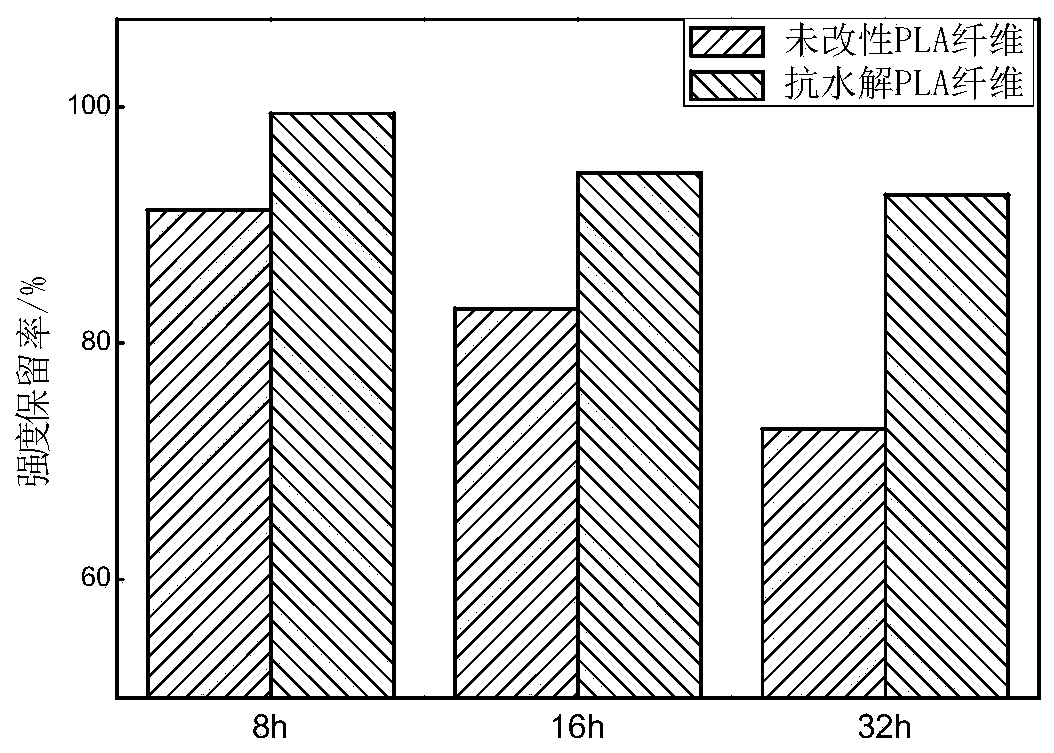
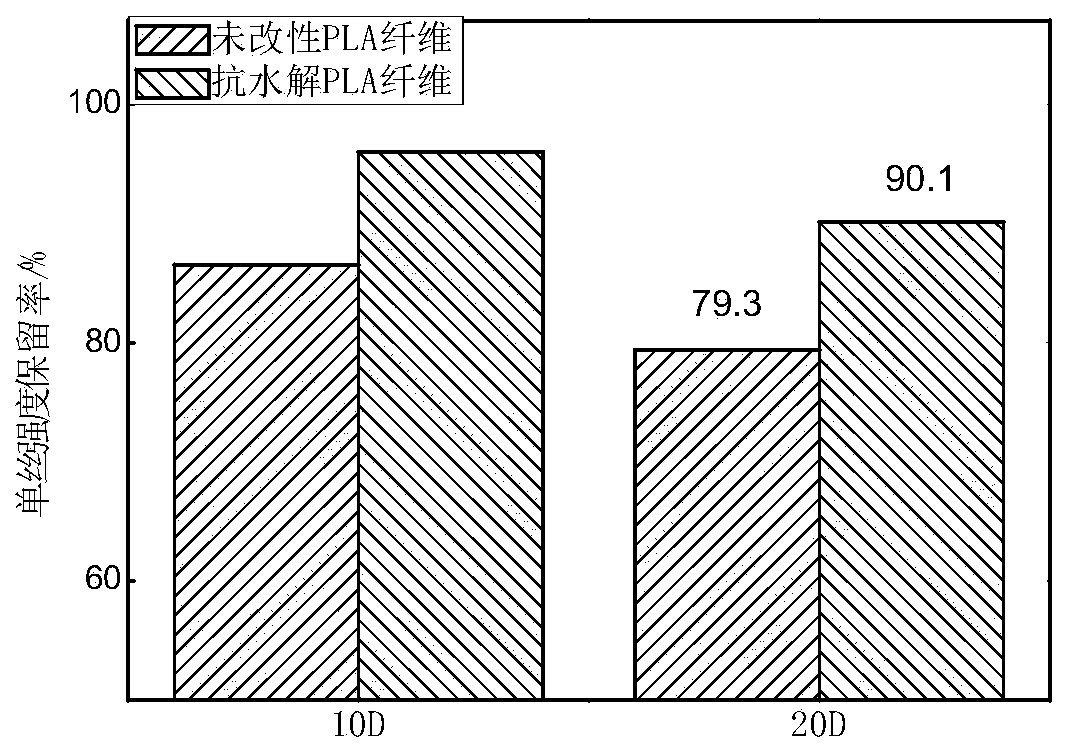
Soft and hydrolysis-resistant PLA (polylactic acid) fiber and preparation method thereof
The technology of polylactic acid fiber and polylactic acid, which is applied in the field of sanitary product fiber and its preparation, can solve the problems such as the decrease of mechanical strength of polylactic acid, and achieve the effects of short drying time, improved hydrophilicity and hand feeling, and improved flexibility.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0037] Step 1: Preparation of PLA / PEG / MDI Composite Masterbatch
[0038] 90 parts of polylactic acid were pre-vacuum-dried at 60°C for 24 hours, then 90 parts of polylactic acid, 7 parts of polyethylene glycol and 0.4 parts of compatibilizer MDI were uniformly mixed in proportion, and added to a twin-screw extruder to granulate to obtain masterbatches. Wherein, the temperature of each zone of the twin-screw extruder is 150°C.
[0039] Step 2: Preparation of PLA / PCDI composite masterbatch
[0040] 90 parts of polylactic acid were vacuum-dried at 70°C for 12 hours in advance, then 90 parts of PLA and 0.1 part of PCDI were pre-mixed in a high-speed mixer, and granulated by a twin-screw extruder to obtain masterbatches. Wherein, the temperature of each zone of the twin-screw extruder is 150° C., and the screw speed is 180 rpm.
[0041] Step 3: Preparation of soft, hydrolysis-resistant PLA fibers
[0042] After vacuum-drying the obtained two kinds of masterbatches at 80°C for 48...
Embodiment 2
[0075] Step 1: Preparation of PLA / PEG / MDI Composite Masterbatch
[0076] Parts of polylactic acid were vacuum-dried at 60°C for 24 hours in advance, and then 92 parts of polylactic acid, 8 parts of polyethylene glycol and 0.6 parts of compatibilizer MDI were uniformly mixed in proportion, and added to a twin-screw extruder to granulate to obtain masterbatches. Wherein, the temperature of each zone of the twin-screw extruder is 160°C.
[0077] Step 2: Preparation of PLA / PCDI composite masterbatch
[0078] 94 parts of polylactic acid were vacuum-dried at 70°C for 12 hours in advance, then 94 parts of PLA and 0.2 part of PCDI were premixed in a high-speed mixer, and granulated by a twin-screw extruder to obtain masterbatches. Wherein, the temperature of each zone of the twin-screw extruder is 160° C., and the screw speed is 220 rpm.
[0079] Step 3: Preparation of soft, hydrolysis-resistant PLA fibers
[0080] After vacuum-drying the obtained two kinds of masterbatches at 80°C...
Embodiment 3
[0082] Step 1: Preparation of PLA / PEG / MDI Composite Masterbatch
[0083] 96 parts of polylactic acid were pre-vacuum-dried at 60°C for 24 hours, then 96 parts of polylactic acid, 9 parts of polyethylene glycol and 0.8 parts of compatibilizer MDI were uniformly mixed in proportion, and added to a twin-screw extruder to granulate to obtain masterbatches. Wherein, the temperature of each zone of the twin-screw extruder is 170°C.
[0084] Step 2: Preparation of PLA / PCDI composite masterbatch
[0085] 98 parts of polylactic acid were vacuum-dried at 70°C for 12 hours in advance, then 98 parts of PLA and 0.4 parts of PCDI were premixed in a high-speed mixer, and granulated by a twin-screw extruder to obtain masterbatches. Wherein, the temperature of each zone of the twin-screw extruder is 170° C., and the screw speed is 250 rpm.
[0086] Step 3: Preparation of soft, hydrolysis-resistant PLA fibers
[0087] The obtained two kinds of masterbatches were vacuum-dried at 80°C for 48 h...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com