Device with digital phase-locked loop and numerical control oscillator and method for measuring phase noise and amplitude noise
A numerically controlled oscillator and digital phase-locked loop technology, which is applied in measurement devices, noise figure or signal-to-noise ratio measurement, measurement of electricity and other directions, can solve the problems of phase noise spectrum power attenuation, etc. The effect of high ratio and high measurement accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 2
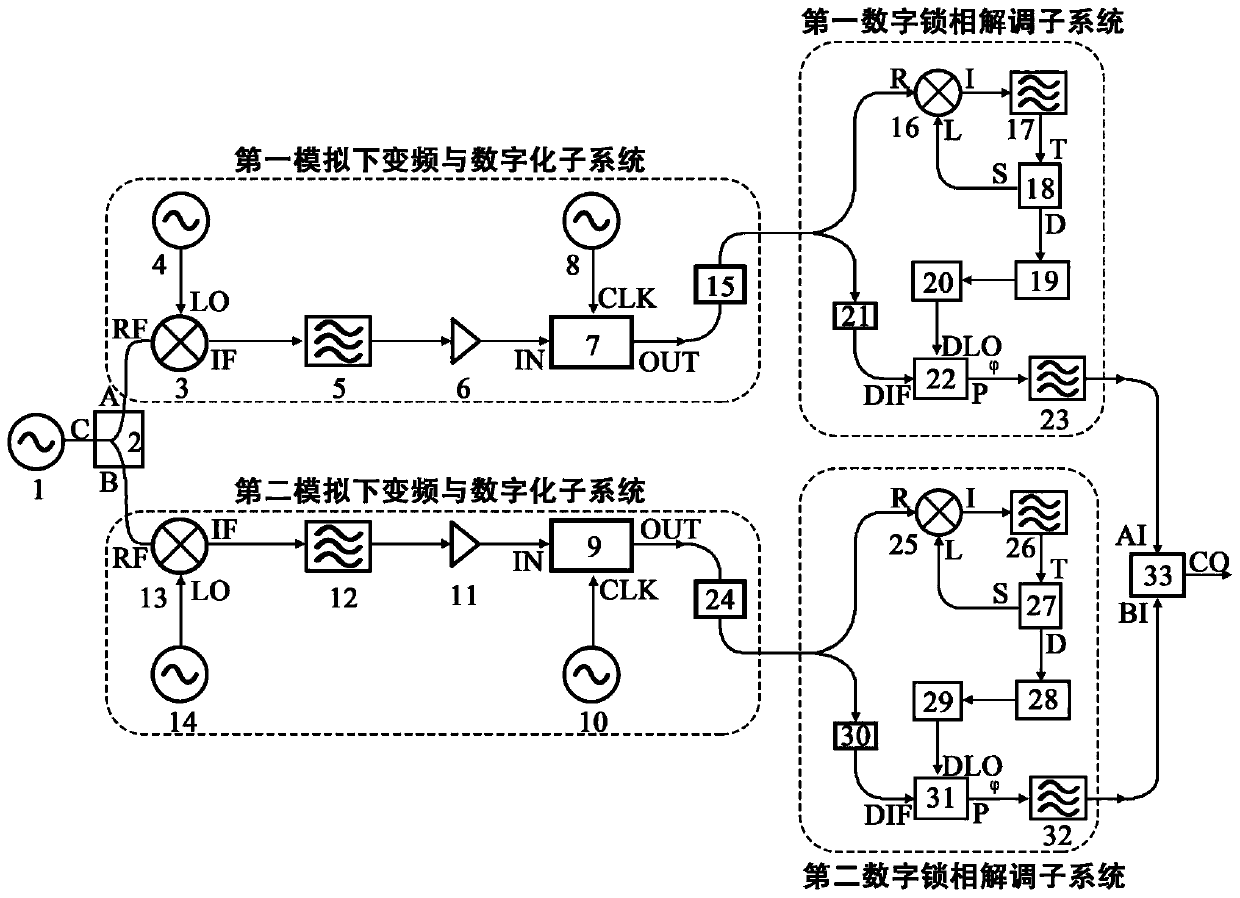
[0047] On the basis of Embodiment 1, this example provides a feasible structure of the power division unit in the device for measuring phase noise and amplitude noise with a digital phase-locked loop and a numerically controlled oscillator, that is, a WDM modulation method Optical isolation structure. Such as figure 2 As shown, the power division unit includes a first laser 101 , a second laser 102 , a multiplexer 103 , a first optical modulator 104 , a splitter 105 , a first optical detector 106 , and a second optical detector 107 . The first laser 101 and the second laser 102 generate laser light with different wavelengths, which respectively enter the L1 port and the L2 port of the multiplexer 103 . The S port output signal of the multiplexer 103 is connected to the I port of the first optical modulator 104 . The signal to be tested 1 is connected to the RF port of the first optical modulator 104 to modulate the signal to be tested onto light. The O port output of the f...
Embodiment 3
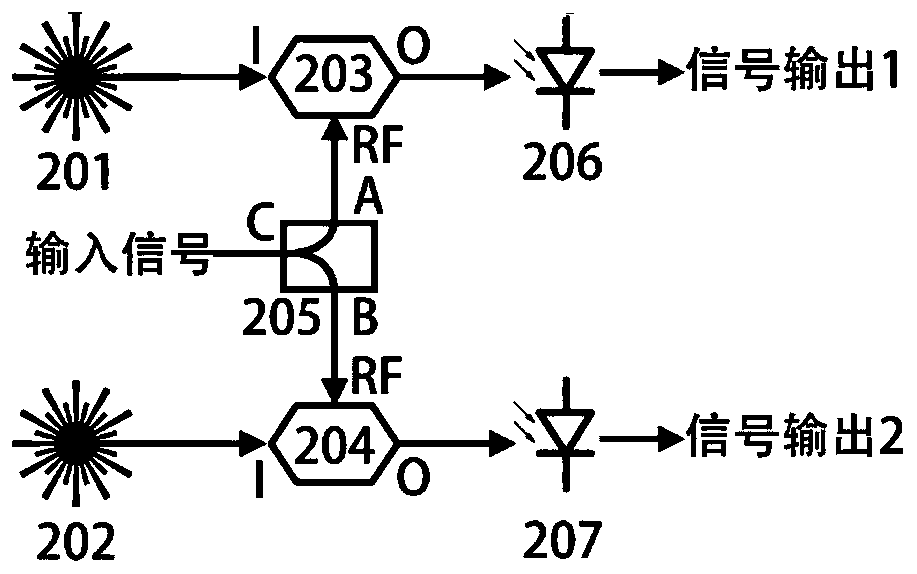
[0049] On the basis of Embodiment 1, this example provides another feasible structure of the power division unit in the device for measuring phase noise and amplitude noise with a digital phase-locked loop and a numerically controlled oscillator, that is, a light wave separately modulated isolation structure. Such as image 3 As shown, the power division unit includes a third laser 201, a fourth laser 202, a second optical modulator 203, a third optical modulator 204, an electric power divider 205, a third optical detector 206, and a fourth optical detector 207 . The third laser 201 sends light into the I port of the second light modulator 203 , and the fourth laser 202 sends light into the I port of the third light modulator 204 . The signal 1 to be tested is connected to the C port of the electric power divider 205, and the signal is divided into two paths, which are respectively output through the A port and the B port, and are respectively connected to the RF port of the...
Embodiment 4
[0051] On the basis of the first to third embodiments, this example provides a feasible mode of the amplitude-phase demodulation unit in the device for measuring phase noise and amplitude noise with a digital phase-locked loop and a numerically controlled oscillator. Both the first phase demodulation unit 22 and the second phase demodulation unit 31 can adopt this structure, as Figure 4 As shown, it specifically includes: a signal phase shifting and distribution unit 401, a first amplitude-phase demodulation mixer 402, a first demodulation filter 403, an amplitude-phase calculation unit 404, and a second amplitude-phase demodulation mixer 405 , the second demodulation filter 406 .
[0052] The digital intermediate frequency signal to be tested is sent to the R port of the first amplitude-phase demodulation mixer 402 and the R port of the second amplitude-phase demodulation mixer 405 . The reference signal is sent into the IN port of the signal phase-shifting and distribution...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com