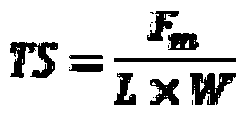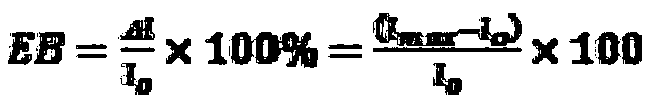Edible inhibition film agent as well as production method and application thereof
A film agent, edible technology, applied in the field of edible bacteriostatic film agent, can solve the problems of no obvious antibacterial effect, sustained bacteriostatic ability and poor bacteriostatic broad spectrum, so as to achieve no peculiar smell, soft and delicious taste, and elastic Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0029] 1, the present embodiment provides a kind of edible antibacterial film agent, and its raw material consists of: 3 parts of sweet potato starch, 1.5 parts of glycerin, 1 part of Tween 80, 3 parts of magnolia bark essential oil, ε-polylysine hydrochloride 3 parts of salt, 88.5 parts of water.
[0030] 2. Prepare edible antibacterial film according to the following steps
[0031] (1) take each raw material successively according to parts by weight;
[0032] (2) Sweet potato starch, glycerin, Tween 80, ε-polylysine hydrochloride, and water are made into a mixed solution, stirred evenly, heated in boiling water for 15 minutes, and then cooled to room temperature;
[0033] (3) Add magnolia bark essential oil to the mixture obtained in step (2), stir at 150 rpm at room temperature for 2 hours, and degas it with a vacuum pump for 0.5 minutes to obtain the product.
[0034] The edible antibacterial film agent that obtains is applied on the plexiglass flat plate, forms film aft...
Embodiment 2
[0039] 1, the present embodiment provides a kind of edible antibacterial film agent, and its raw material is composed of: 3 parts of sweet potato starch, 1.5 parts of glycerin, 1 part of Tween 80, 2 parts of magnolia bark essential oil, ε-polylysine hydrochloride 2 parts of salt, 90.5 parts of water.
[0040] 2. Prepare edible antibacterial film according to the following steps
[0041] (1) take each raw material successively according to parts by weight;
[0042] (2) Sweet potato starch, glycerin, Tween 80, ε-polylysine hydrochloride, and water are made into a mixed solution, stirred evenly, heated in boiling water for 15 minutes, and then cooled to room temperature;
[0043] (3) Add magnolia bark essential oil to the mixture obtained in step (2), stir at 150 rpm at room temperature for 2 hours, and degas it with a vacuum pump for 0.5 minutes to obtain the product.
[0044] 3. Follow the steps below to make steamed buns
[0045] Weigh 300g of all-purpose flour, 3g of yeast...
experiment example 1
[0056] Experimental example 1 Mechanical performance measurement experiment of edible antibacterial film
[0057] By embodiment 1,2, the edible bacteriostatic film agent described in comparative example 1,2,3 is applied on the plexiglass plate, forms edible bacteriostatic film after drying, film is peeled off, measures film stretching and fracture Elongation.
[0058] 1. Determination of film tensile and elongation at break
[0059] Tensile test: Select a flat, uniform and defect-free film, cut it into strips of 12mm×65mm, and fix it on the A / TG tensile probe of the TAXT2 texture analyzer. The probe is stretched 50mm at a constant speed of 0.8mm / s. Record the tensile strength and elongation at break, and repeat the experiment 10 times.
[0060] Tensile strength calculation formula:
[0061]
[0062] In the formula, TS-tensile strength, (MPa);
[0063] f m - the maximum tension that the specimen bears when it breaks, (N);
[0064] L-film thickness, (m);
[0065] W-fi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com