Vector controlled "dead-time effect" compensation method for permanent magnet synchronous motor
A permanent magnet synchronous motor, dead-time compensation technology, applied in motor control, vector control system, motor generator control and other directions, can solve the problem of compensation effect dependence, adding additional hardware, complex calculation, etc., to save hardware cost, calculation Accurate and fast dead zone compensation effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0050] A specific embodiment of the present invention discloses a compensation method for "dead zone effect" of permanent magnet synchronous motor vector control, figure 1 A schematic flow chart of the method;
[0051] Described method specifically comprises the following steps:
[0052] Step S1, collect the phase current i of the permanent magnet synchronous motor a , i b , i c ;
[0053] Step S2, respectively judge |i a |, |i b |, |i c |with zero-crossing threshold i H size, if|i a |, |i b |or|i c |Less than zero-crossing threshold i H , then carry out dead zone compensation, jump to step S3, otherwise do not perform dead zone compensation;
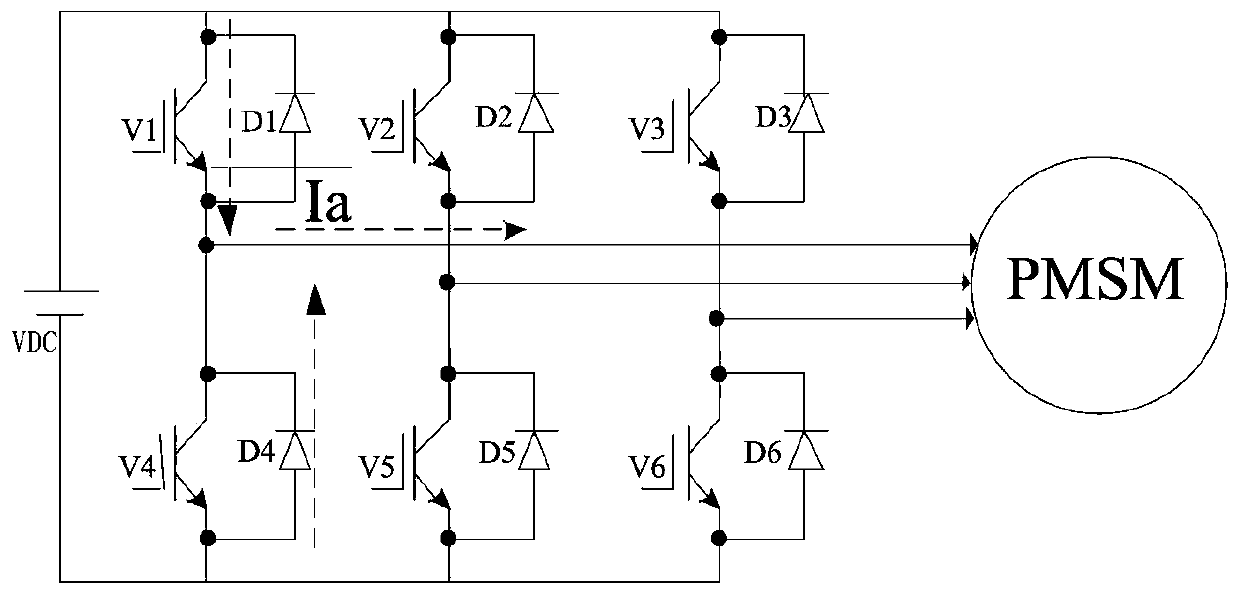
[0054] figure 2 It is the main circuit structure diagram of the three-phase voltage source PWM inverter motor load, the PWM inverter is connected to the PWM load, and the influence of the dead time on the output voltage is analyzed by taking the a-phase bridge arm as an example, and the current polarity is defined by Posi...
Embodiment 2
[0086] Another specific embodiment of the present invention discloses a permanent magnet synchronous motor vector control "dead zone effect" compensation system, the structural diagram of the system is as follows Image 6 As shown; the system includes a phase current acquisition module, a dead zone compensation execution discrimination module, a compensation voltage vector angle determination module and a dead zone compensation module,
[0087] The phase current acquisition module is used to acquire the phase current i of the permanent magnet synchronous motor a , i b , i c ;
[0088] The dead zone compensation execution judgment module is used to determine whether to perform dead zone compensation, if |i a |, |i b |or|i c |Less than zero-crossing threshold i H , the dead zone compensation is performed, otherwise no dead zone compensation is performed;
[0089] When performing dead zone compensation, the current vector angle calculation module is used to calculate the c...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com