A dyeing method for observing the internal microstructure of plants
A technology of microstructure and staining method, which is applied in testing plant materials, preparation of test samples, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of large workload of freehand sectioning, easy evaporation of sectioning, long time, etc., and achieve flexible dyeing experiment time. , reduce workload, slice complete effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0021] The invention provides a dyeing method for observing the internal microstructure of plants, comprising the steps of:
[0022] Step 1. Making freehand slices: use a blade to cut the small piece of plant root into slices with a thickness of 0.2-0.5 mm.
[0023] Step 2. Put the freehand slices into glycerin and save them for later use;
[0024] Step 3, drug preparation:
[0025] (1) Preparation of 0.05% (w / v) toluidine blue (TBO) dye solution: Take 0.05g TBO, dissolve in 100mL distilled water, mix well to prepare 0.05% TBO.
[0026] (2) Preparation of 5% (w / v) phloroglucinol solution: take 4 to 5 g of phloroglucinol, dissolve it in 100 ml of 95% alcohol, mix well to form phloroglucinol-alcohol solution, and prepare it now Use (solution yellow-brown failure).
[0027] (3) Preparation of 0.1% (w / v) Sudan 7B solution: Weigh 50 mg of Sudan 7B and dissolve it in 25 mL of PEG-300, then cool in a 90°C water bath for 1 hour, add an equal volume of 90% glycerol, and store at roo...
experiment example
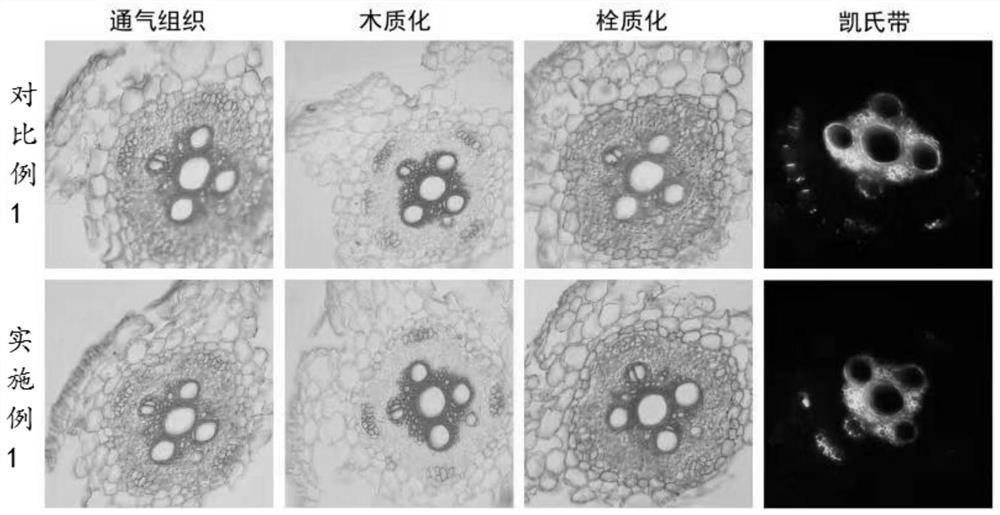
[0040] Record and count the microstructural diagrams of the aerenchyma, lignification, suberinization, and Caspian bands obtained in Example 1 and Comparative Example 1. figure 1 shown.
[0041] Depend on figure 1 It can be seen that both Example 1 and Comparative Example 1 can clearly see the microstructure of aerenchyma, lignification, suberinization, and Kjeldahl bands.
[0042] The method of the embodiment 1 of the present invention has obtained the same or similar results through repeated trials and experiments, showing that the method is stable and reliable, the observation result is clear, and the internal structure of the root can be seen clearly. Compared with the existing method, it can be carried out successively. 4 staining observations (air tissue, lignification, suberinization and Kjeldahl band), greatly reducing the workload of freehand sectioning, saving experimental materials and improving experimental efficiency.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com