Near infrared antibiotic fluorescent probe detecting agent and preparing method and application thereof
A technology of fluorescent probes and detection reagents, applied in the direction of fluorescence/phosphorescence, chemical instruments and methods, luminescent materials, etc., can solve the problems of complex design, single detection, and insufficient sensitivity, and achieve simple design, cost saving, and improved sensitivity Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0054] In one embodiment, the preparation method of the near-infrared carbon quantum dots comprises: using a microwave-assisted solvent method or a solvothermal method to make a uniformly mixed reaction system containing glutathione, polyethyleneimine and a solvent at 140-180 °C for 1-8 hours to form the near-infrared carbon quantum dots.
[0055] Further, the microwave power used in the microwave-assisted solvent method is 200-400W.
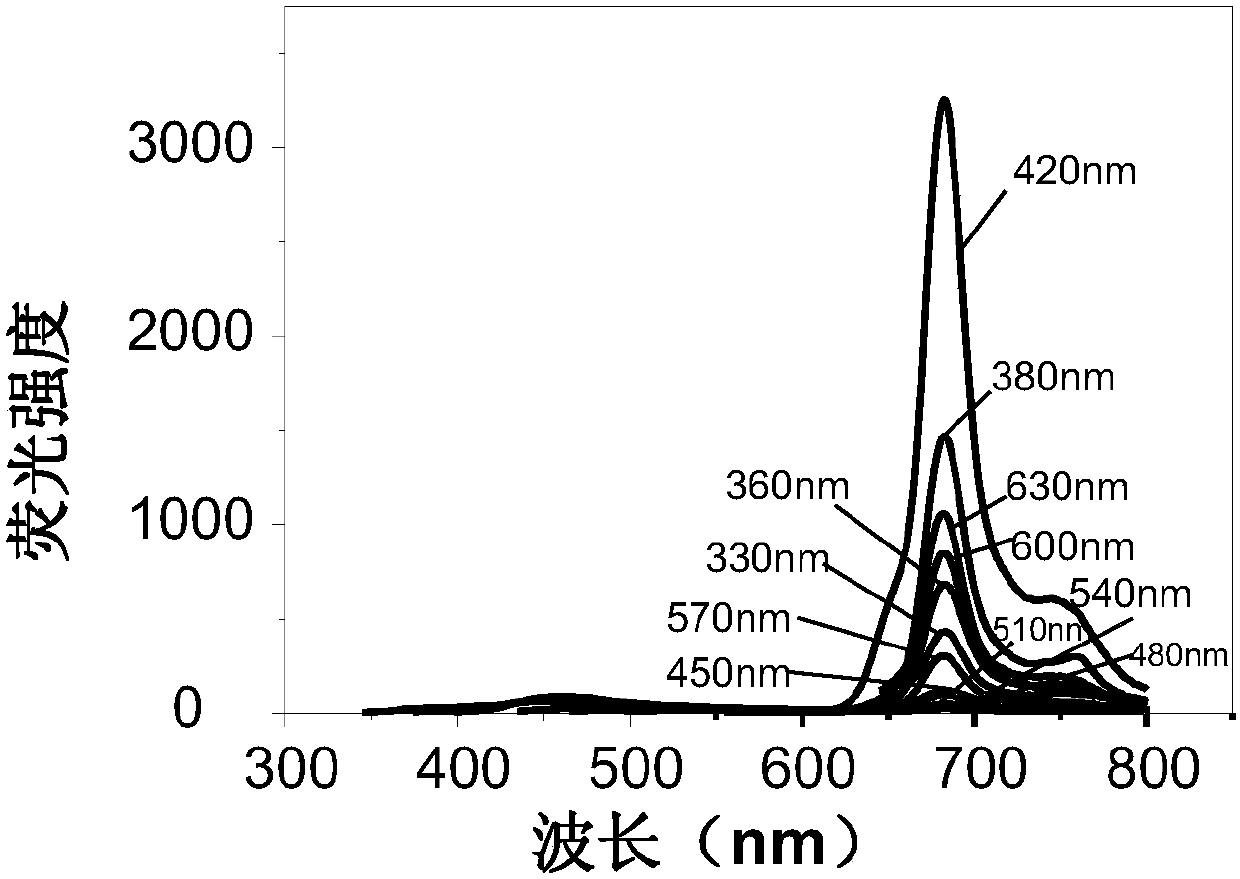
[0056] In the preparation process of near-infrared carbon quantum dots, the regulation of fluorescence spectrum and functional group modification of near-infrared carbon quantum dots can be realized by controlling the reaction time, reaction temperature, and the ratio of reactants.
[0057] In one embodiment, functional groups are distributed on the surface of the fluorescent nanomaterial.
[0058] Further, the functional group includes any one or a combination of two or more of carboxyl, amino, and hydroxyl, but is not limited thereto.
[005...
Embodiment 1
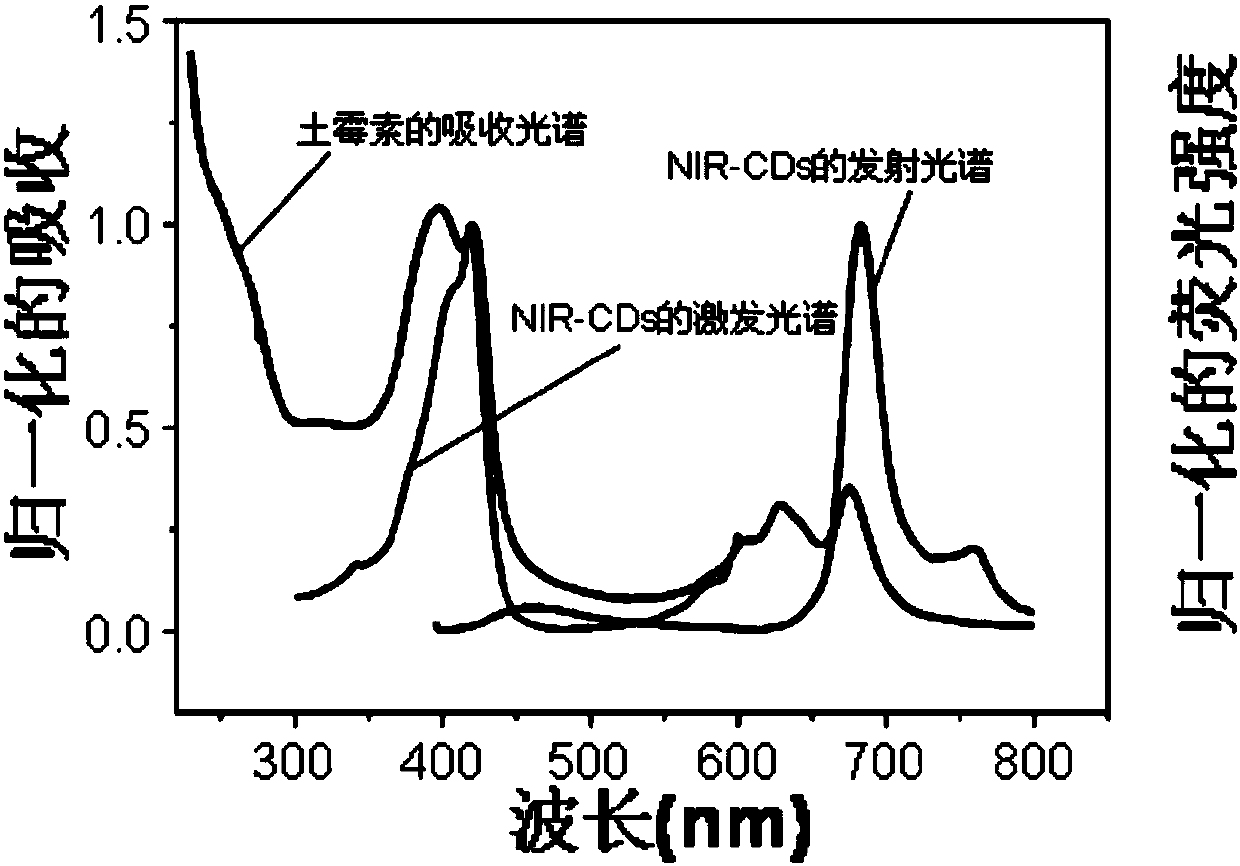
[0093] Example 1 Construction of highly sensitive near-infrared detection fluorescent nanoprobes
[0094] (1) Preparation of polyethyleneimine-modified near-infrared carbon quantum dots:
[0095] Using the common solvothermal method, weigh glutathione and polyethyleneimine (PEI) with a molecular weight of 600 in a beaker, dissolve them with 15 mL of formamide, and mix them uniformly by ultrasonic, wherein glutathione accounts for the mass of formamide The percentage concentration is 3%, and the mass percentage concentration of PEI in glutathione is 30%. After mixing evenly, a transparent solution is obtained. The above solution is transferred to a polytetrafluoroethylene-lined reactor and reacted in an oven at 160°C. 4h, naturally cooled to room temperature. After diluting the reaction mixture with deionized water, it was directly dialyzed with a dialysis bag with a molecular weight cut-off of 3500Da for one week to remove unreacted raw materials and small molecules. Filter ...
Embodiment 2
[0099] Example 2 Construction of highly sensitive near-infrared detection fluorescent nanoprobes
[0100] (1) Preparation of polyethyleneimine-modified near-infrared carbon quantum dots:
[0101] Using the common solvothermal method, weigh glutathione and polyethyleneimine (PEI) with a molecular weight of 600 in a beaker, dissolve them with 15 mL of formamide, and mix them uniformly by ultrasonic, wherein glutathione accounts for the mass of formamide The percentage concentration is 5%, and the mass percentage concentration of PEI accounts for glutathione is 60%. After mixing evenly, a transparent solution is obtained. The above solution is transferred to a polytetrafluoroethylene-lined reaction kettle and placed in an oven at 140°C. Reaction 8h, naturally cooled to room temperature. After diluting the reaction mixture with deionized water, it was directly dialyzed with a dialysis bag with a molecular weight cut-off of 1000 Da for one week to remove unreacted raw materials an...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com