Bacterial cellulose nanofiber reinforced konjac glucomannan edible film and preparation method thereof
A technology of bacterial cellulose and nanofibers, applied in the field of food packaging materials, can solve the problems of low mechanical strength, complex process conditions, and poor antibacterial ability of pure KGM films, and achieve the effects of difficult complete peeling, wide sources, and easy operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0024] 1. Preparation of bacterial cellulose nanofibers (BCNs)
[0025] CICC 10529 strain (Komagataeibacter xylinus, Beijing, China, China Industrial Culture Collection Center) was used to culture and ferment under static conditions at 30°C, and the medium (pH 5.0) contained glucose 2% (w / v), yeast extract 0.5% ( w / v), K 2 HPO 4 0.1% (w / v), MgSO 4 1.5% (w / v) and ethanol 2% (v / v). After 14 days of static culture, the whole piece of cellulose film can be obtained in the culture medium. Rinse the cellulose membrane with tap water overnight, then soak it in 0.1M sodium hydroxide solution at 80°C for 2 hours, and then rinse it repeatedly with deionized water to completely remove the alkali to obtain bacterial cellulose.
[0026] 5.0 g of bacterial cellulose was mixed with 75 mL of HCl (2.5 M), and then magnetically stirred (200 rpm) at 70° C. for 4 h to hydrolyze it. After hydrolysis, cool to room temperature, centrifuge at 10,000×g for 10 minutes to collect the hydrolyzed p...
Embodiment 2
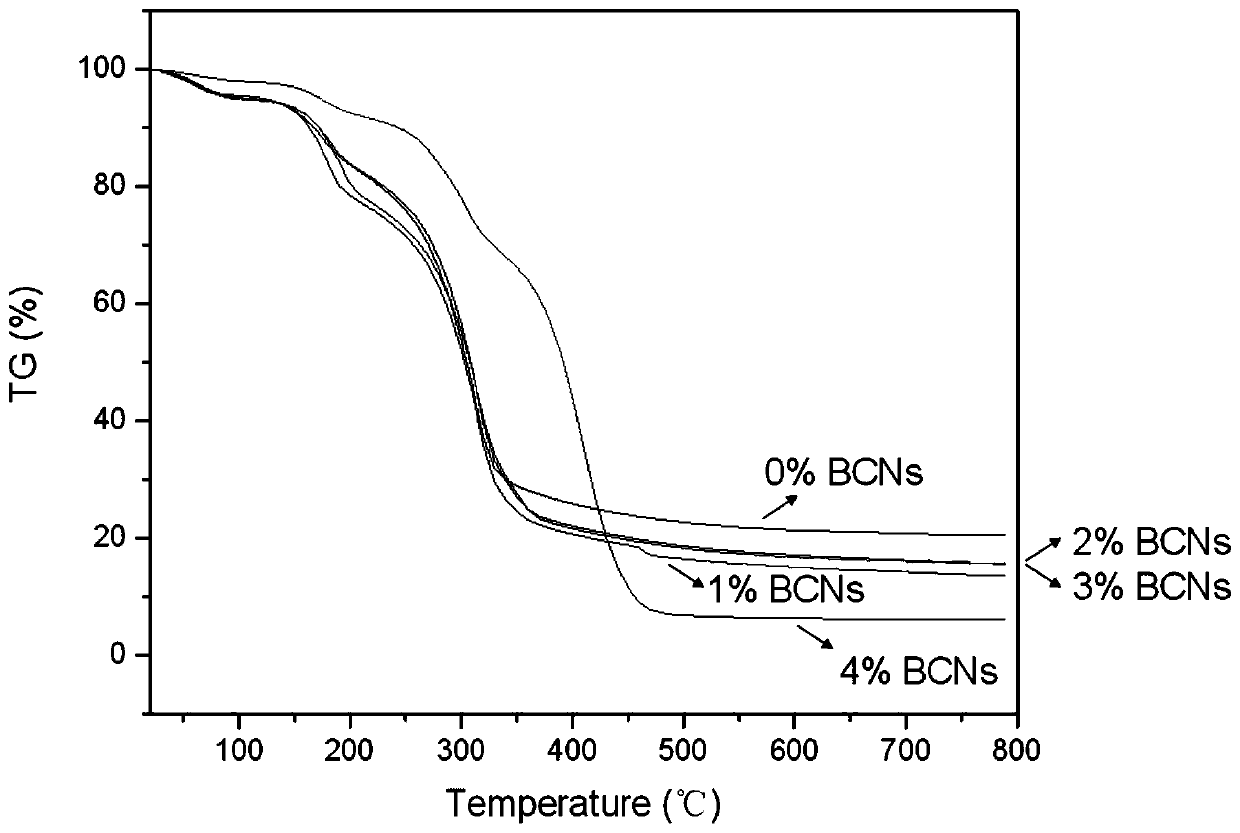
[0031] The difference between the present embodiment and Example 1 is: konjac gum powder in step 2: glycerin: bacterial cellulose nanofiber: the weight ratio of distilled water is 1:0.3:0.02:100. The obtained konjac gum base edible film of embodiment 2 is analyzed, and its tensile strength, elongation at break, water vapor permeability and water solubility are respectively 69.43Mpa, 9.44%, 5.03 × 10 -10 g·m / Pa·s·m 2 and 68.97%, thermal stability see figure 1 .
Embodiment 3
[0033] The difference between the present embodiment and Example 1 is: konjac gum powder in step 2: glycerin: bacterial cellulose nanofiber: the weight ratio of distilled water is 1:0.3:0.03:100. The obtained konjac gum base edible film of embodiment 3 is analyzed, and its tensile strength, elongation at break, water vapor permeability and water solubility are respectively 74.50Mpa, 8.911%, 4.56 × 10 -10 g·m / Pa·s·m 2 and 61.50%, thermal stability see figure 1 .
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Water soluble | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com