A slow-wave structure suitable for multi-electron injector return-wave tubes in the millimeter-wave terahertz band
A slow-wave structure and terahertz technology, applied in the field of slow-wave structures, can solve problems such as inability to expand arbitrarily, strong competition between modes, complex modes, etc., to solve the problem of mode competition, easy to adjust coupling impedance, and simple geometric structure Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
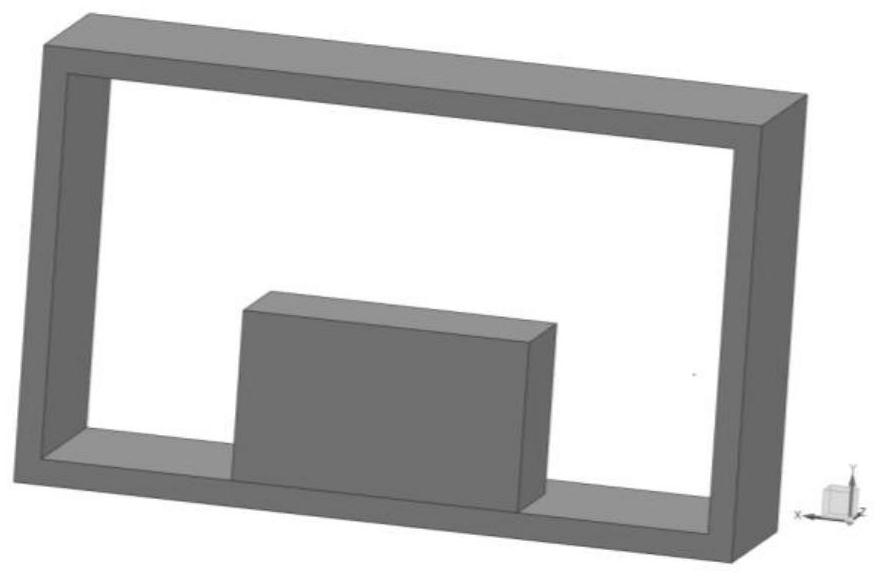
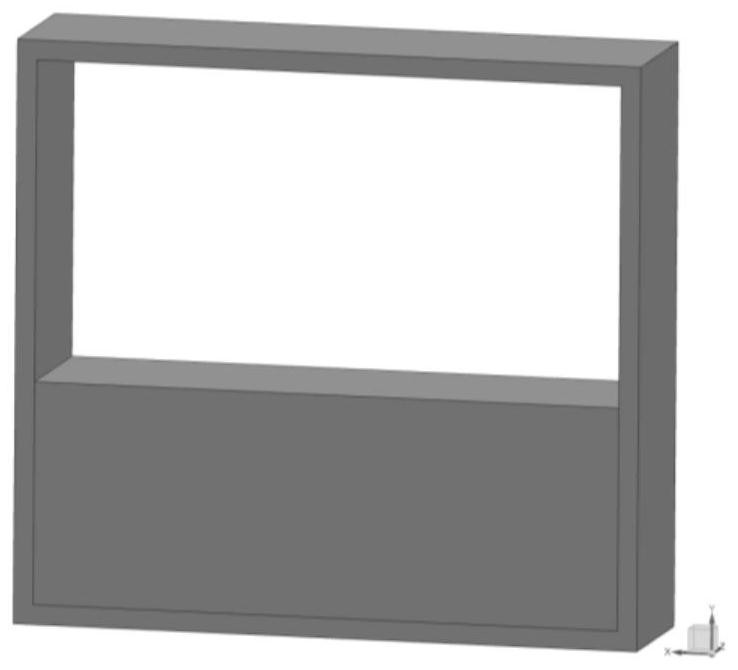
[0041] Figure 7 It is a schematic diagram of a single period of the slow wave structure of Example 1 of the present invention, that is, a schematic diagram of a slow wave structural unit. As shown in the figure, the present invention includes a rectangular waveguide 71, a unit ridge composed of rectangular grid teeth 72 and 73 arranged and extended periodically along the axial direction on the lower bottom surface and the upper top surface of the rectangular waveguide, and band-shaped electronic bands on the left and right sides of the unit ridge. Note channels 74 and 75. The main function of the rectangular waveguide is to support the internal structure and transmit electromagnetic waves; the electron beam channel is the empty part inside the rectangular waveguide 71, which is filled with air, and the above structure constitutes a complete slow wave structure. Specific dimensions such as Figure 9 , Figure 10 as shown ( Figure 9 is the front view of the structure, Fi...
Embodiment 2
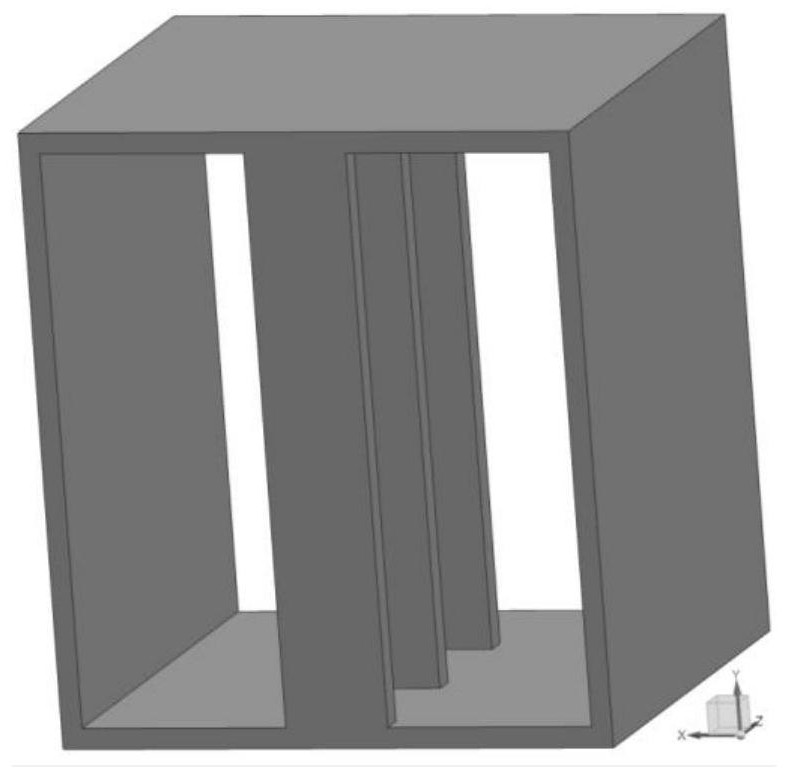
[0045] Figure 11 , Figure 12 It is a schematic diagram of the slow wave structure of the parallel coupled multi-electron injector return wave tube. The structure shown in the figure is the unit ridge structure in Embodiment 1 formed in parallel along the vertical direction or along the horizontal direction. The multi-beam coupling slow wave structure formed by this parallel connection can shorten the saturated tube length and increase the output power. Its bandwidth, dispersion characteristics and coupling impedance are the same as Figure 7 The slow wave structure shown is similar. Figure 15 , Figure 16 It is the dispersion curve and normalized phase velocity curve of the slow-wave structure of the multi-electron injector return wave tube coupled in parallel in the horizontal direction. The figure shows that the Mode1 frequency band of this slow-wave structure is 747-1038GHz, and the Mode2 frequency band is 755-1038GHz. The Mode3 frequency band ranges from 755-1279GH...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com