Urea terminated butadiene polymers and butadiene acrylonitrile copolymers
A polybutadiene acrylonitrile and polymer technology, applied in the field of butadiene acrylonitrile copolymers, can solve the problems of accelerated curing reaction, lower glass transition temperature, no generation, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
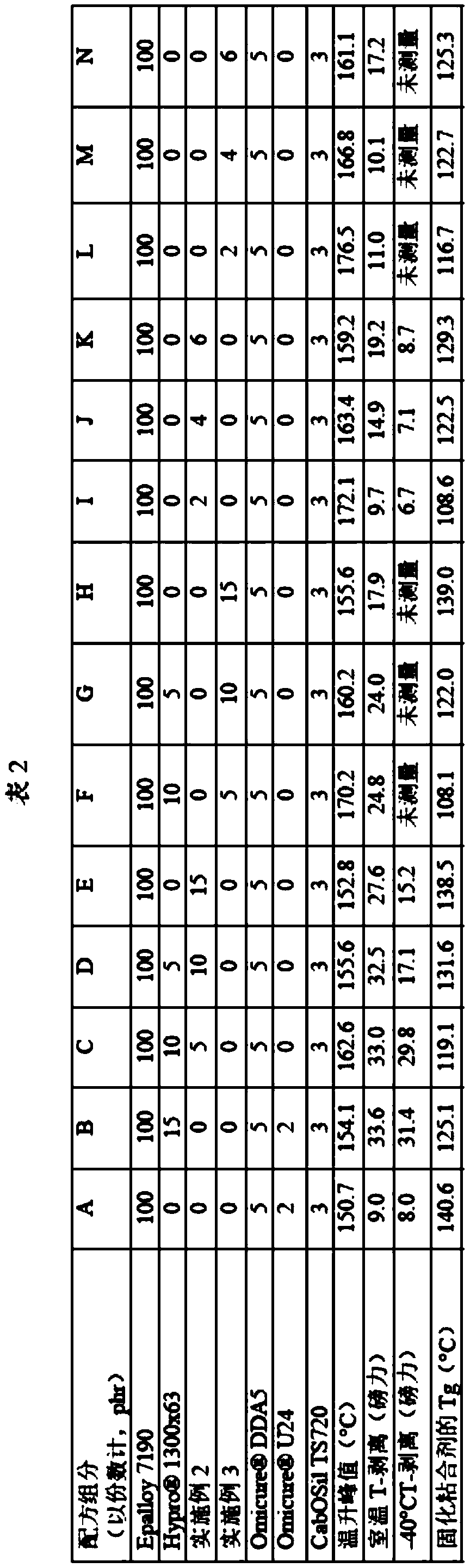
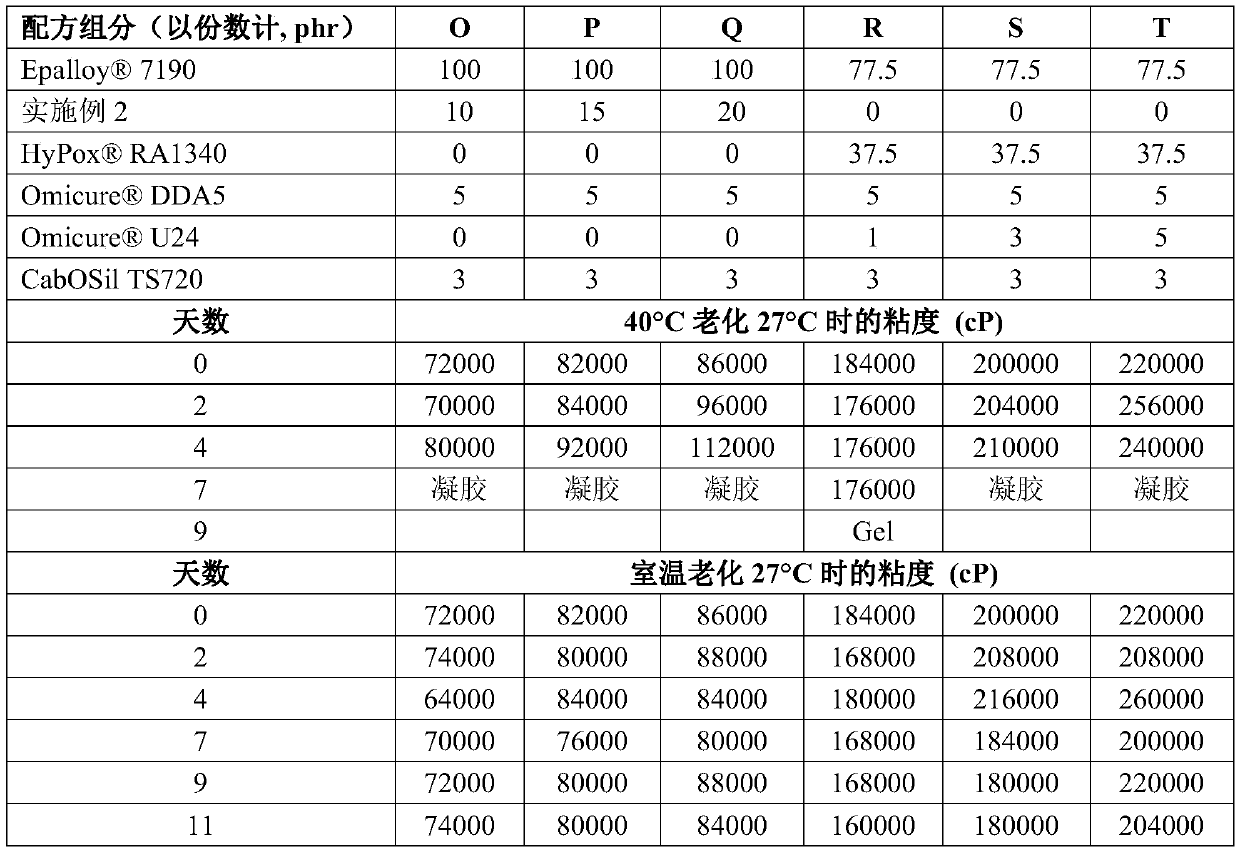
Examples
Embodiment 1
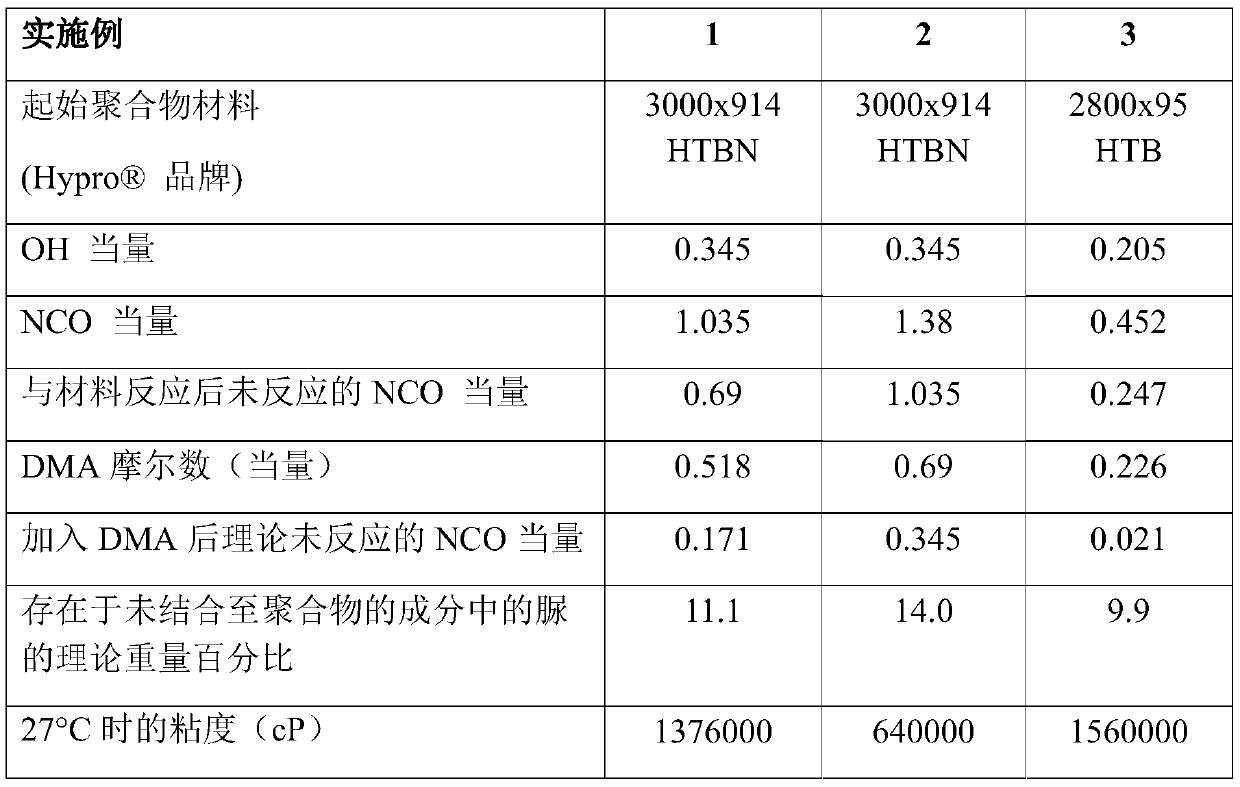
[0047] Example 1 shows the use of 3000x914HTBN (Example 1 and Example 2) or 2800x95HTB (Example 3) Starting Material Synthesis of urea-terminated polymers of the invention using the general method described in this application. Table 1 reflects the variation of the reaction stoichiometry and the amount of starting material. The urea-terminated polymers of the present invention were prepared using various amounts (expressed as equivalents (moles of reactive groups)) of polymeric material, diisocyanate (NCO) and dimethylamine described below.
[0048] 500 g of the indicated polymeric material was weighed into a 3 necked round bottom flask equipped with mechanical stirring and vacuum distillation. The flask was heated to 100°C in an oil bath with stirring under vacuum and allowed to degas for a period of 1 hour before reducing the temperature to 45°C. After the oil bath reached 45°C, 300 g of xylene was added, and the reaction mixture was stirred for 20 minutes until homogen...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com