Traditional Chinese medicinal gel plaster and substrate thereof
A technology of traditional Chinese medicine and gel, which is applied in the field of traditional Chinese medicine gel plaster and its matrix, which can solve the problems of affecting the rate and degree of transdermal release, unfavorable drug quality control system, and increasing the difficulty of sample preparation, so as to improve hydration and skin penetration rate, eliminate penetration spots, and realize the effect of continuous production and closed production
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0046] Example 1 Screening without emulsifier and having "direct seal-in-bag crosslinking / curing" gel plaster base test
[0047] Preparation Process:
[0048] (1) Take Corydalis Corydalis, Notopterygium, Duhuo, Angelica, Angelica dahurica, Chuanxiong, Zanthoxylum bungeanum, Myrrh, Woody Fragrance, Clove, Kaempferia, Safflower, Dipsacus, Asarum, and Cinnamon 15 oil-containing traditional Chinese medicines, 90% ethanol extraction, Concentrate to a relative density of 1.1-1.2 (80°C) to obtain an extract for use.
[0049] (2) Dissolve tartaric acid and EDTA-2Na (if there is no EDTA-2Na in the prescription, do not add it) in water, cool to room temperature, and obtain substance 2.
[0050] (3) Povidone (K-90) was added to substance 2, stirred, pre-swollen, and left overnight to obtain substance 3.
[0051] (4) Add the extract prepared in step (1) into glycerin, stir and disperse to obtain substance 4.
[0052] (5) Add gelatin to substance 3, fully swell in a water bath environme...
Embodiment 2
[0078] Example 2 Contains no emulsifier and has "direct seal-in-bag crosslinking / curing" gel plaster matrix verification test
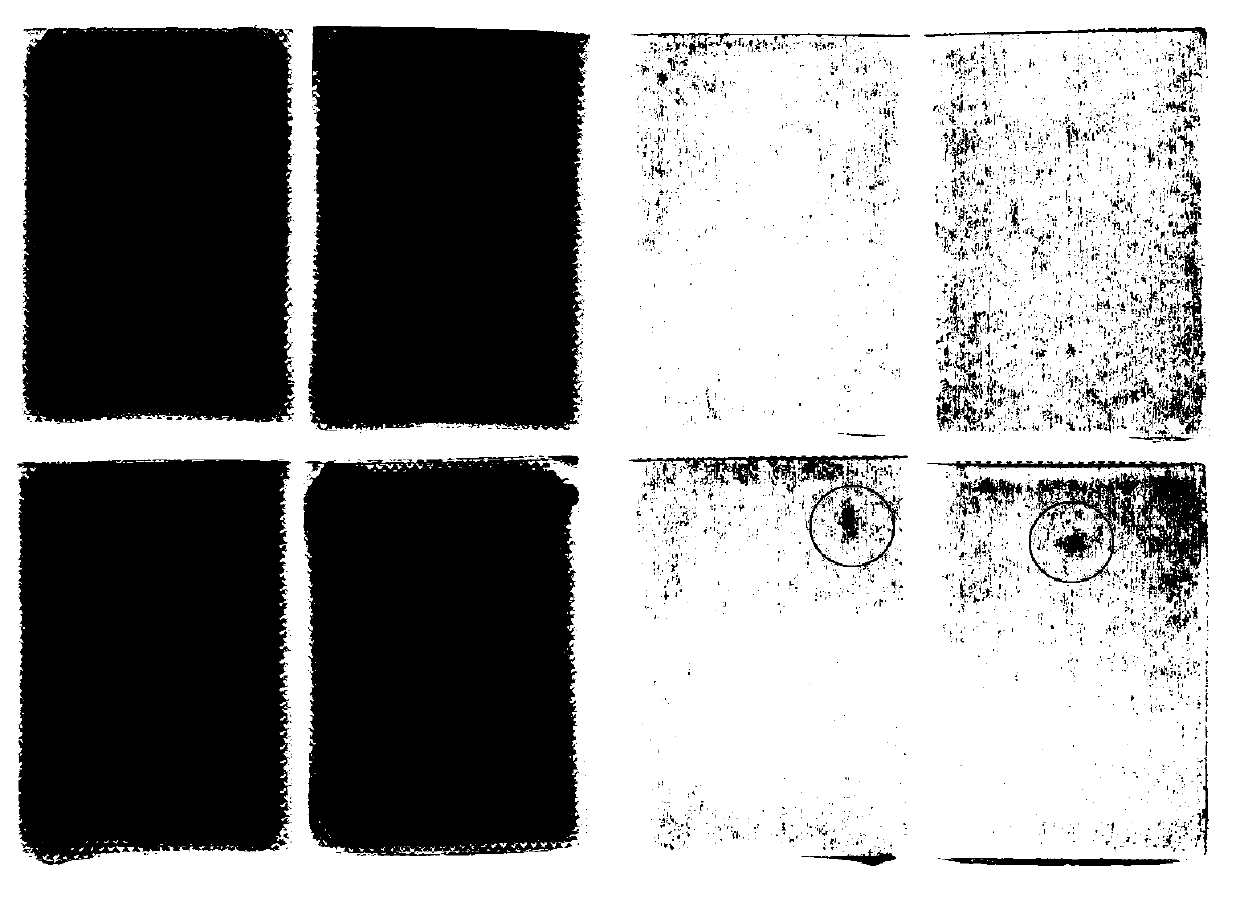
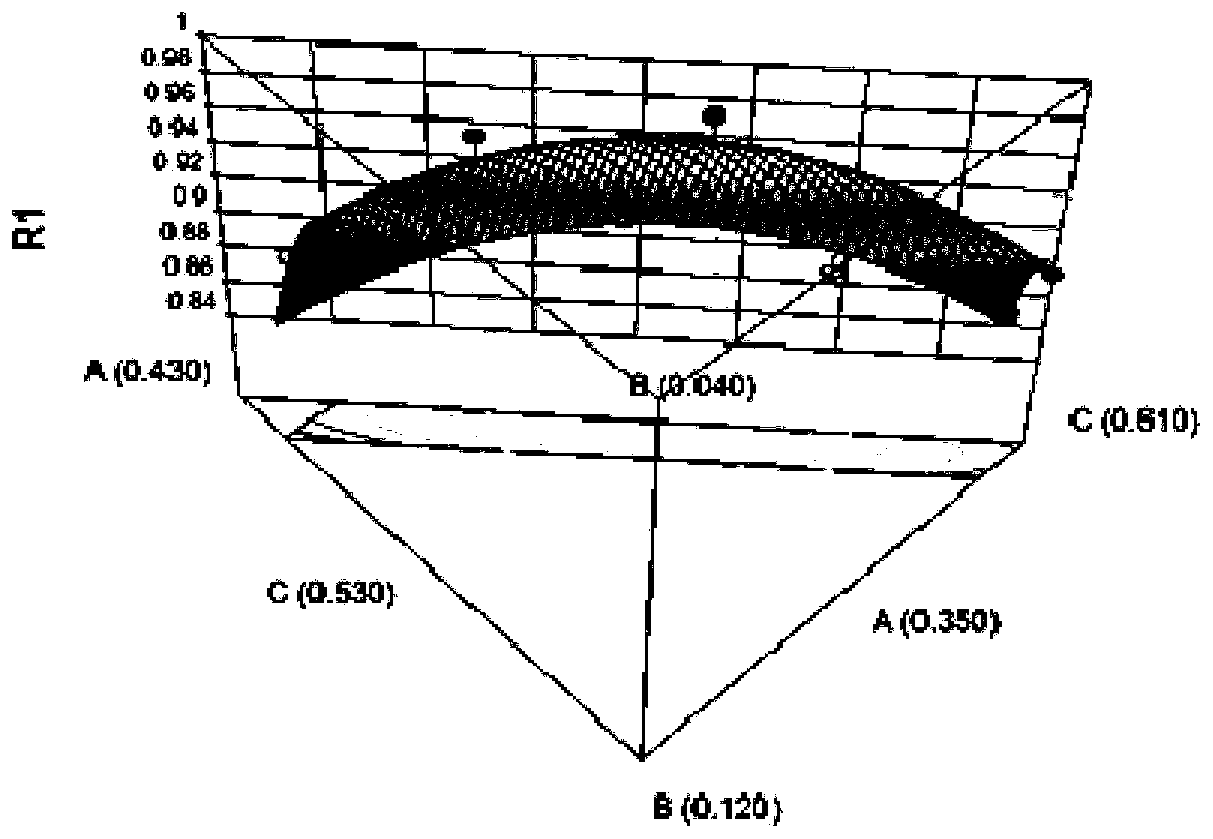
[0079] Prepare 3 batches of samples according to the matrix prescription (see Table 5 for specific prescription) and process screened out by the mixture design in Example 1. The test results and comprehensive scores are shown in Table 6. The results show that the “direct seal-in-bag cross-linking” gel plaster matrix preparation can be realized without adding emulsifiers, and it is relatively stable, but dialysis spots still appear in the paste .
[0080] Table 5. Validation Prescription
[0081] components Weight (g) Proportion(%) NP700 1.79 3.98 Aluminum glycylate 0.08 0.17 tartaric acid 0.05 0.11 glycerin 15.33 34.15 K-90 2.56 5.69 extract 0.82 1.82 Menthol 0.23 0.51 ice flakes 0.18 0.40 Camphor 0.18 0.40 Azone 0.26 0.57 Propylene Glycol 4.09 9.11 Potassi...
Embodiment 3
[0086] Embodiment 3 Direct sealing-in-bag crosslinking / curing control test
[0087] Sodium polyacrylate (NP-700) is a cross-linked skeleton material, by adding a cross-linking agent and a cross-linking regulator. In an acidic environment, the aluminum ions of the cross-linking agent are gradually released, resulting in a cross-linking / curing reaction, and the linear molecular chains of the polymer are bonded to each other to form a cross-linked network structure. Cross-linking modifiers control the Al 3+ The release rate and degree of release make the paste have suitable cohesion and viscosity, and at the same time, it is beneficial to stirring, coating and cutting. Based on Example 2, add EDTA-2Na to the verified prescription, and investigate the effect of adding ratios of aluminum glycolate and EDTA-2Na at 6:1, 3:1, 3:1.5 and 3:2 on the properties of the paste. The prescription is shown in Table 7 . The results show that the paste completed crosslinking / curing in 15 days,...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com