Characterization method of extracellular vesicle
A vesicle and characterization technology, applied in the field of biochemistry, can solve the problems of unfavorable application and promotion of hospitals and disease detection centers, high cost of nanometer flow meters, etc., and achieve the effect of improving the accuracy of characterization
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
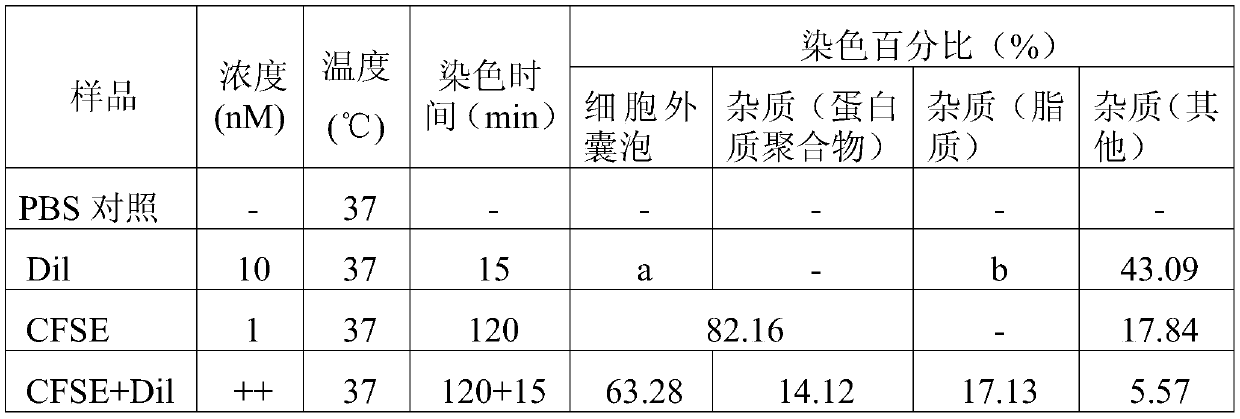
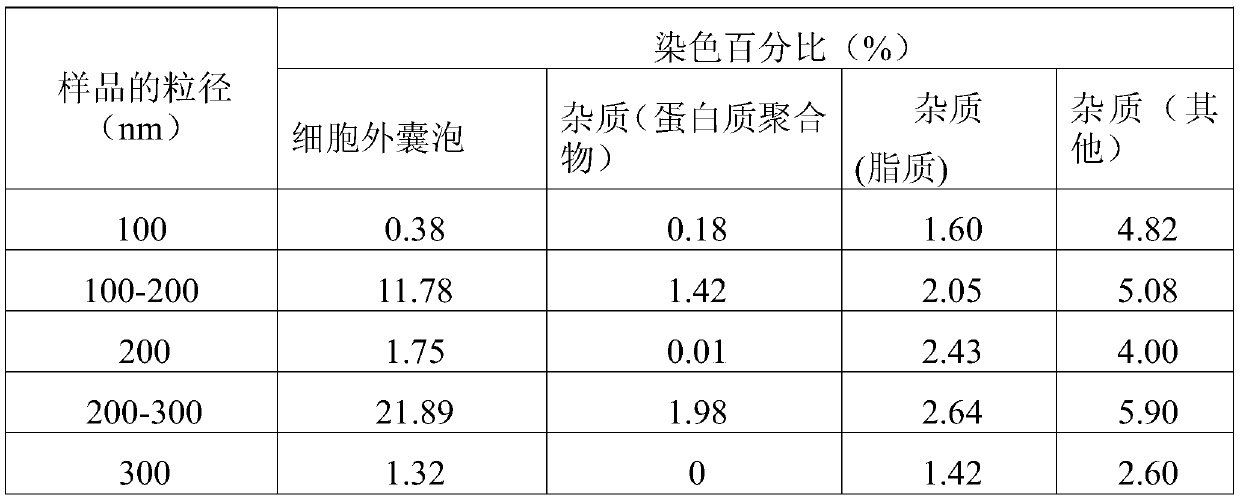
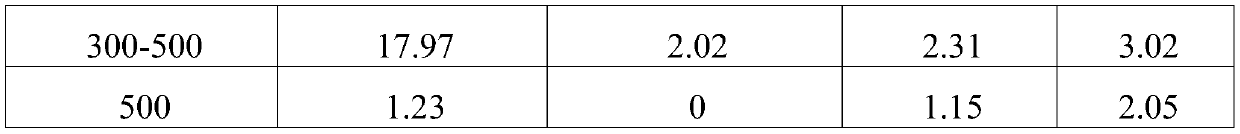
[0053] Serum culture without exosomes 1 × 10 6 HeLa cells at 37 °C and 5% CO 2 Under the conditions, the medium supernatant was collected after 6 hours for the separation and extraction of microvesicles and exosomes.
[0054] 4°C, 100,000g ultracentrifugation for 2 hours, after two ultrahigh-speed centrifugation, and then redissolved in PBS solution to obtain the extracted exosomes.
[0055] Carboxyfluorescein diacetate succinimidyl ester (eBioscience TM CFSE, product number: 65-0850-84, Thermo fisher) solution and exosomes, co-incubated in a 37°C incubator in the dark for 1.5h;
[0056] Then, lipophilic carbocyanine fluorescent dye ('DiI'; DiIC18(3), product number: D282, Thermo fisher) solution and exosomes with a final concentration of 1 nM were co-incubated at 37°C for 10min in the dark or at room temperature ( 24°C) and incubated in the dark for 20min.
[0057] The stained samples were diluted 100-fold for subsequent flow cytometric data collection and analysis.
[0...
Embodiment 2
[0060] Serum culture without exosomes 1 × 10 6 HeLa cells at 37 °C and 5% CO 2 Under the conditions, the medium supernatant was collected after 6 hours for the separation and extraction of microvesicles and exosomes.
[0061] 4°C, 100,000g ultracentrifugation for 2 hours, after two ultrahigh-speed centrifugation, and then redissolved in PBS solution to obtain the extracted exosomes.
[0062] Carboxyfluorescein diacetate succinimidyl ester (eBioscience TM CFSE, product number: 65-0850-84, Thermo fisher) solution and exosomes, co-incubated in a 37°C incubator in the dark for 0.2h;
[0063] Then, lipophilic carbocyanine fluorescent dye ('DiI'; DiIC18(3), product number: D282, Thermo fisher) solution and exosomes with a final concentration of 2nM were co-incubated at 37°C for 1min in the dark or at room temperature ( 24°C) and incubated in the dark for 10 minutes.
[0064] The stained samples were diluted 1000 times for subsequent flow cytometric data collection and analysis. ...
Embodiment 3
[0067] Serum culture without exosomes 1 × 10 6 HeLa cells at 37 °C and 5% CO 2 Under the conditions, the medium supernatant was collected after 6 hours for the separation and extraction of microvesicles and exosomes.
[0068] 4°C, 100,000g ultracentrifugation for 2 hours, after two ultrahigh-speed centrifugation, and then redissolved in PBS solution to obtain the extracted exosomes.
[0069] Carboxyfluorescein diacetate succinimidyl ester (eBioscience TM CFSE, product number: 65-0850-84, Thermo fisher) solution and exosomes, co-incubated in a 37°C incubator in the dark for 3h;
[0070] Then, lipophilic carbocyanine fluorescent dye ('DiI'; DiIC18(3), product number: D282, Thermo fisher) solution and exosomes with a final concentration of 0.5nM were co-incubated at 37°C for 15min in the dark or at room temperature. (24°C) and incubate for 30 min in the dark.
[0071] The stained samples were diluted 10 times for subsequent flow cytometric data collection and analysis.
[00...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com