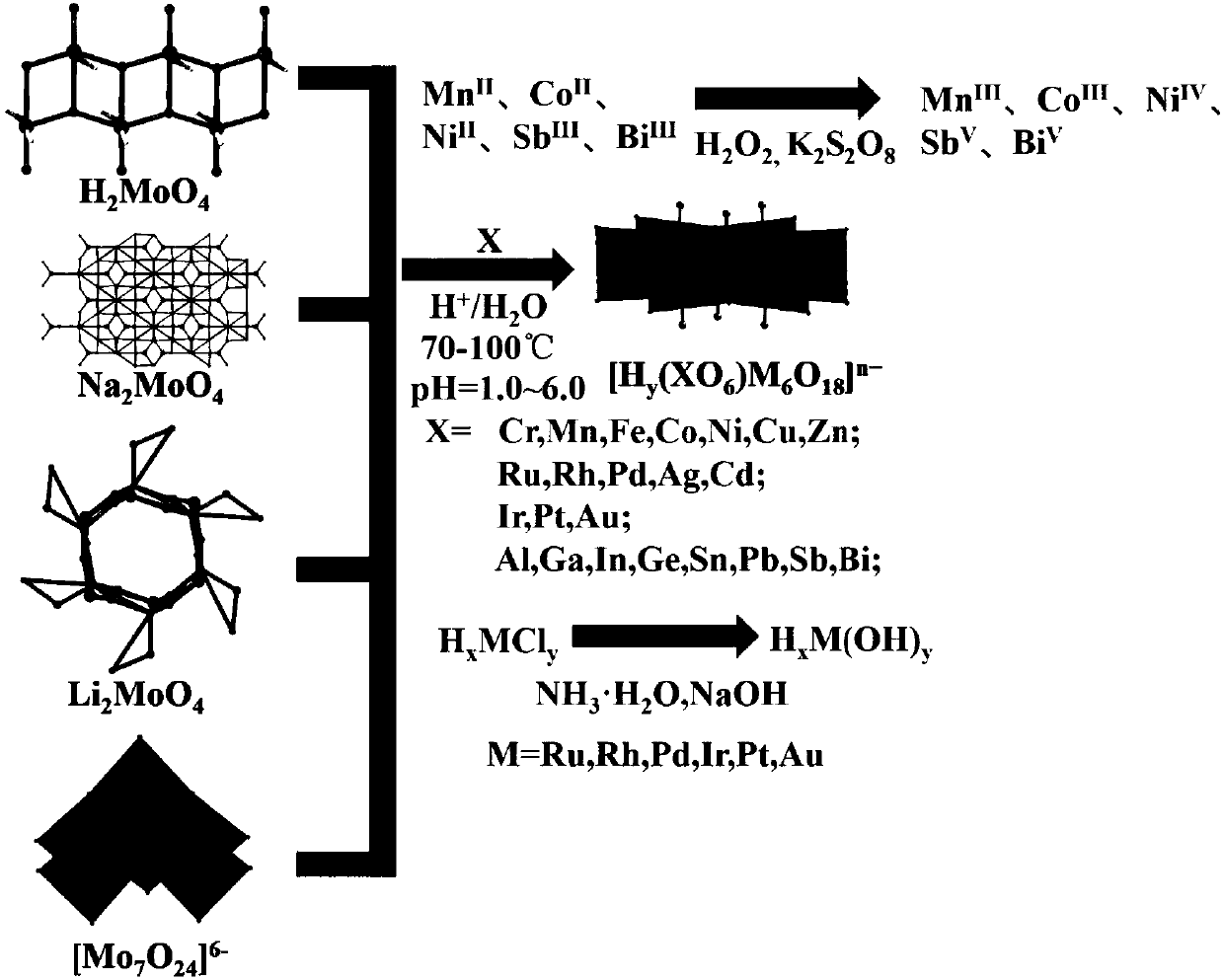
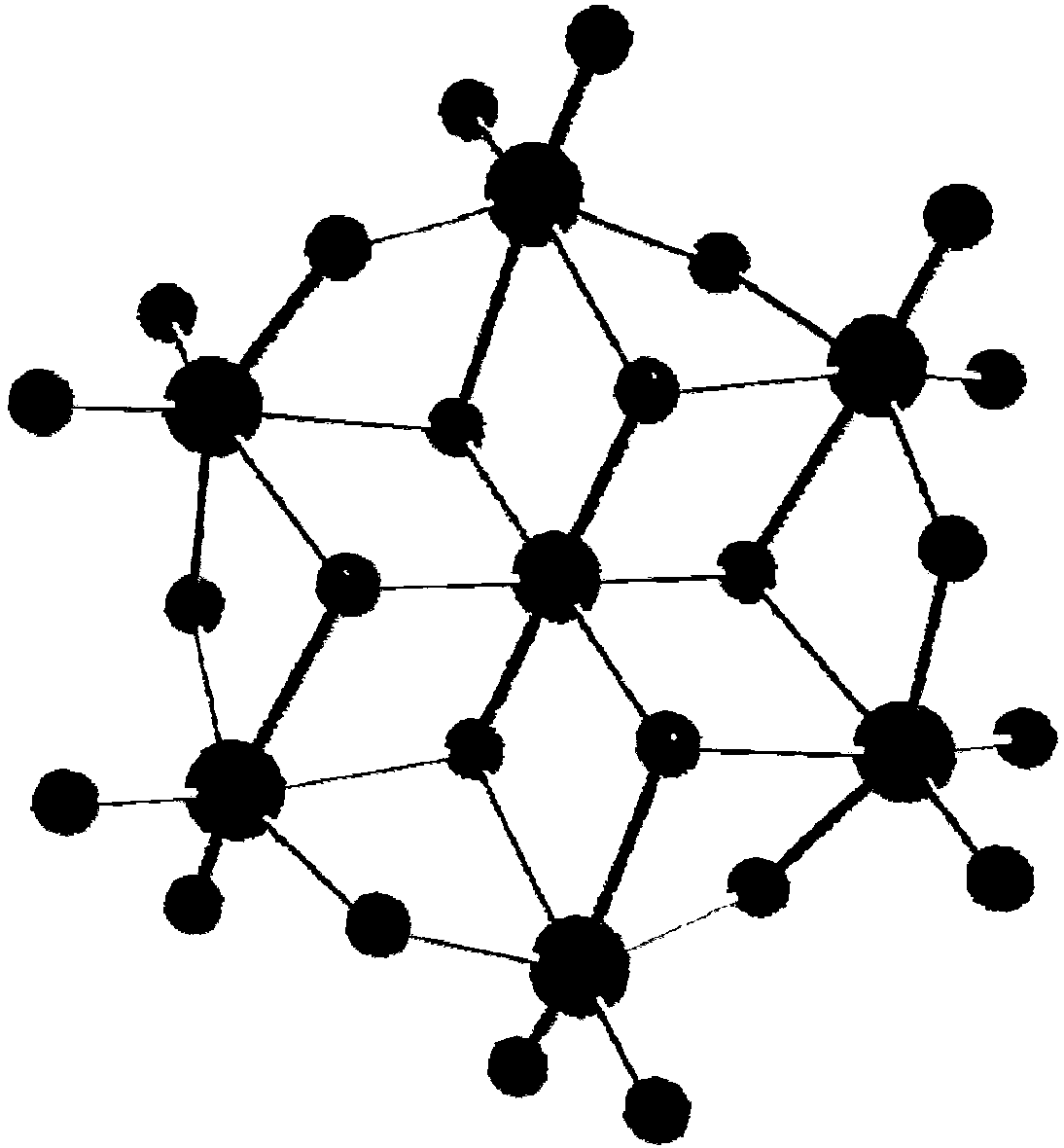
Method for preparing protonated B-type Anderson-type heteropoly acid by aqueous phase method
A technology for protonation and heteropolyacids, which is applied in the field of synthesis and characterization of protonated B-type Anderson-type heteropolyacids by aqueous method, which can solve the problems of restricting the research of Anderson-type heteropolyacids, low stability, etc., and achieves a high yield High, high purity, economical effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 2
[0055] Example 2 (NH 4 ) 3 [Mn(OH) 6 Mo 6 o 18 ]Synthesis
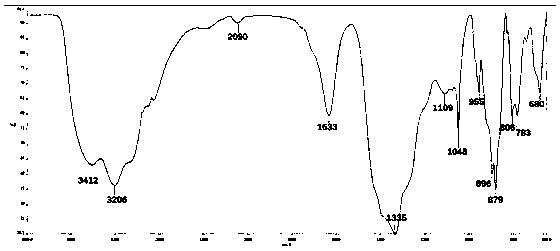
[0056] 741g ammonium molybdate (NH 4 ) 6 Mo 7 o 24 Dissolve in 1L of water, heat to 70-90°C, acidify the solution to pH 5.5 with 1M nitric acid, and add 50ml of oxidant H at the same time 2 o 2 , nitric acid not only plays an acidifying role, but also reacts with H 2 o 2 together to oxide Mn II Form Mn III role. Then 118gMnSO 4 Add it into the solution, stir vigorously and react for 15-20min, the orange-red B-type Anderson-type heteropolyacid powder is precipitated from the solution, and then the product is obtained by suction filtration. By infrared spectrum, 955, 896, 879, 806, 783cm -1 Indicating the formation of Anderson framework structure. If a non-oxidizing acid such as HCl is used, only Mn can be obtained as Mn II The product (NH 4 ) 4 [Mn(OH) 6 Mo 6 o 18 ], but the topology remains unchanged.
Embodiment 3
[0057] Example 3Li 3 [Fe(OH) 6 Mo 6 o 18 ]Synthesis
[0058] 726g lithium molybdate Li 2 MoO 4 Dissolve in 1L of water, heat to 70-90°C, and acidify the solution with 1M acetic acid to pH 5.5. Then 113gFeCl 3 Add it into the solution, stir vigorously and react for 15 minutes, the maroon type B Anderson type heteropolyacid powder is precipitated from the solution, and then the product is obtained by suction filtration. By infrared spectrum, 910, 758, 620cm -1 Indicating the formation of Anderson framework structure.
Embodiment 4
[0059] Embodiment 4 (NH 4 ) 3 [Co(OH) 6 Mo 6 o 18 ]Synthesis
[0060] 741g ammonium molybdate (NH 4 ) 6 Mo 7 o 24 Dissolve in 1L of water, heat to 70-90°C, acidify the solution to pH 5.0 with 1M nitric acid, and add 189g of oxidant K at the same time 2 S 2 o 8 , nitric acid not only plays an acidifying role, but also reacts with K 2 S 2 o 8 together to oxidized Co II Form Co III role. Then 128gCo(NO 3 ) 2 Add it into the solution, stir vigorously and react for 20-25min, dark green B-type Anderson-type heteropolyacid powder precipitates out of the solution, and then suction filter to obtain the product. By infrared spectrum, 977, 952, 884cm -1 Indicating the formation of Anderson framework structure. If a non-oxidizing acid such as HCl is used, only Co can be obtained as Co II The product (NH 4 ) 4 [Co(OH) 6 Mo 6 o 18 ], but the topology remains unchanged. The atomically accurate B-type Anderson-type heteropolyacid structure can be obtained by single ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com