Method for identifying MHC I binding peptide motif
An identification method and a technology for binding peptides, applied in the field of biomedicine, can solve the problems of long time and low accuracy of peptide binding motif determination, and achieve the effects of efficient screening, short time-consuming and reliable results.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0045]Example 1 Porcine SLA I polypeptide motif identification and synthesis of binding polypeptide
[0046] 1.1 Synthesis of random 9-peptide
[0047] Using the Fmoc method to synthesize a 9-peptide library with random sequences, the specific steps are as follows:
[0048] (1) Polypeptide-solid phase carrier cross-linking: 19 kinds of α-amino protecting group amino acids (except cysteine) were prepared by Fmoc (9-fluorenylmethoxycarbonyl), in DMSO at 20-25°C Reaction with alkoxybenzyl alcohol resin;
[0049] (2) Combined deprotection: 19 kinds of cross-linked polypeptide-solid phase carriers were thoroughly mixed, and the amino groups were deprotected by TFA (trifluoroacetic acid);
[0050] (3) Neutralization and washing: neutralize the free amino terminal with triethylamine and fully wash;
[0051] (4) Grouping and condensation: Divide the washed mixture into 19 equal parts, activate the carboxyl group of a new round of amino acids through DCC, and add 19 kinds of amino a...
Embodiment 2
[0105] Example 2 Duck Anpl - MHC I peptide motif identification
[0106] According to the method of Example 1, random sampling was performed on ducks from a duck breeding farm, and lymphocytes were separated by lymphocyte separation medium (Tianjin Haoyang Biological Products Technology Co., Ltd.), and the separation method was carried out with reference to the instructions. The obtained cDNA was reverse-transcribed, and the primer sequences are shown in Table 2:
[0107] Table 2 Anpl -MHC I α chain and β chain primers
[0108] .
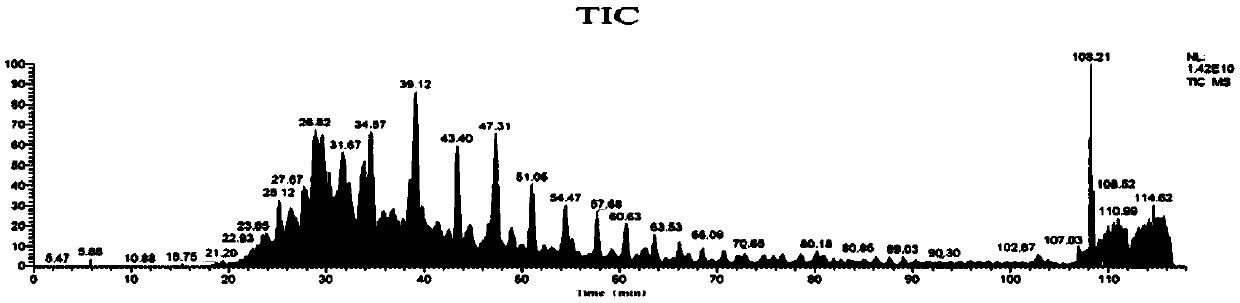
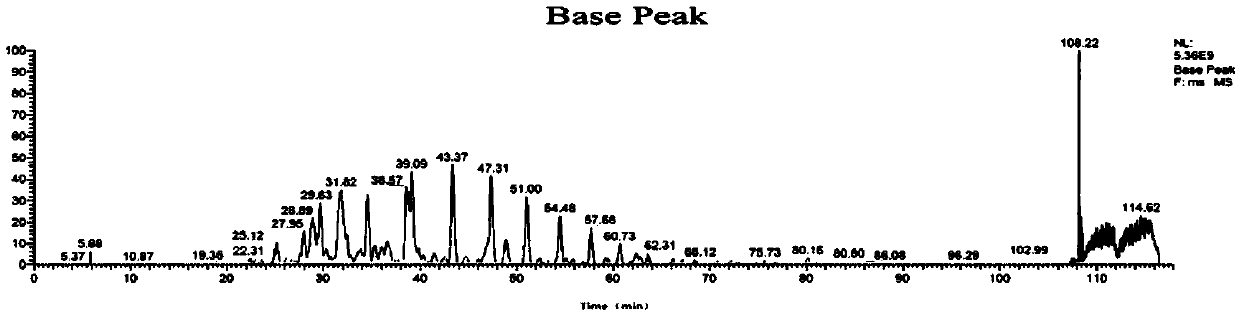
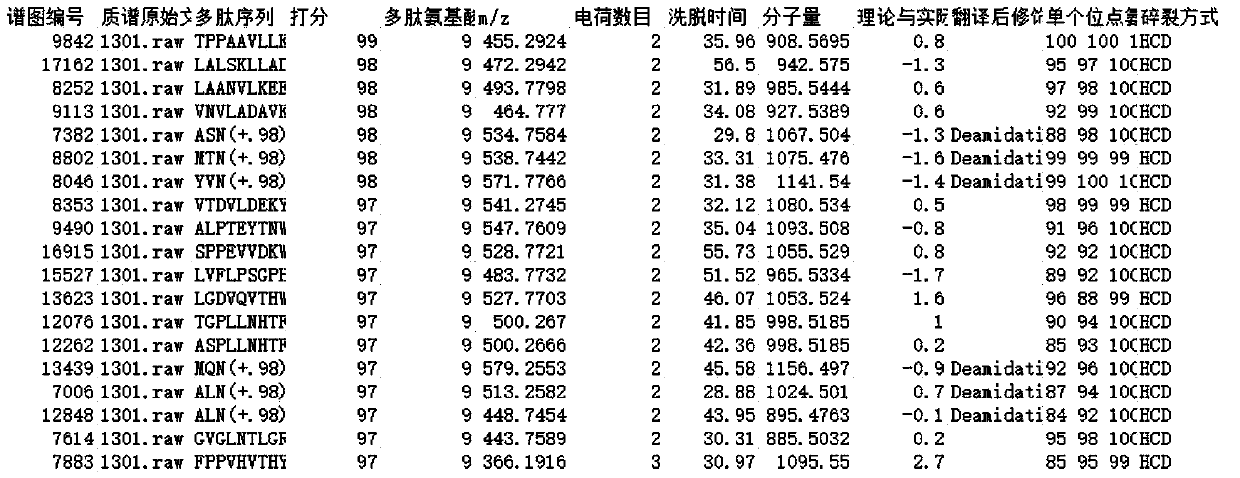
[0109] According to the method of Example 1, using cDNA as a template to obtain two Anpl -MHC I, and eventually two Anpl - MHC I binding peptides, and perform LC-MS / MS mass spectrometry sequencing and analysis and data analysis. The result is as Figure 7-13 As shown, the analysis obtained two Anpl - MHC I preference for binding to different sites of the polypeptide. Depend on Figure 13 and Figure 14 It can be seen that Anpl -...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com