Self-wetting nanometer fluid capable of enhancing micro-nano structure heat transfer, preparation method and applications thereof
A nanofluid and self-wetting technology, applied in the field of enhanced heat transfer, can solve the problems of reduced heat transfer coefficient and critical heat flow, nanoparticle blocking capillary structure, unstable heat transfer performance, etc., to improve critical heat flow and enhance heat transfer Performance, the effect of improving local heat transfer
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
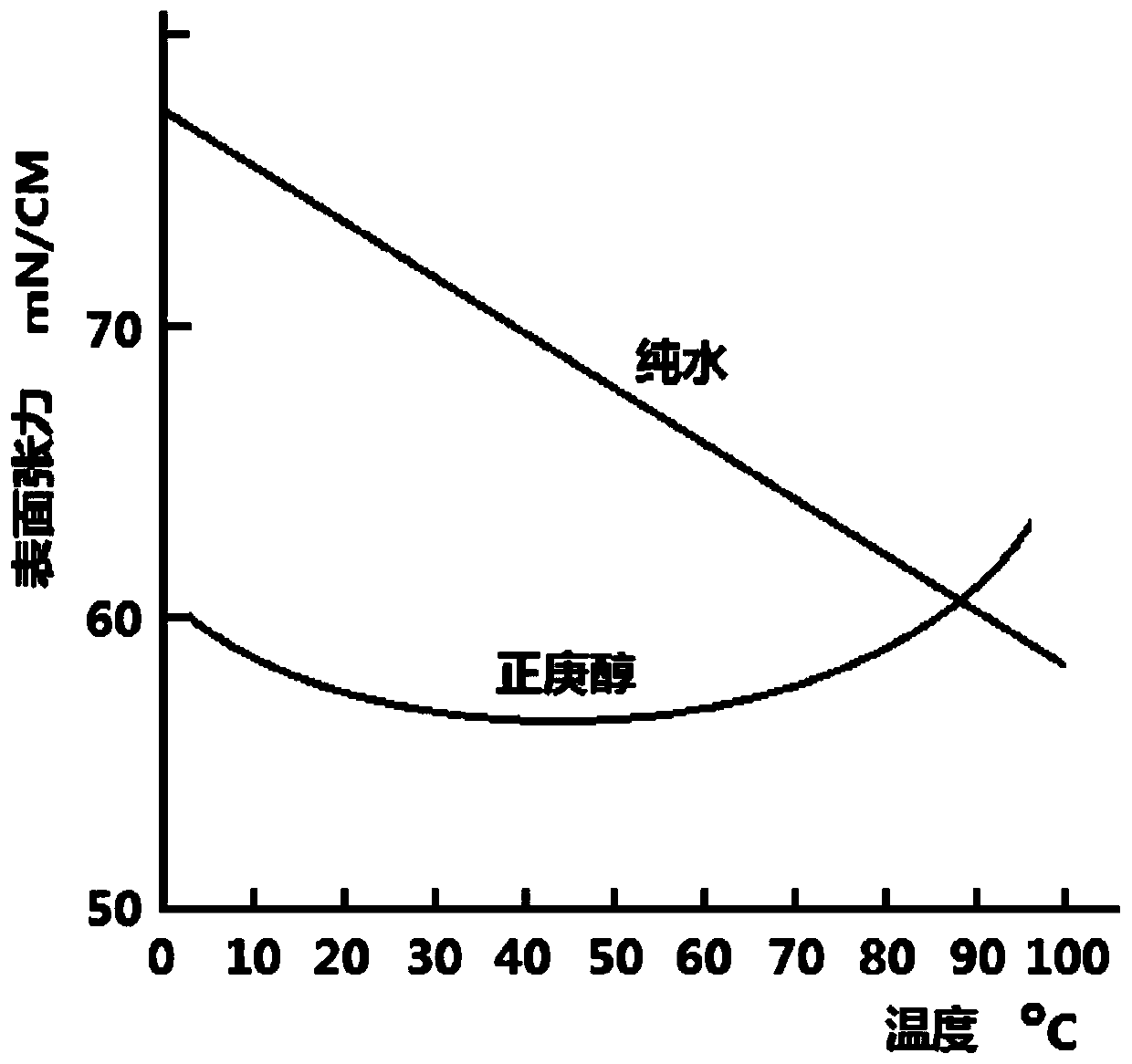
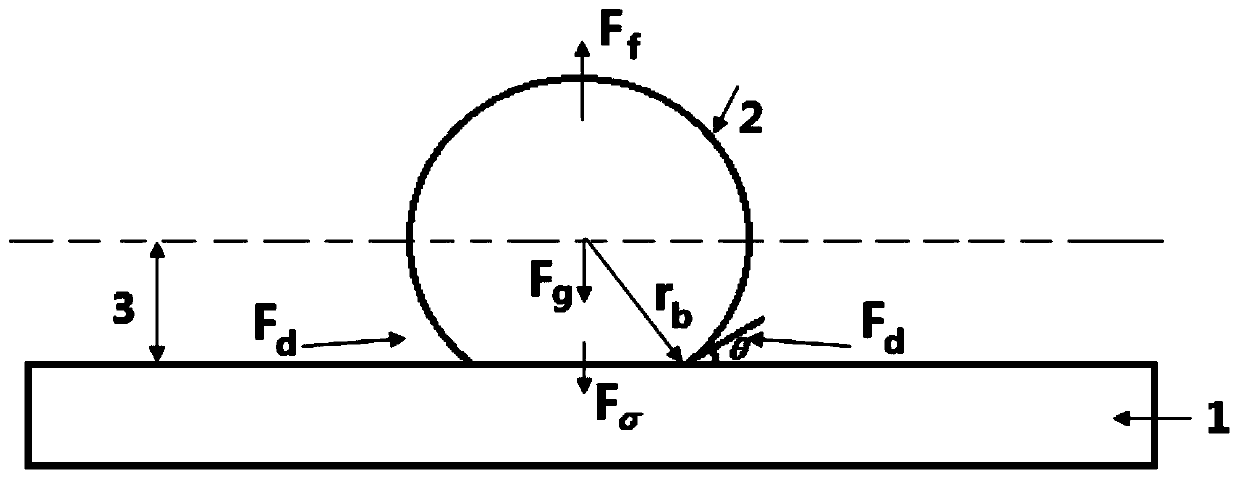
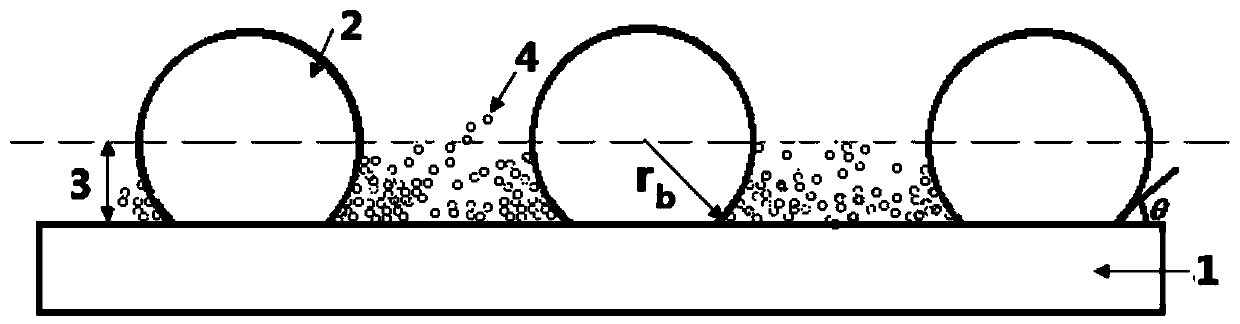
[0029] Weigh Cu nanoparticles (average particle diameter 50nm, bulk density 0.25g / cm 3 ), n-heptanol aqueous solution, and polyoxyethylene 40 stearate were mixed directly, and the prepared mixed solution was stirred by a magnetic stirrer for 15 minutes, then dispersed by ultrasonic oscillation for 2 hours, and finally stirred by a magnetic stirrer for 15 minutes, so that the mixed solution could form a uniform Self-wetting nanofluid with special wettability and good dispersibility and stability (the mass concentration of Cu nanoparticles is 1.5%, the concentration of n-heptanol is 2.0×10 -3 mol / l, polyoxyethylene 40 stearate concentration 1.0×10 -7 mol / l).
Embodiment 2
[0031] Under vacuum conditions, put the self-wetting Cu nanofluid prepared in Example 1 into a double-layer glass reactor container, heat the self-wetting Cu nanofluid in the reactor for 20 minutes, recover the liquid after steam condensation, and measure the volume of the recovered liquid . The same volume of conventional Cu nanofluid was used instead of the self-wetting nanofluid, and the previous experiment was repeated under the same experimental conditions. The conventional Cu nanofluid preparation method is basically the same as the self-wetting Cu nanofluid preparation method in Example 1, the difference is that deionized water is used instead of n-heptanol aqueous solution as the base liquid, specifically with a concentration of 1.0 × 10 -7 The mol / l sodium dodecylbenzenesulfonate solution replaces the compound n-heptanol aqueous solution and polyoxyethylene 40 stearate as a dispersant.
[0032] Comparing the volumes of liquid collected in the two experiments, it was ...
Embodiment 3
[0036] The preparation process of the self-wetting nanofluid is basically the same as in Example 1, the only difference is that the average particle diameter of the Cu nanoparticles is replaced by 20nm and 80nm respectively, and the stirring time of the magnetic stirrer before and after the two times is adjusted to 12min, The self-wetting nanofluids were prepared separately. And replace the self-wetting nanofluid in Example 2 with the above-mentioned self-wetting nanofluid, and find that the steam condensate obtained by the above-mentioned self-wetting nanofluid is 21.0% and 19.9% more than the steam condensate obtained by the conventional Cu nanofluid , Comparing the conductivity of the steam condensate obtained from the above self-wetting nanofluid with the conductivity of the base liquid, it is found that the difference between the two is 8.5% and 7.9%, respectively. In this example, the base liquid refers to an aqueous solution of n-heptanol at the same concentration as ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com