Hydrogel base material and preparation method thereof, and applications of hydrogel base material in the biomedical field
A hydrogel and base material technology, which is applied in the field of hydrogel base material and its preparation, can solve the problems of weak adhesion and difficulty in storage, and achieve the effects of easy detachment, low water loss and fast adhesion
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0047] 12gN, N-dimethylacrylamide, 40mgN, N'-methylenebisacrylamide, 48g water, 12g glycerol, 12g polyacrylic acid (M w =5000) and 50 mg of ammonium persulfate were uniformly mixed, and reacted for 24 hours in an inert gas atmosphere and at 70° C. to obtain a biomedical hydrogel substrate.
[0048] Aluminum panels were used to test the adhesion of the hydrogel substrates. The bonding strength of the hydrogel substrate on the aluminum plate measured by the universal material testing machine is 56±8kPa.
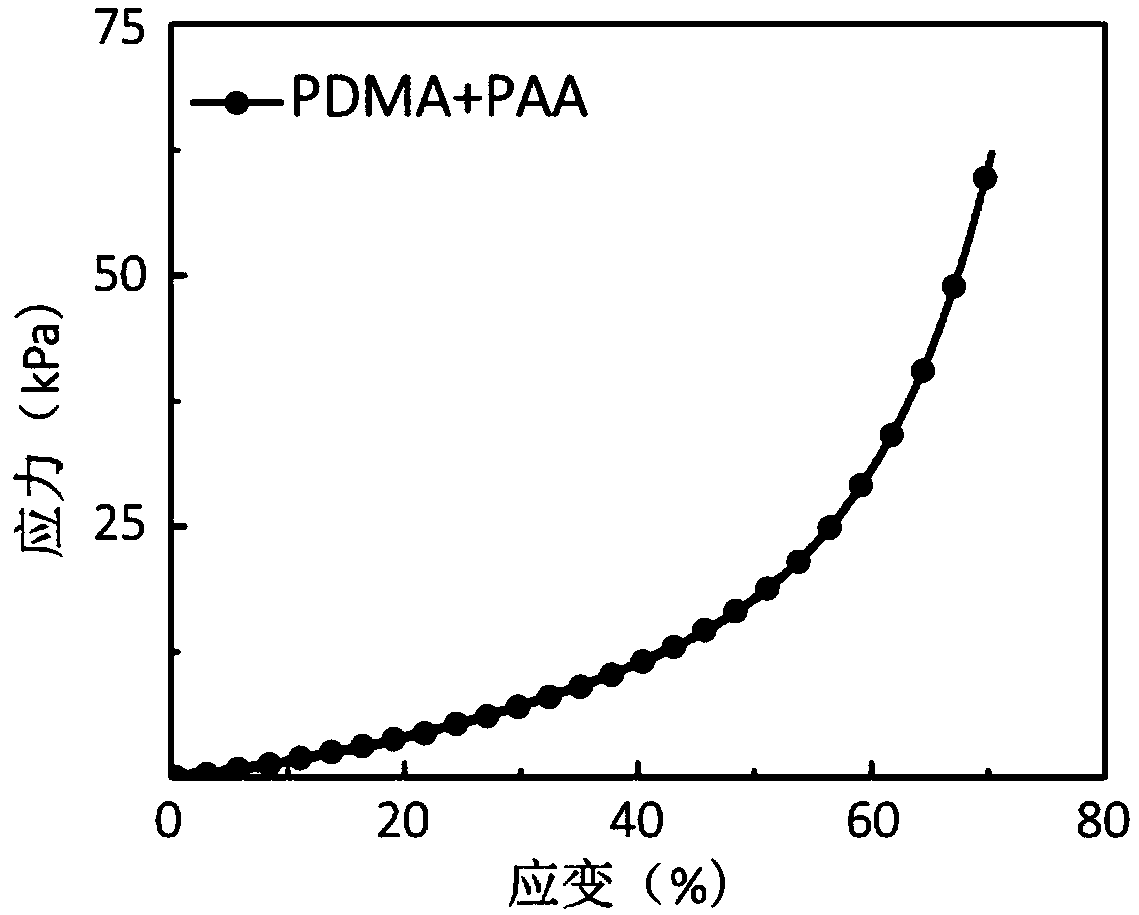
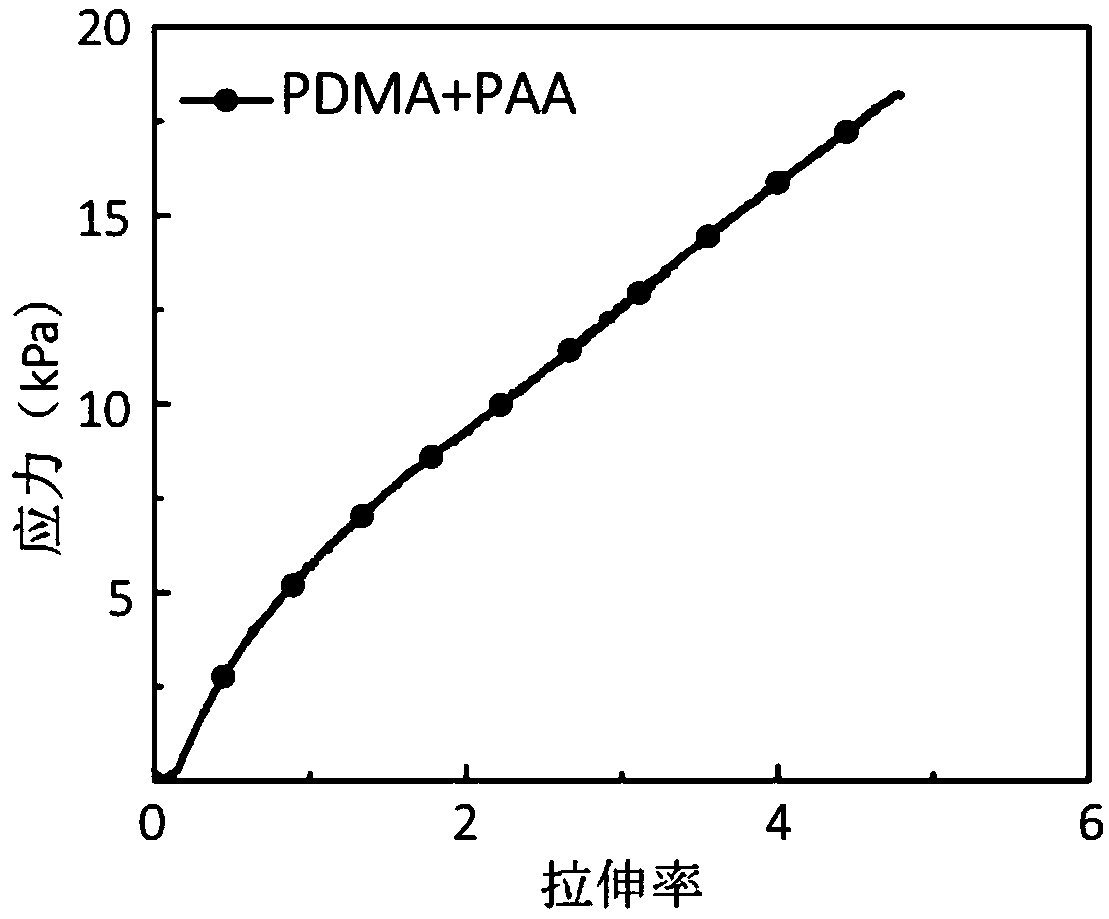
[0049] Make a strip-shaped substrate in a specific mold and test its mechanical behavior on a universal material testing machine. The compression modulus is 2.0±0.2kPa, and the compression deformation can reach 70% (see figure 1 ). Its tensile modulus is 11.1±2.0kPa, and the elongation rate reaches 5 times (see figure 2 ).
Embodiment 2
[0051] 12g acrylamide, 20mgN, N'-methylenebisacrylamide, 48g water, 12g glycerol, 12g polyacrylic acid (M w =5000) and 50 mg of ammonium persulfate were uniformly mixed, and reacted for 24 hours in an inert gas atmosphere and at 70° C. to obtain a biomedical hydrogel substrate.
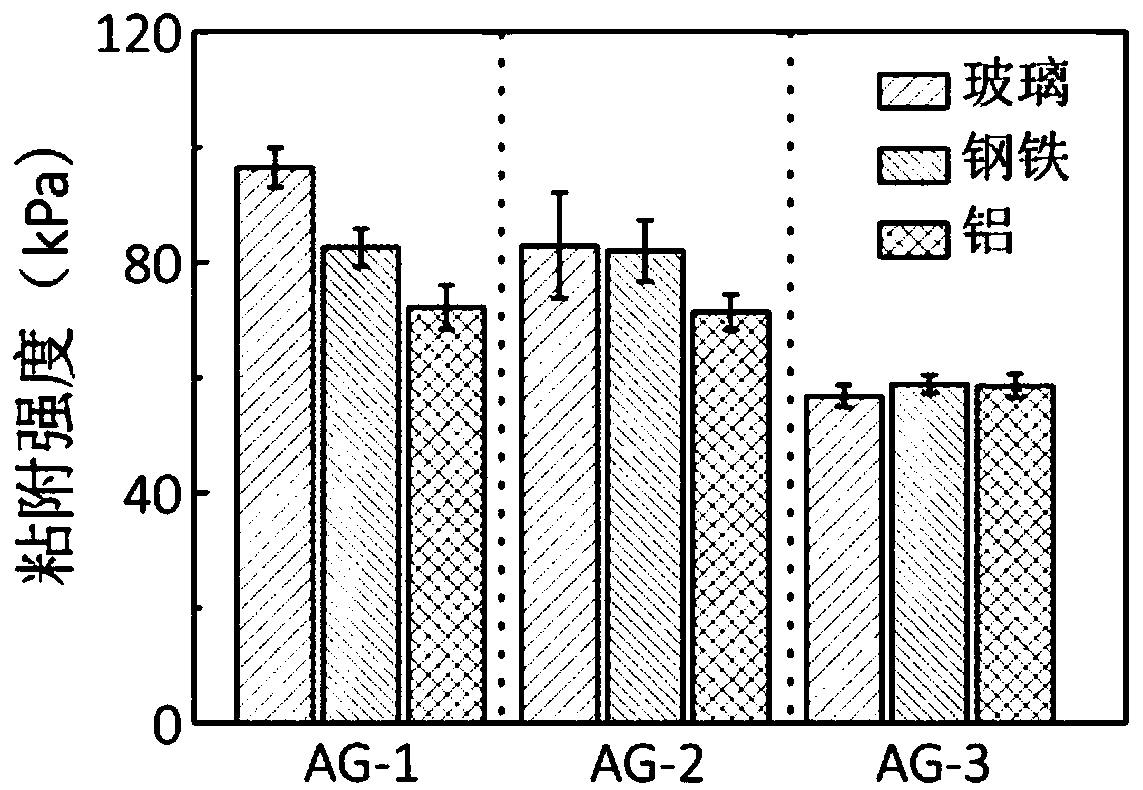
[0052] The adhesion of the substrates is tested with aluminum, iron and glass plates. It is 73 ± 4kPa that this hydrogel base material is measured on the universal material testing machine on the aluminum plate, and the bond strength on the iron plate is 83 ± 3kPa, and the bond strength on the glass is 96 ± 3kPa (see image 3 Middle AG-1).
[0053] Make a strip-shaped substrate in a specific mold and test its mechanical behavior on a universal material testing machine. The compression modulus is 3.8±0.5kPa, and the compression deformation can reach 90% (see Figure 4 Middle AG-1). Its tensile modulus is 11.1±0.4kPa, and the elongation rate reaches 10.5 times (see Figure 5 Middle AG-1).
Embodiment 3
[0055] 12g acrylamide, 30mgN, N'-methylenebisacrylamide, 48g water, 12g glycerol, 12g polyacrylic acid (M w =5000) and 50 mg of ammonium persulfate were uniformly mixed, and reacted for 24 hours in an inert gas atmosphere and at 70° C. to obtain a biomedical hydrogel substrate.
[0056] The adhesion of the substrates is tested with aluminum, iron and glass plates. It is 72 ± 3kPa that this hydrogel base material is measured on the universal material testing machine on the aluminum plate, and the bond strength on the iron plate is 82 ± 5kPa, and the bond strength on the glass is 83 ± 9kPa (see image 3 Middle AG-2).
[0057] Make a strip-shaped base material in a specific mold and test its mechanical behavior on a universal material testing machine. Its compression modulus is 4.9 ± 0.3kPa, and its compression deformation can reach 90% (see Figure 4 Middle AG-2). Its tensile modulus is 20.1±0.7kPa, and the elongation rate reaches 7 times (see Figure 5 Middle AG-2).
[005...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| compressive modulus | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| compressive modulus | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| compressive modulus | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com