Semiconductor laser
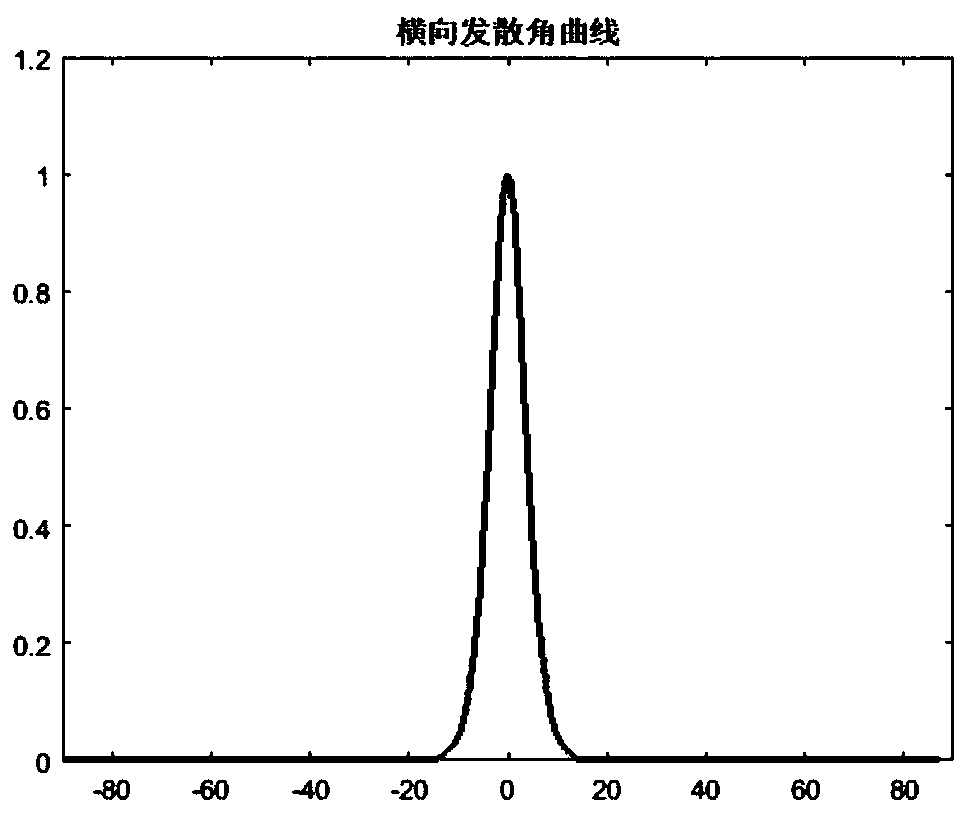
A technology of lasers and semiconductors, applied in semiconductor lasers, structural details of semiconductor lasers, lasers, etc., can solve problems such as poor far-field quality, unsatisfactory small divergence angles, etc., achieve small far-field divergence angles, and reduce catastrophic optical damage risk, the effect of low packaging cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0051] Embodiment 1, the first semiconductor laser with a small divergence angle based on the present invention.
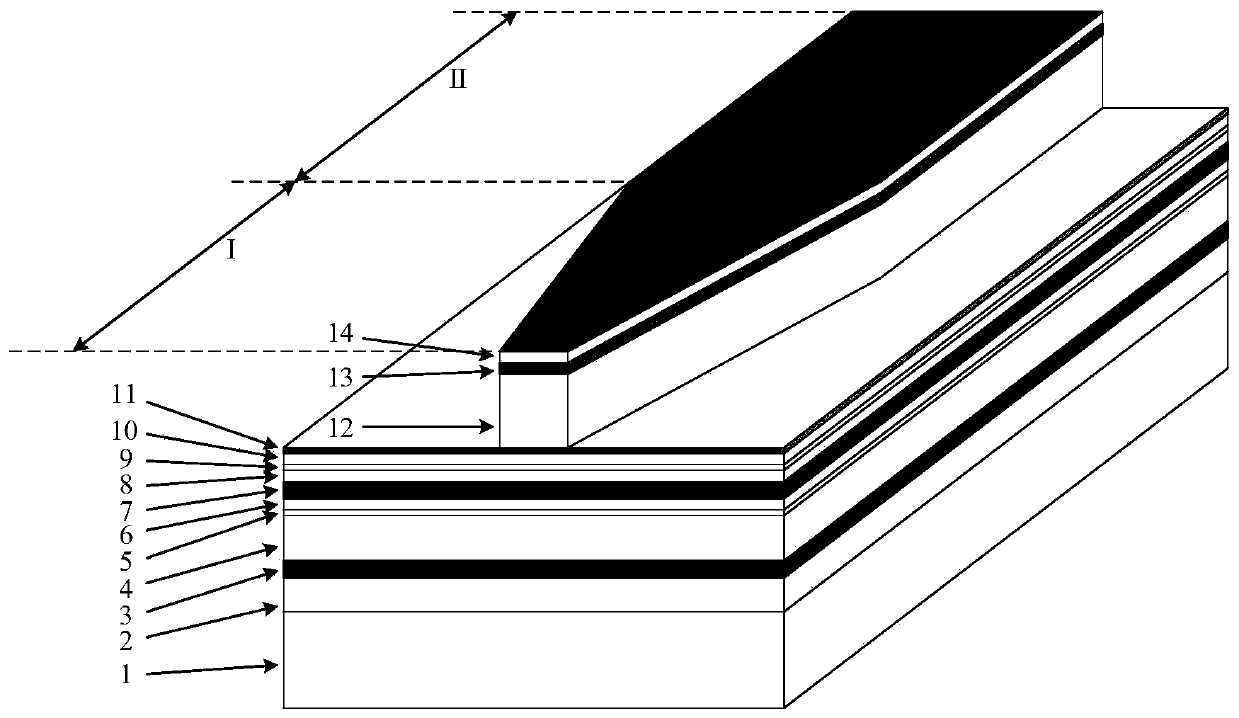
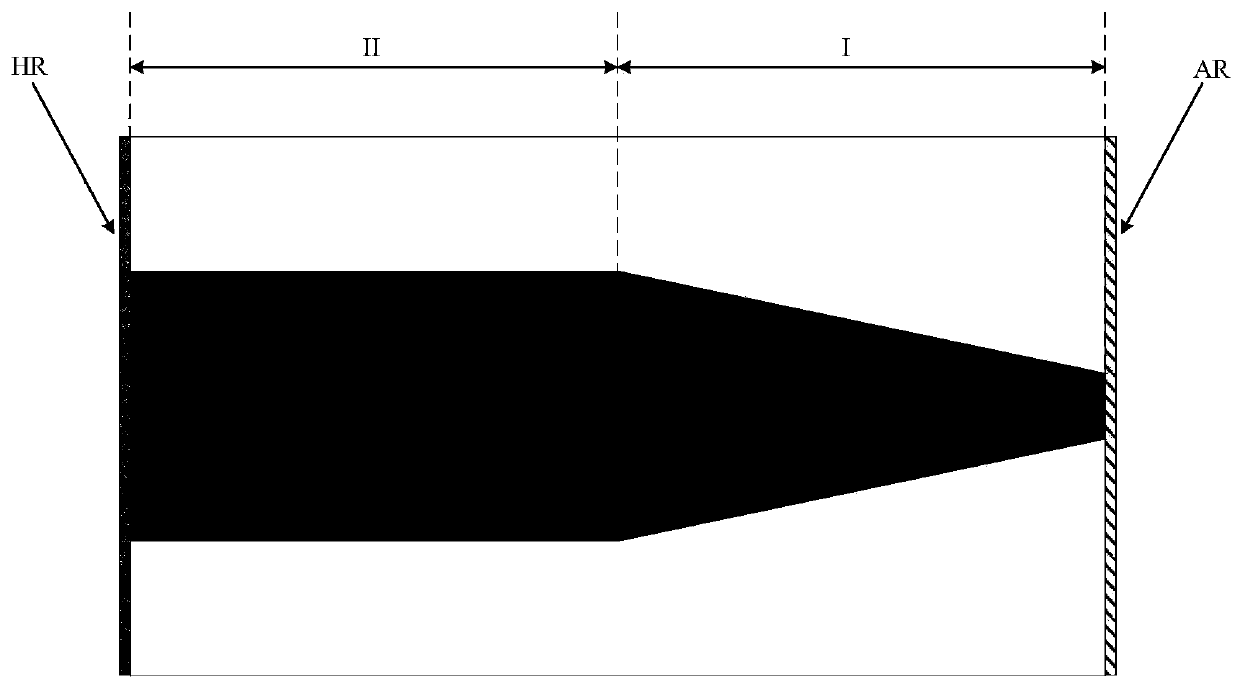
[0052] The working wavelength of the semiconductor laser in this example is 1310nm, and its three-dimensional structure diagram is attached figure 1 , From the substrate layer to the top cover layer are: substrate layer 1, buffer layer 2, lower waveguide core layer 3, lower spacer layer 4, lower barrier layer 5, lower confinement layer 6, active layer 7, upper confinement layer 8. The upper barrier layer 9, the upper spacer layer 10, the corrosion stop layer 11, the upper cladding layer 12, the secondary covering layer 13, and the top covering layer 14. The materials, doping types and thicknesses of each layer are shown in Table 1:
[0053] Table 1 The material, doping type and thickness of each layer in Example 1
[0054]
[0055] Wherein, layer 12, layer 13 and layer 14 constitute the ridge of the device by etching, and the bottom of layer 1 and the top of layer 14 are...
Embodiment 2
[0058] Embodiment 2, a second semiconductor laser with a small divergence angle based on the present invention.
[0059] The working wavelength of the semiconductor laser in this example is also 1310nm, and the three-dimensional structure diagram is attached figure 1 , From the substrate layer to the top cover layer are: substrate layer 1, buffer layer 2, lower waveguide core layer 3, lower spacer layer 4, lower barrier layer 5, lower confinement layer 6, active layer 7, upper confinement layer 8. The upper barrier layer 9, the upper spacer layer 10, the corrosion stop layer 11, the upper cladding layer 12, the secondary covering layer 13, and the top covering layer 14. The materials, doping types and thicknesses of each layer are shown in Table 2:
[0060] Table 2 Example 2 Material, doping type and thickness of each layer
[0061] Dielectric layer
material
Doping type
Thickness (nm)
Remarks
Underlayer 1
InP
Type N
---
Buffer layer 2
InP
Type N
300
Lower waveguide co...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com