step 3: adding a pH regulator to the mixture obtained in step 2 to make its pH 2-12;
[0057] Step 4: heat-treating the mixture obtained in Step 3 to obtain the carbon nano fluorescent material;
[0058]Wherein, the ratio of the volume of the passivating agent to the sum of the mass of the carbon source A and the nitrogen source B is 1:15-3:1;
[0059] Preferably, the ratio of the volume of the passivating agent to the sum of the mass of the carbon source A and the nitrogen source B is 1:15-1.5:1.
[0060] Preferably, wherein, the pH regulator described in step 3 is selected from NaOH, KOH, HCl and H 2 SO 4 one or more of them.
[0061] Preferably, whe...
Embodiment 1
[0074] 1) Mix 5.1 g of monomeric citric acid and 1.7 g of ethylenediamine into a mixed solution and place it in a beaker;
[0075] 2) Passivate by adding 0.5mL of ammonia water to obtain a solution;
[0076] 3) adding HCl to the solution obtained in step 2 to adjust the pH value to 4;
[0077] 4) The solution obtained in step 3 was heated at 180° C. for 2 hours to obtain carbon nano fluorescent material A.
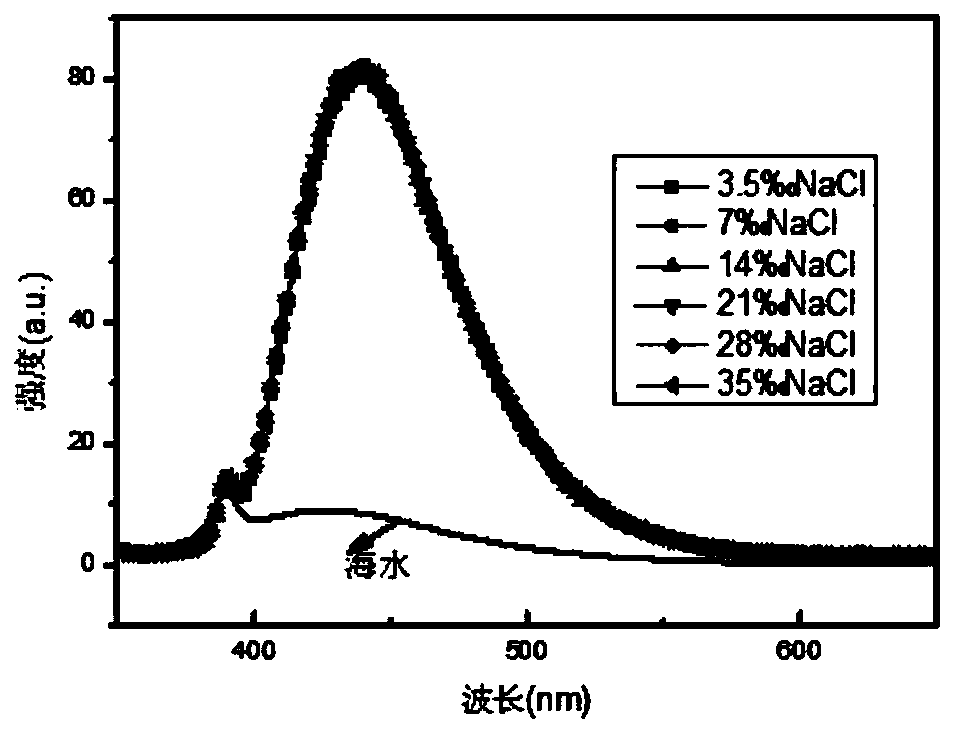
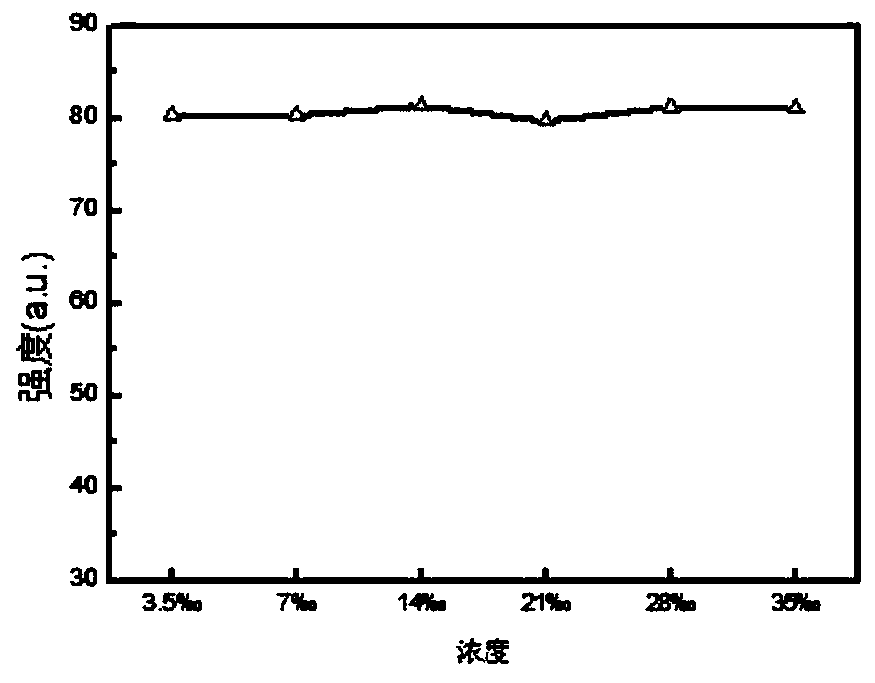
[0078] Use 3.5‰, 7‰, 14‰, 21‰, 28‰ and 35‰ NaCl solutions to prepare 0.1mg / L (on a dry basis) carbon nano-fluorescent material A solution, and the resulting solution is detected using a fluorescence spectrophotometer. Under the conditions of 2.5nm grating, 343nm excitation light and emission wavelength of 434nm, the obtained fluorescence spectrum is as follows figure 1 with figure 2 .
[0079] from figure 1 It can be seen that the fluorescence spectra of the prepared carbon nano-fluorescent material A in 3.5‰, 7‰, 14‰, 21‰, 28‰ and 35‰ NaCl solutions overlap each oth...
Embodiment 2
[0082] 1) 2.3 g of monomeric sodium citrate and 4.5 g of triethylamine are formulated into a mixed solution;
[0083] 2) Add 0.5mL of PEG200 for passivation to obtain a solution;
[0084] 3) adding KOH to the solution obtained in step 2 to adjust the pH value to 12;
[0085] 4) heating the solution obtained in step 3 at 160° C. for 8 hours to obtain carbon nano fluorescent material B;
[0086] Prepare 0.1mg / L (on a dry basis) carbon nano-fluorescent material B solution with seawater, test the fluorescent properties of the gained solution and seawater under the condition of 343nm excitation wavelength at a 5nm grating, such as Figure 4 As shown, the fluorescence intensity of the material was significantly higher than that of the seawater substrate, and the test was repeated after 24 hours, and the results obtained did not change significantly.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com