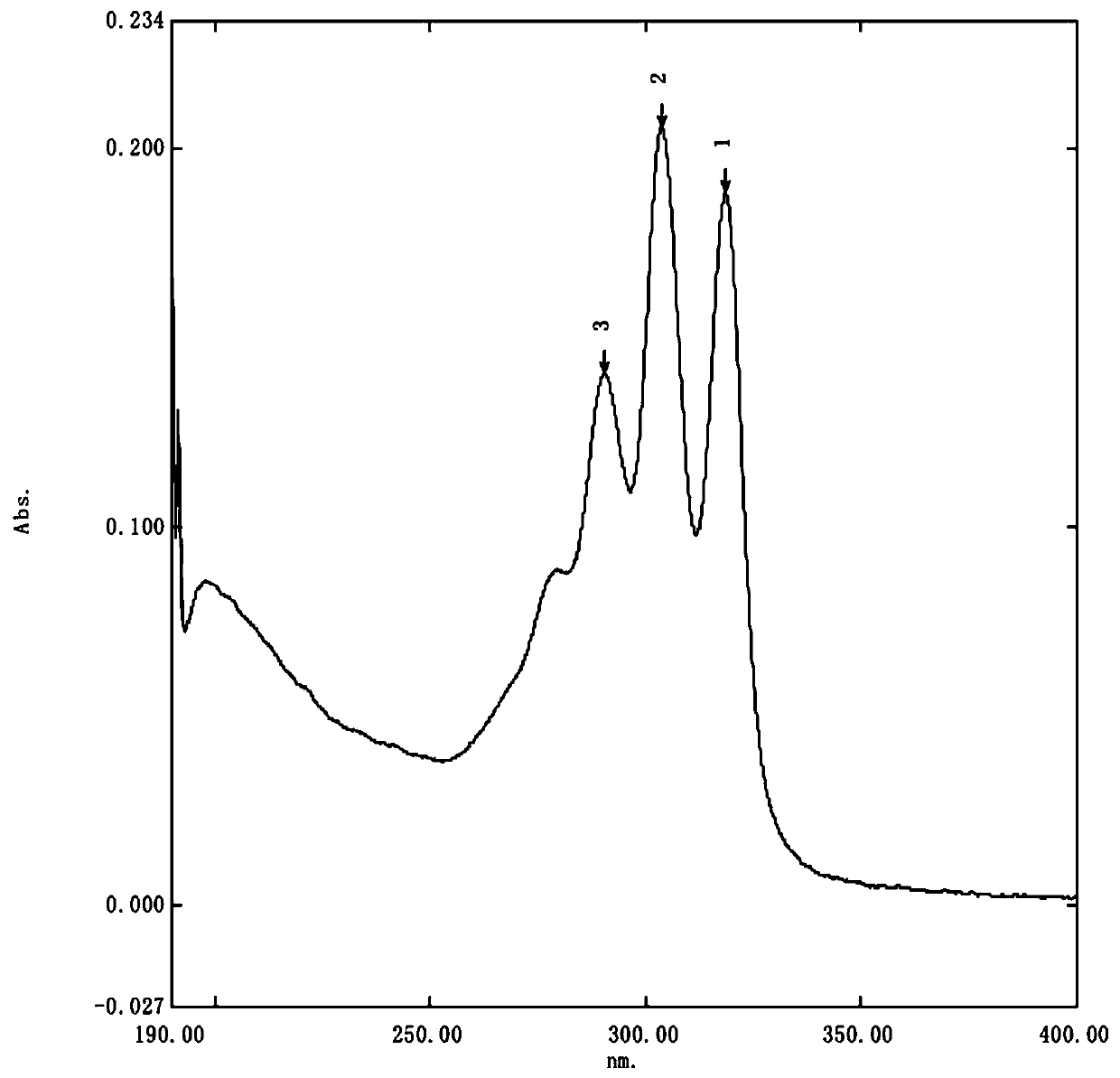
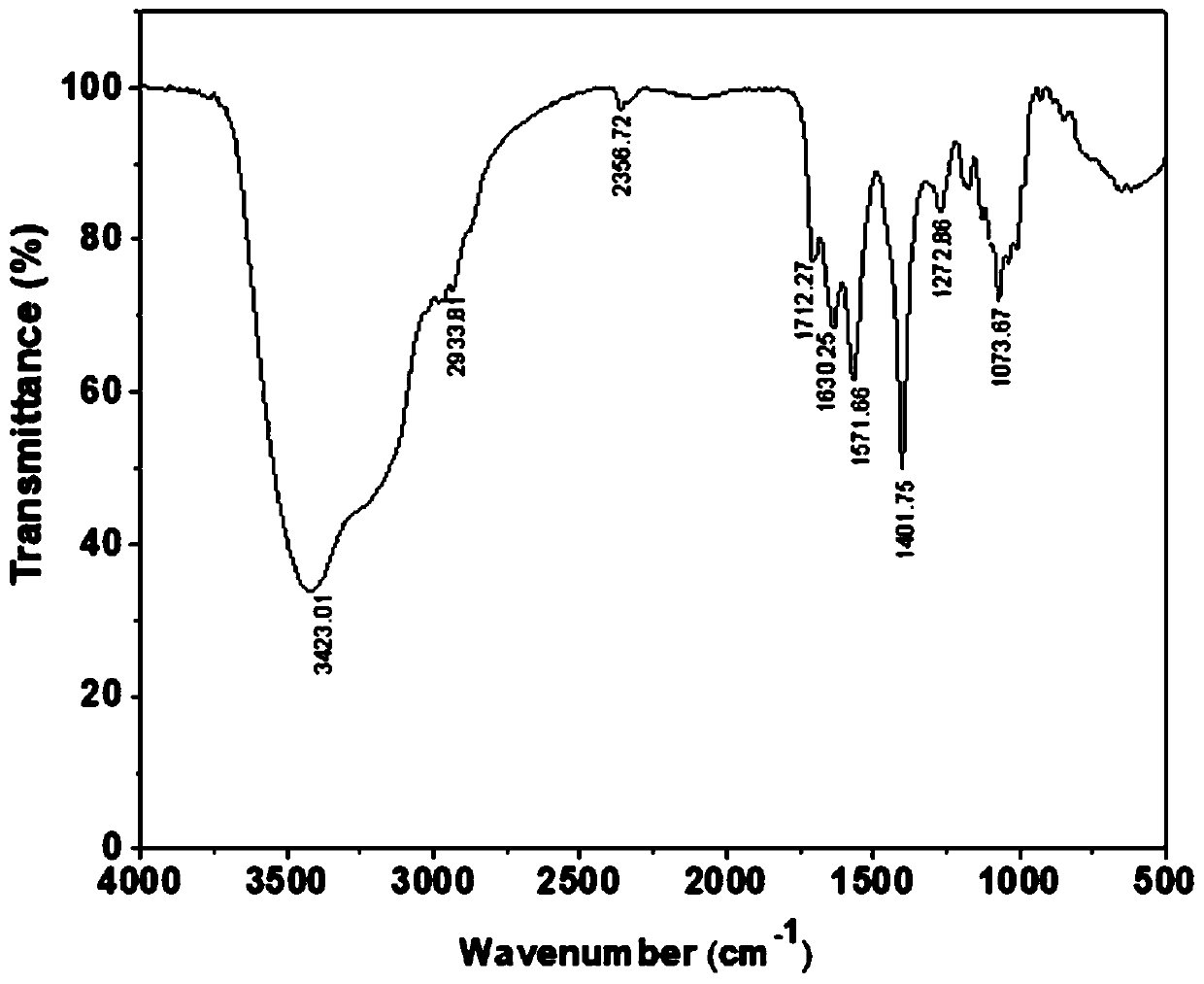
Bacterial strain for increasing yield of tetramycin Z and method for preparing tetramycin Z by using same
A technology of tetramycin and strain, applied in the field of microorganisms, can solve the problems of high randomness, time-consuming and laborious, difficulty in increasing the yield of natural products such as antibiotics, etc., and achieve the effects of increasing yield and strong inhibitory effect.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] Example 1: Acquisition of low-concentration streptomycin-resistant mutants (first round of screening of drug-resistant mutants)
[0028] A GYM solid plate with a final concentration of 30 μg / mL of low-concentration streptomycin was prepared, that is, the concentration of streptomycin in the GYM solid plate was 30 μg / mL. Pipette 100 μL of Streptomyces chromogenes D spore suspension (1×10 6 colonies / mL) on the GYM solid plate, spread evenly with a sterile spreader bar, placed in a 28°C incubator for 7 days, and pick a single colony to a new GYM solid plate (one colony) containing 20 μg / mL streptomycin. A single colony was drawn on a plate), placed in a 28°C incubator for 5 days, and the strain that could grow again on the new GYM solid plate was the streptomycin-resistant mutant. A total of 15 low-concentration streptomycin-resistant mutant strains were obtained, numbered fz1 to fz15, and the 15 mutant strains were subjected to liquid fermentation culture according to st...
Embodiment 2
[0029] Example 2: Obtainment of high-concentration streptomycin-resistant mutants (second round of screening of drug-resistant mutants)
[0030] A GYM solid plate with a final streptomycin concentration of 300 μg / mL was prepared, that is, the streptomycin concentration in the GYM solid plate was 300 μg / mL. Pipette 1000 μL of low-concentration streptomycin-resistant mutant fz9 spore suspension (1×10 12 colonies / mL) on the GYM solid plate, spread evenly with a sterile coating rod, and culture in a 28°C incubator for 10 to 15 days. Pick a single colony to a new GYM solid plate containing 300 μg / mL streptomycin. (One single colony is drawn on one plate), and cultured in a 28°C incubator for 7 to 10 days. The strains that can grow again on the new GYM solid plate are high-concentration streptomycin-resistant mutants. A total of 3 high-concentration streptomycin-resistant mutant strains were obtained, numbered sz2-1, sz2-2 and sz2-3 respectively, and the three mutant strains were s...
Embodiment 3
[0031] Example 3: Acquisition of rifampicin-resistant mutants (the third round of screening of drug-resistant mutants)
[0032] A GYM solid plate with a final concentration of rifampicin of 20 μg / mL was prepared, that is, the concentration of rifampicin in the GYM solid plate was 20 μg / mL. Pipette 100 μL of the mutant sz2-3 spore suspension (1×10) obtained from the second round of screening with a pipette. 10 colonies / mL) on a GYM solid plate containing 20 μg / mL rifampicin, spread evenly with a sterile coating rod, and culture in a 28°C incubator for 7 days. The GYM solid plate of Fuping (a single colony is drawn on a plate), placed in a 28°C incubator for 5 days, and the strain that can grow again on the new GYM solid plate is the rifampicin-resistant mutant. A total of 2 rifampicin-resistant mutants were obtained in this screening, numbered tz3-1 and tz3-2.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com