Selenium-containing maleimide polymer as well as preparation method and application thereof
A maleimide and polymer technology, applied in the field of polymer materials, can solve the problems of poor thermal stability and uncontrollable molecular weight, and achieve the effects of increasing the refractive index, increasing the refractive index, and extending the application.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0055] Embodiment 1: 4-phenyl selenide phenylmaleimide (SePMI) monomer and styrene monomer copolymerization
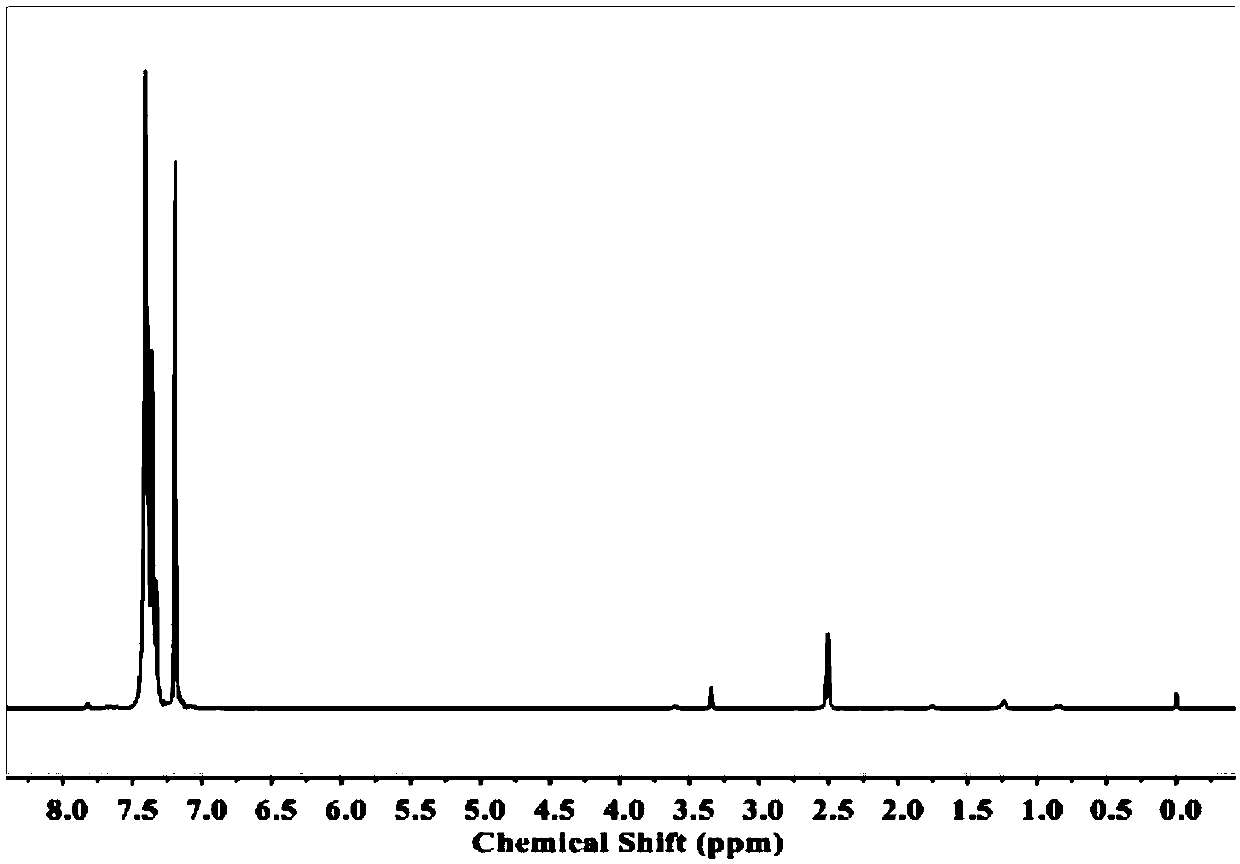
[0056] Polymerization process is: SePMI (nuclear magnetic spectrum see image 3 ), styrene, azobisisobutyronitrile (AIBN), 2-cyano-2-propyl-1-dithionaphthoate (CPDN) with a molar ratio of 200:200:1:2 as raw materials Ratio; Quantitative SePMI is 2mol in the present embodiment, just can obtain the consumption of other raw materials, and adds 4ml toluene as solvent. After adding all the raw materials, add a stirring bar, freeze and deoxygenate, seal and react at 60°C for 8 hours to obtain a viscous polymer solution. Add a small amount of tetrahydrofuran, dilute, slowly drop into methanol to precipitate the polymer, and then filter, wash, and vacuum dry to obtain the final polymer, which is named P3-50%. attached Figure 5 Molecular weight information for the resulting polymers is provided in ; Figure 6 Structural information of the resulting polymers is provided in ...
Embodiment 2
[0057] Example 2: Copolymerization of 4-phenylselenide phenylmaleimide (SePMI) monomer and 4-phenylselenide styrene (PhSeSt) monomer
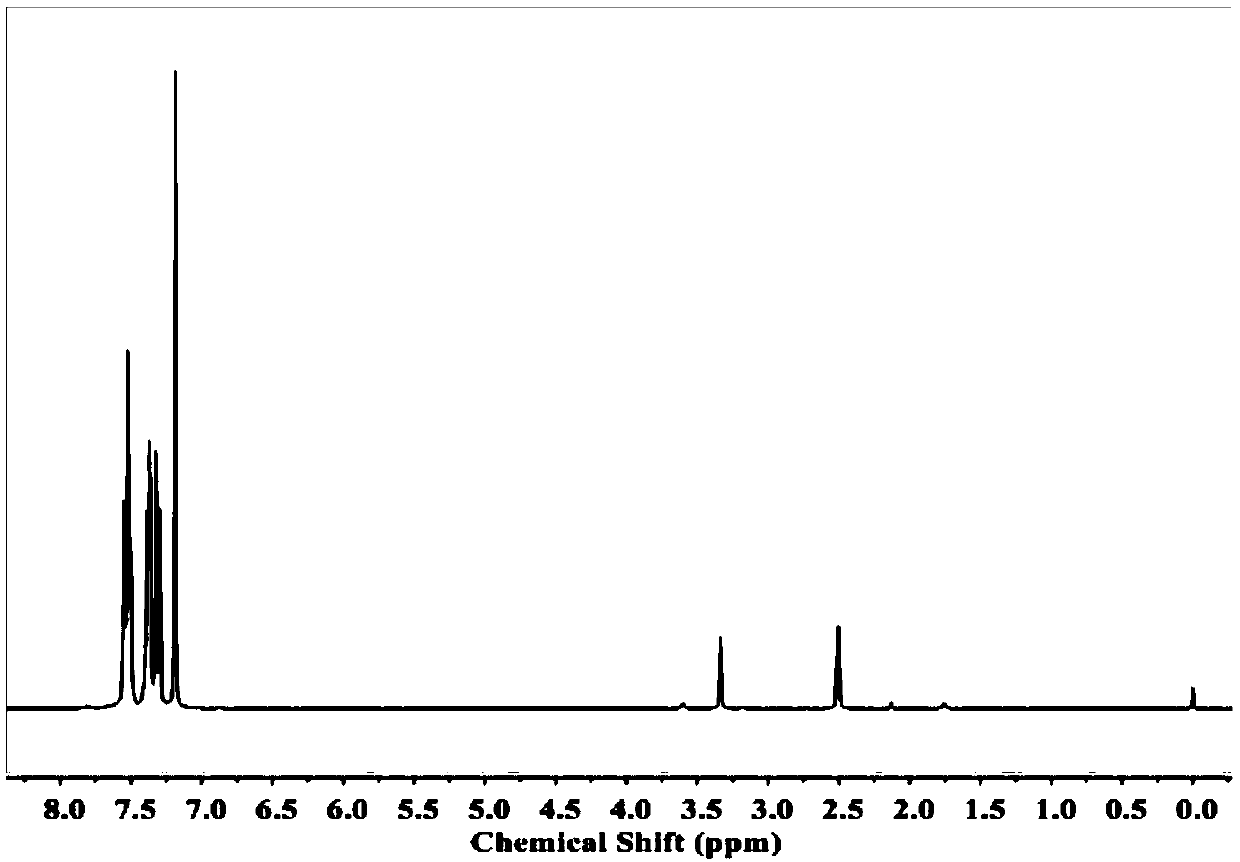
[0058] The steps of this embodiment are basically the same as in Example 1, the difference being that the styrene monomer is replaced by a 4-phenylselenide styrene (PhSeSt) monomer (see Figure 4 ), the polymer obtained was named as P4-50%. also attached Figure 5 Molecular weight information for the resulting polymers is provided in ; Figure 6 Structural information of the resulting polymers is provided in .
[0059] The following are comparative examples, the preparation of selenium-free maleimide polymers:
Embodiment 3
[0060] Embodiment 3: Copolymerization of 4-phenylsulfide phenylmaleimide (SPMI) monomer and styrene monomer
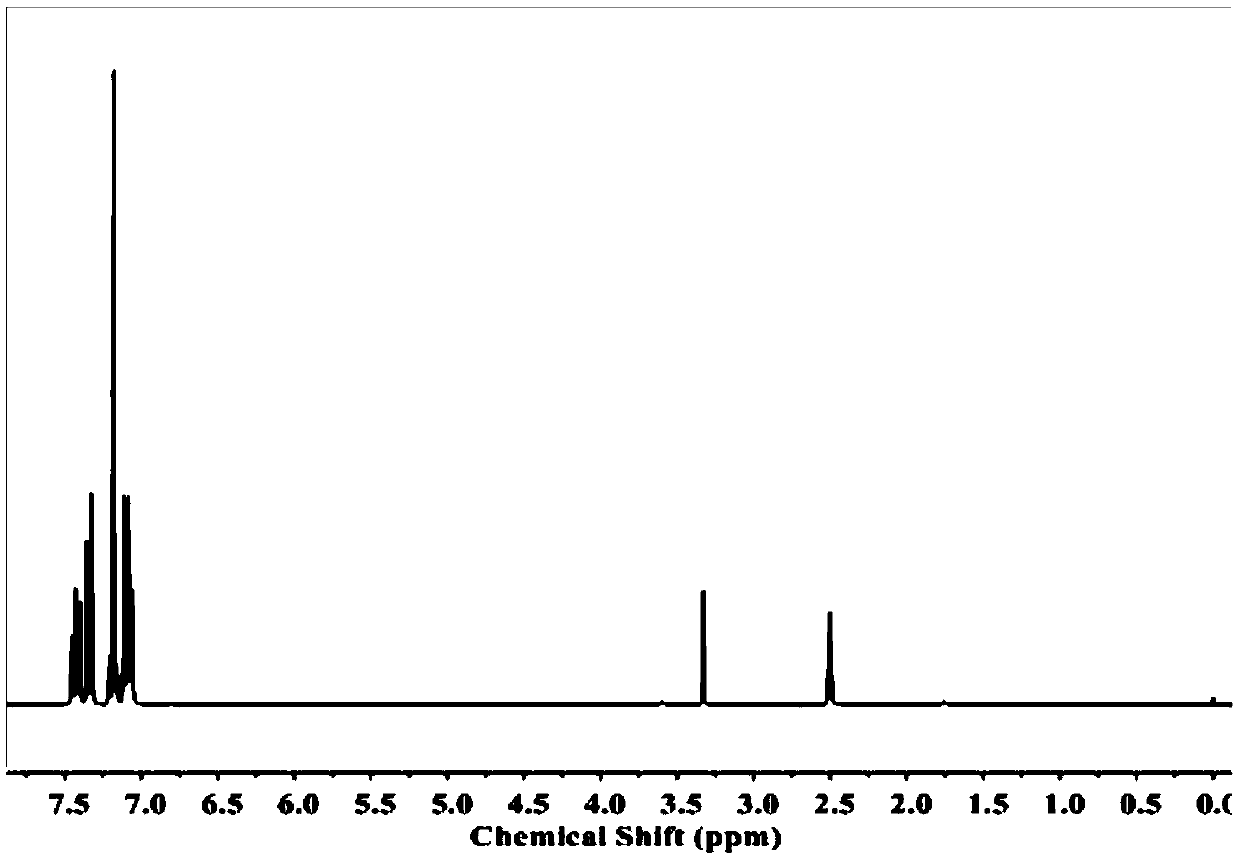
[0061] The steps of this embodiment are basically the same as in Example 1, the difference being: 4-phenyl selenide phenyl maleimide (SePMI) monomer is replaced by 4-phenyl sulfide phenyl maleimide (SPMI ) monomer (see NMR figure 2 ), the polymer obtained was named as P2-50%. also attached Figure 5 Molecular weight information for the resulting polymers is provided in ; Figure 6 Structural information of the resulting polymers is provided in .
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com