Preparation method of grain boundary diffusion heavy rare earth neodymium iron boron magnet and neodymium iron boron magnet
A grain boundary diffusion, NdFeB technology, applied in magnetic objects, inductance/transformer/magnet manufacturing, magnetic materials, etc., can solve the problems of small coercivity improvement of NdFeB magnet materials and poor effect of heavy rare earth elements, etc. To achieve the effect of improving the diffusion efficiency of grain boundaries, improving internal stress and crystal structure arrangement, and improving stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
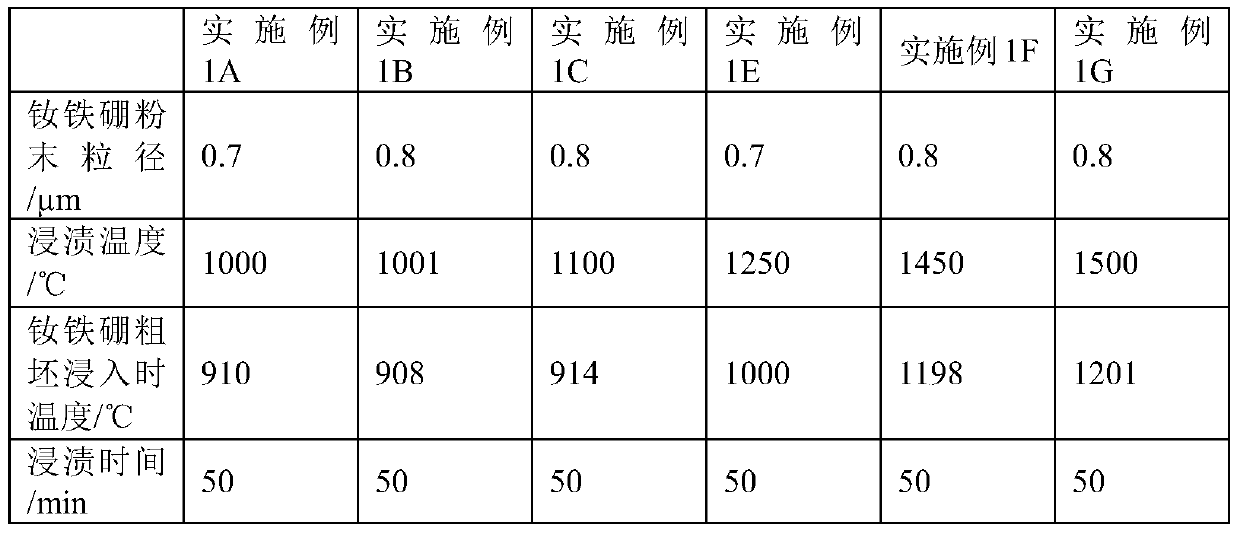
[0049] A method for preparing a grain boundary diffused heavy rare earth NdFeB magnet, comprising the following steps:
[0050] S1: NdFeB powder with a particle size of 2.0-2.5 μm is obtained by distributing ingredients according to the design, casting and smelting, hydrogen crushing, and jet milling;
[0051] S2: The NdFeB powder is subjected to oriented static pressure molding on the mixture in a 1.5T magnetic field to obtain a rough NdFeB blank with gaps or pores;
[0052] S3: Mix the material containing heavy rare earth elements with NdFeB powder and heat it to the immersion temperature and keep it in a molten state. The immersion temperature is 1100±5°C to obtain a heavy rare earth source melt;
[0053] S4: Put the NdFeB rough blank in a cage or basket and move it above the liquid level of the heavy rare earth source melt, and heat the NdFeB rough blank;
[0054] S5: When the NdFeB rough billet is heated to a temperature lower than the dipping temperature of 85-95°C or 1...
Embodiment 2
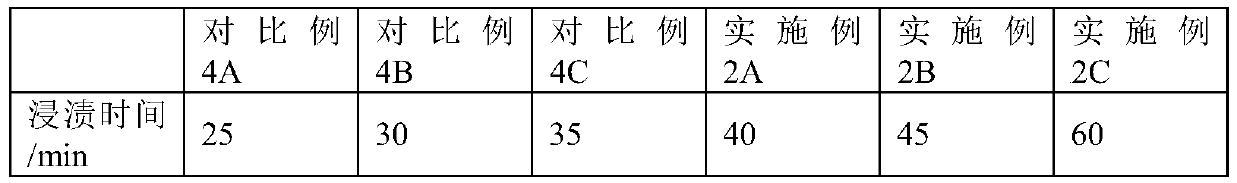
[0093] A method for preparing a grain boundary diffused heavy rare earth NdFeB magnet. On the basis of Example 1F, Example 2A-2C is set. The difference between Example 2A-2C and Example 1F is that the immersion time is different, and the immersion time is different. Less than 40min.
Embodiment 3
[0101] A method for preparing a grain boundary diffused heavy rare earth NdFeB magnet, based on the first embodiment, the difference is that the NdFeB powder in S2 is mixed with a binder and then oriented static pressure molding, the binder The mass ratio of NdFeB powder to NdFeB powder is 0.02-0.03:1, and the binder is a low molecular weight carbon chain polymer. At the same time, the oriented static pressure forming and compaction in S2 obtains the NdFeB rough billet;
[0102] The finished NdFeB magnet is a disc with a diameter of 25mm and a thickness of 10mm. The element composition of finished NdFeB magnets is as follows:
[0103] PrNd: 19-20wt%, Ce: 2.2-2.3wt%, Y: 2.4-2.5wt%, Dy: 0.8-0.9wt%, B: 0.80-0.96wt%, Al: 0.3-0.4wt%, Co: 0.8 -1.1wt%, Zr: 0.10-0.12wt%, Cu: 0.10-0.18wt%, the rest is iron and unavoidable impurities.
[0104] The grain boundary diffused heavy rare earth NdFeB magnets with different thicknesses were prepared according to the above preparation method,...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com