Conductive aqueous binder applied to lithium ion battery and preparation method and application thereof
A technology of lithium-ion batteries and water-based binders, applied in battery electrodes, secondary batteries, circuits, etc., can solve the problems of not being able to reduce the internal resistance of pole pieces, short service life of binders, and affecting battery performance, and achieve enhanced Effects of improving mechanical properties, improving cohesive force, and improving dispersion effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
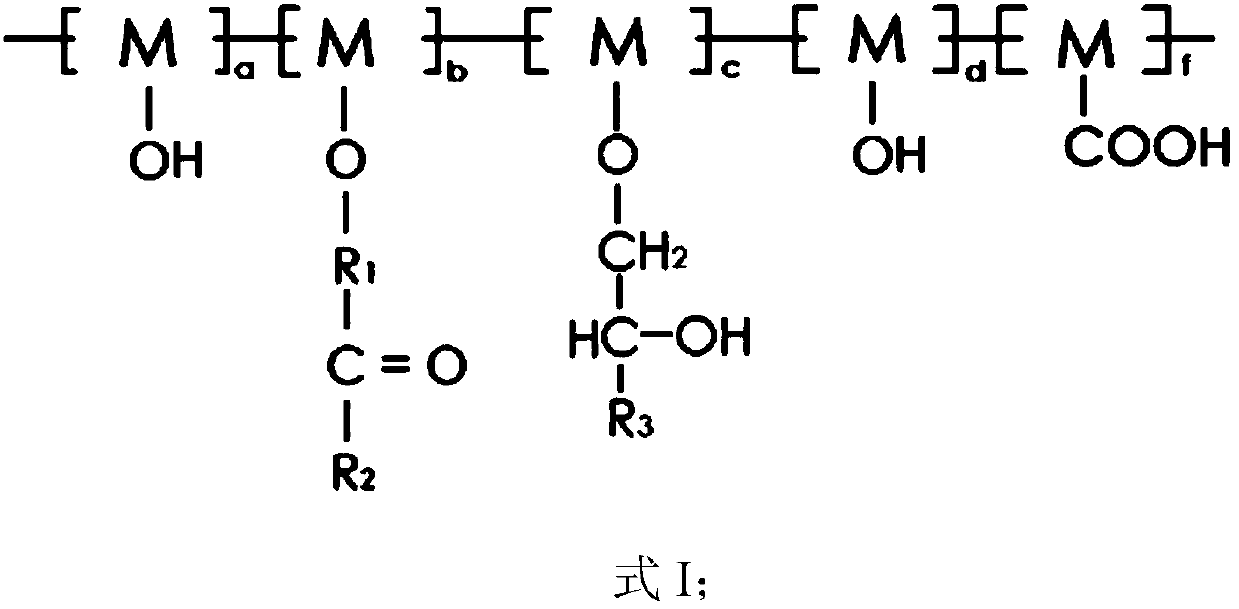
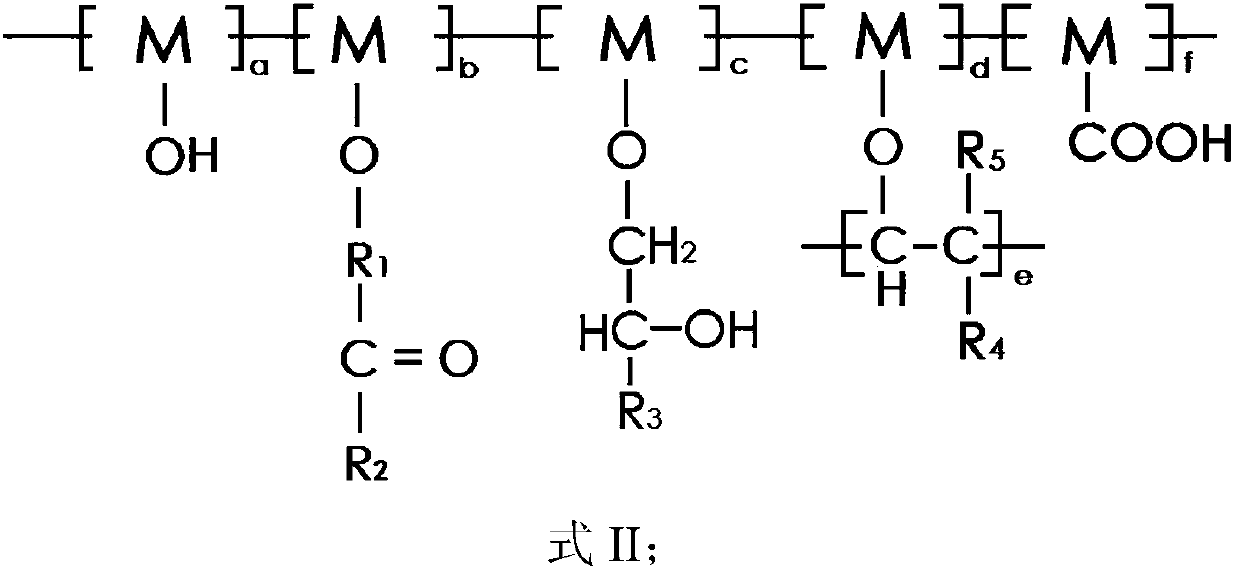
[0097] The conductive aqueous binder for lithium ion batteries provided in this embodiment has a three-dimensional conductive grid structure, and the structure is shown in formula II.
[0098] The preparation method is as follows:
[0099] (1) 10g of lithium silicate and 50g of acrylamide are dissolved in water to obtain an aqueous solution with a mass fraction of lithium silicate of 5%, and the aqueous solution is added dropwise to 80g of polyvinyl alcohol (the molar number of the repeating unit M is 1.82mol), Stir at 30°C for 10 hours to obtain a water-soluble polymer represented by formula I.
[0100] (2) the water-soluble polymer 57g that step (1) obtains, 13.7g silver particle (being 5% of binding agent quality) and methacrylic acid are under the triggering of 4g ammonium persulfate, polymerized 20 hours at 0 ℃, A conductive aqueous binder for lithium ion batteries is obtained.
Embodiment 2
[0102] The conductive aqueous binder for lithium ion batteries provided in this embodiment has a three-dimensional conductive grid structure, and the structure is shown in formula II.
[0103] (1) 10g lithium silicate, 6g acrylamide and 5g propylene oxide are dissolved in water, obtain lithium silicate mass fraction and be the aqueous solution of 20%, the aqueous solution is added dropwise to 80g polyvinyl alcohol (the number of moles of repeating unit M is 1.82mol), stirred at 90°C for 0.5 hour to obtain the water-soluble polymer represented by formula I.
[0104] (2) the water-soluble polymer 141g that step (1) obtains, 137g conductive polymer (being 50% of binding agent quality) and methacrylic acid are under the initiation of 4g ammonium persulfate, polymerized 1 hour at 100 ℃, A conductive aqueous binder for lithium ion batteries is obtained.
Embodiment 3
[0106] The conductive aqueous binder for lithium ion batteries provided in this embodiment has a three-dimensional conductive grid structure, and the structure is shown in formula II.
[0107] (1) 10g lithium silicate, 0.01g acrylamide and 0.01g propylene oxide are dissolved in water, obtain lithium silicate mass fraction and be the aqueous solution of 90%, the aqueous solution is added dropwise to 80g polyvinyl alcohol (the mole of repeating unit M number is 1.82mol), stirred at 60°C for 4 hours to obtain a water-soluble polymer represented by formula I.
[0108] (2) 7g of the water-soluble polymer obtained in step (1), 78g of silver particles (5% of the mass of the binder) and acrylic acid were polymerized at 50°C for 10 hours under the initiation of 0.004g of ammonium persulfate to obtain lithium Conductive aqueous binder for ion batteries.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Specific surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Viscosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com