DNA coding compound library and compound screening method
A compound library and screening method technology, which is applied in the field of DNA-encoded compound library and compound screening, can solve the problems of limited application range, degradation, loss of function of DNA tags, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0074] Embodiment 1, the synthesis of the starting DNA raw material of DNA coding compound library
[0075] Synthetic method one:
[0076] Step 1, the synthesis of compound 1
[0077]
[0078] The compound HUB1 (82nmol) was dissolved in sodium borate buffer (82 μL, pH=9.4, concentration 250mM / L) to form an initial solution with a concentration of 1mM / L; then the DMA solution of 4-azido-benzoic acid ( 8.2μmol, concentration 200mM / L), the DMA solution of HATU (8.2μmol, concentration 400mM / L) and the DMA solution of DIPEA (8.2μmol, concentration 400mM / L) were respectively placed in -20 ℃ refrigerator and mixed after cooling, the The mixture was vortexed to mix thoroughly, and then stored in a refrigerator at 4°C for 5 minutes. The above mixed solution was added to the starting solution of compound HUB1, vortexed and thoroughly mixed, and reacted at room temperature for 12 hours. Add 100 μL dd-H to 1 μL reaction solution 2 O dilution, LCMS to monitor the reaction. After th...
Embodiment 2
[0089] Embodiment 2, DNA coding compound library and screening
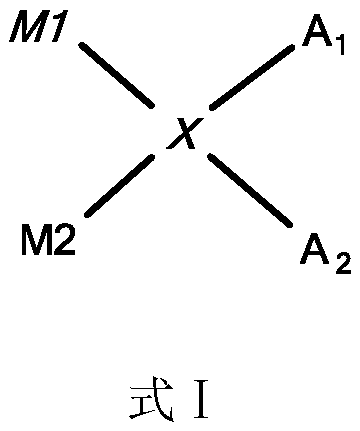
[0090] Using the starting DNA material prepared in Example 1, a DNA-encoded compound library with the following structure was constructed:
[0091]
[0092] The above-mentioned DNA-encoded compound library is screened according to the following steps:
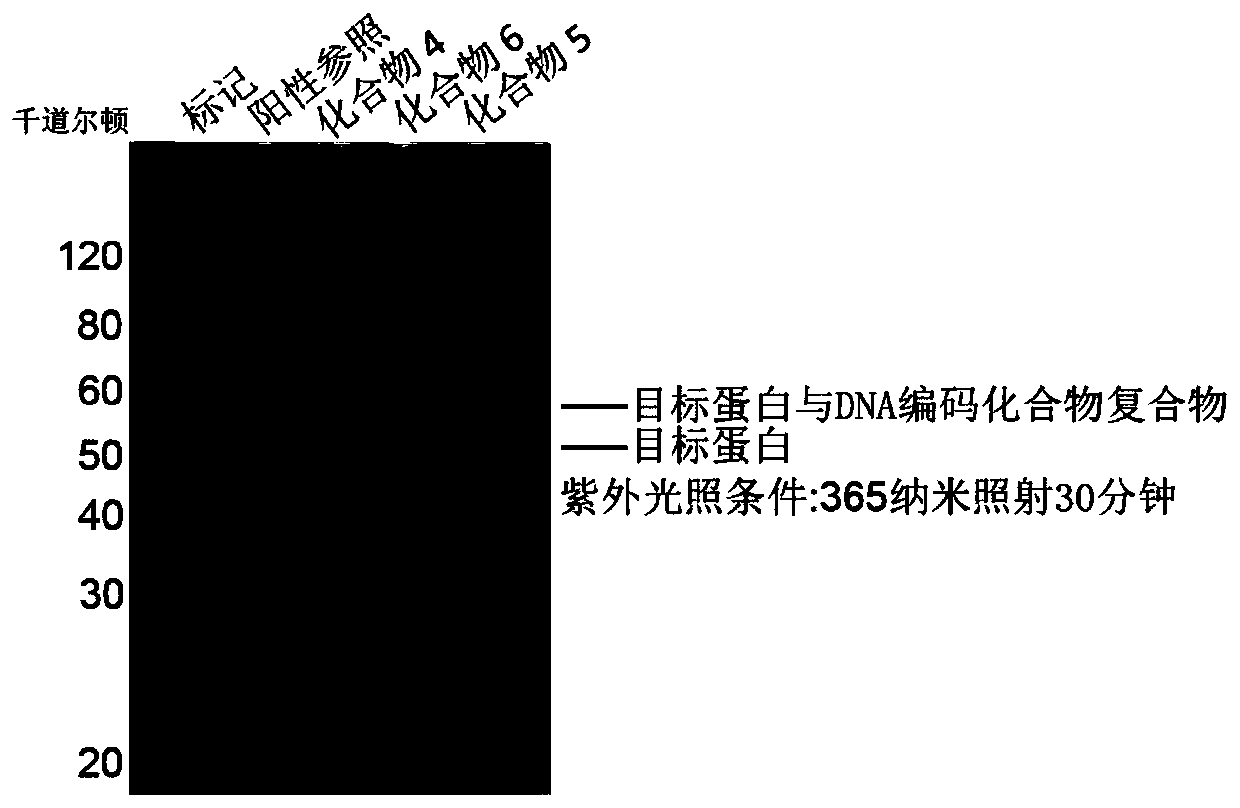
[0093] 1) Incubate the above DNA-encoded compound library with the target protein ROCK2 in 100 μL buffer system for 60 minutes, and then react under 365nm light conditions for 60 seconds;
[0094] 2) Heat the reaction solution to 90°C to denature the protein, separate it by preparative SDS-PAGE (12-15%), recover and extract the corresponding target protein-DNA-encoded compound covalently cross-linked complex by gel cutting the strip;
[0095] 3) Perform PCR amplification and DNA sequencing on the recovered samples, read the DNA sequences corresponding to the enriched small molecular compounds, and then obtain the structural information of the compounds.
Embodiment 3
[0096] Embodiment 3, DNA coding compound synthesis
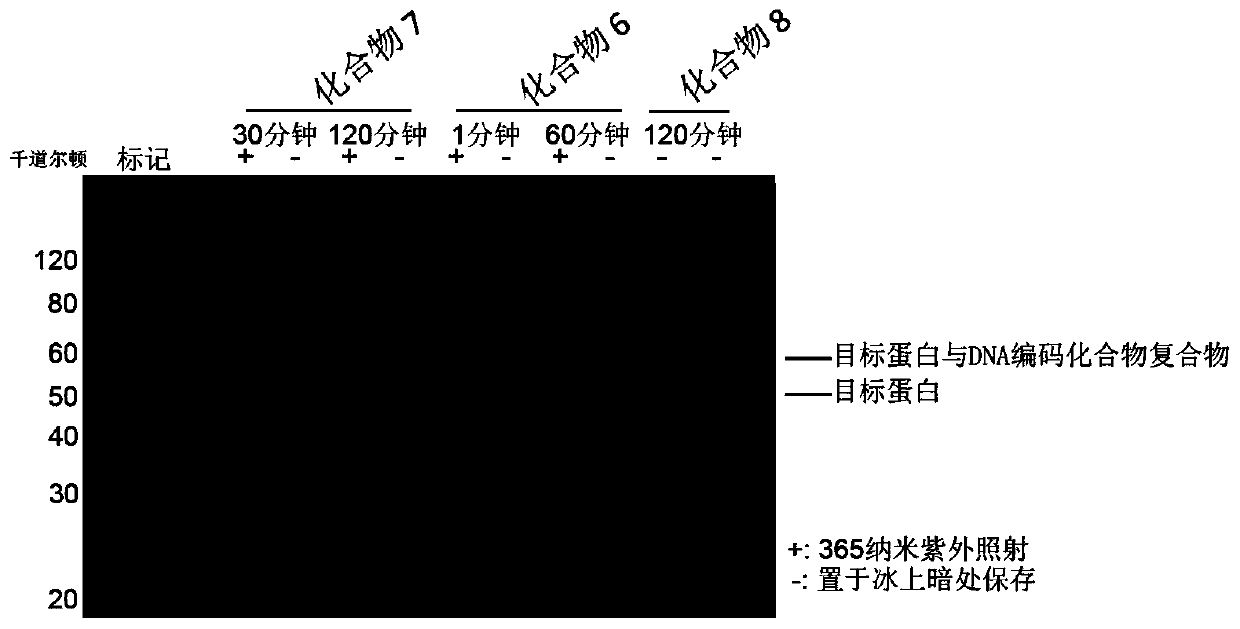
[0097] Through the screening of the DNA-encoded compound library in Example 2, after analyzing the structure of the compound, a compound without a DNA tag was re-synthesized, and its inhibitory activity IC on ROCK2 50 About 50nM. Use it as a tool compound to synthesize DNA-encoded compounds, and further verify the covalent cross-linking.
[0098] Step 1: Synthesis of compound 5
[0099]
[0100]Compound 3 (5 μmol) was dissolved in sodium borate buffer (5mL, pH=9.4, concentration 250mM / L) to make a starting solution with a concentration of 1mM / L; then the DMA solution of SM01 (10μmol, concentration 20mM / L ), the DMA solution of HATU (10 μmol, concentration 20mM / L) and the DMA solution of DIPEA (10 μmol, concentration 20mM / L) were respectively placed in a -20°C refrigerator and mixed, and the mixed solution was vortexed and thoroughly mixed. Then store in a refrigerator at 4°C for 5 minutes. The above mixed solution was...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com