Soil treatment method for preventing and controlling plant parasitic nematodes
A soil treatment and soil technology, applied in land preparation methods, devices for trapping or killing insects, agricultural machinery and implements, etc., can solve the problems of high price and high toxicity, reduce the amount of use, reduce the amount of application, and have no environmental risks Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0024] Embodiment one, soil liquid ammonia disinfection
[0025] (1) Plow the soil of facilities with serious root-knot nematode disease to a depth of 25 cm, and when the soil moisture content is below 30%, perform liquid ammonia disinfection treatment.
[0026] (2) The steel pipe of the liquid ammonia cylinder and the ditching tool are bound together, the steel pipe and the ditching tool are inserted into the soil to a depth of 15 cm, and the valve is opened to disinfect the soil with liquid ammonia. During the liquid ammonia disinfection process, the ditching tool and the steel pipe move forward at a constant speed. The forward speed of disinfection is determined according to the amount of disinfectant ammonia, and the application amount of liquid ammonia is preferably between 10-50kg / mu. The distance between disinfection rows is about 30cm. After disinfection, carry out coating treatment. Membrane closed for 5-10 days.
[0027] (3) After sealing the film for 5-10 days, ...
Embodiment 2
[0029] Embodiment two, the influence of liquid ammonia disinfection on cucumber planting
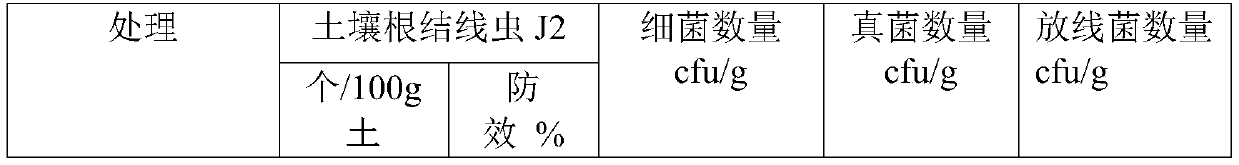
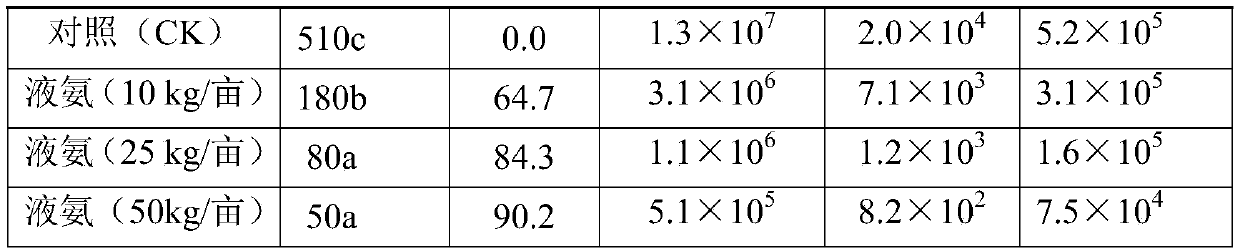
[0030] Select the soil with severe root-knot nematode disease, and evaluate the effect of the facility soil used for cucumber planting. There are 5 treatments in the experiment: control (CK); 10kg / mu of liquid ammonia for disinfection; 25kg / mu of liquid ammonia for disinfection; The treatment before transplanting was the same as that of the control). After the soil treatment was completed, the cucumber seedlings (Jinyou 35) were transplanted and routinely managed. During the whole process, different treatments were carried out according to the final equal amount of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium.
[0031] Carry out the detection of root-knot nematode (second instar larvae J2) quantity and cultivable microorganism (bacterium, fungus and actinomycetes) quantity in the soil after soil disinfection and film removal (all treatments are covered with film) 7-10 days respectively; Harvest...
Embodiment 3
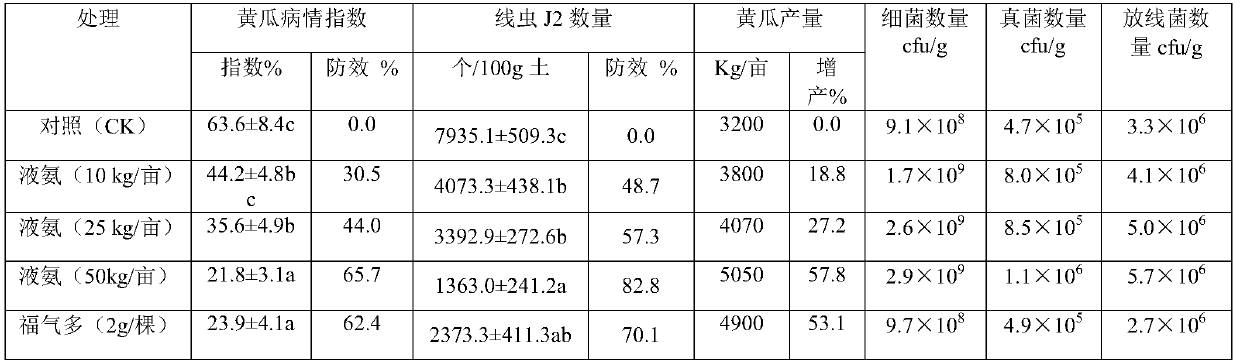
[0047] Embodiment three, the influence of liquid ammonia disinfection on tomato cultivation
[0048] The root-knot nematode disease occurrence was selected, and the effect evaluation was carried out on the facility soil used for tomato planting. There are 5 treatments in the experiment: control (CK); 10kg / mu of liquid ammonia for disinfection; 25kg / mu of liquid ammonia for disinfection; The treatment before transplanting was the same as that of the control). After the soil treatment was completed, the tomato seedlings (Kufen No. 8) were transplanted and routinely managed. During the whole process, different treatments were carried out according to the final equal amount of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium. The number of root-knot nematodes (J2) before soil treatment was 276 / 100g soil.
[0049] Other experimental methods, experimental schemes, and detection indicators are the same as "Example 2" unless otherwise specified.
[0050] Table 3 The number of different microorg...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com