Biological agent for promoting osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells
A technology of bone marrow mesenchyme and biological preparations, applied in the field of biomedicine, can solve problems such as unclear biological functions of lncRNA
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0128] Example 1: Identification of LncAIS as a significantly differentially expressed lncRNA down-regulated in bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (BM-MSC) of AIS patients
[0129] In order to identify the key lncRNA involved in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis (AIS), we performed microarray analysis on BM-MSCs from 5 healthy donors and 12 AIS patients. In the BM-MSC of normal BM-MSC and AIS patients, 1483 lncRNA showed differential expression, of which 718 were up-regulated and 765 were down-regulated. figure 1 shown in a. Among the most down-regulated lncRNAs in the BM-MSCs of AIS patients, we focused on the uncharacterized lncRNA that we called lncAIS (gene symbol: ENST00000453347). LncAIS is located on human chromosome 1, contains 4 exons and is a transcript of 476 nt in full length. lncAIS was identified as a conserved locus, such as figure 1 Shown in b.
[0130] Perform real-time qPCR according to routine operations to analyze LncAIS transcripts in BM-MSCs of normal healthy ...
Embodiment 2
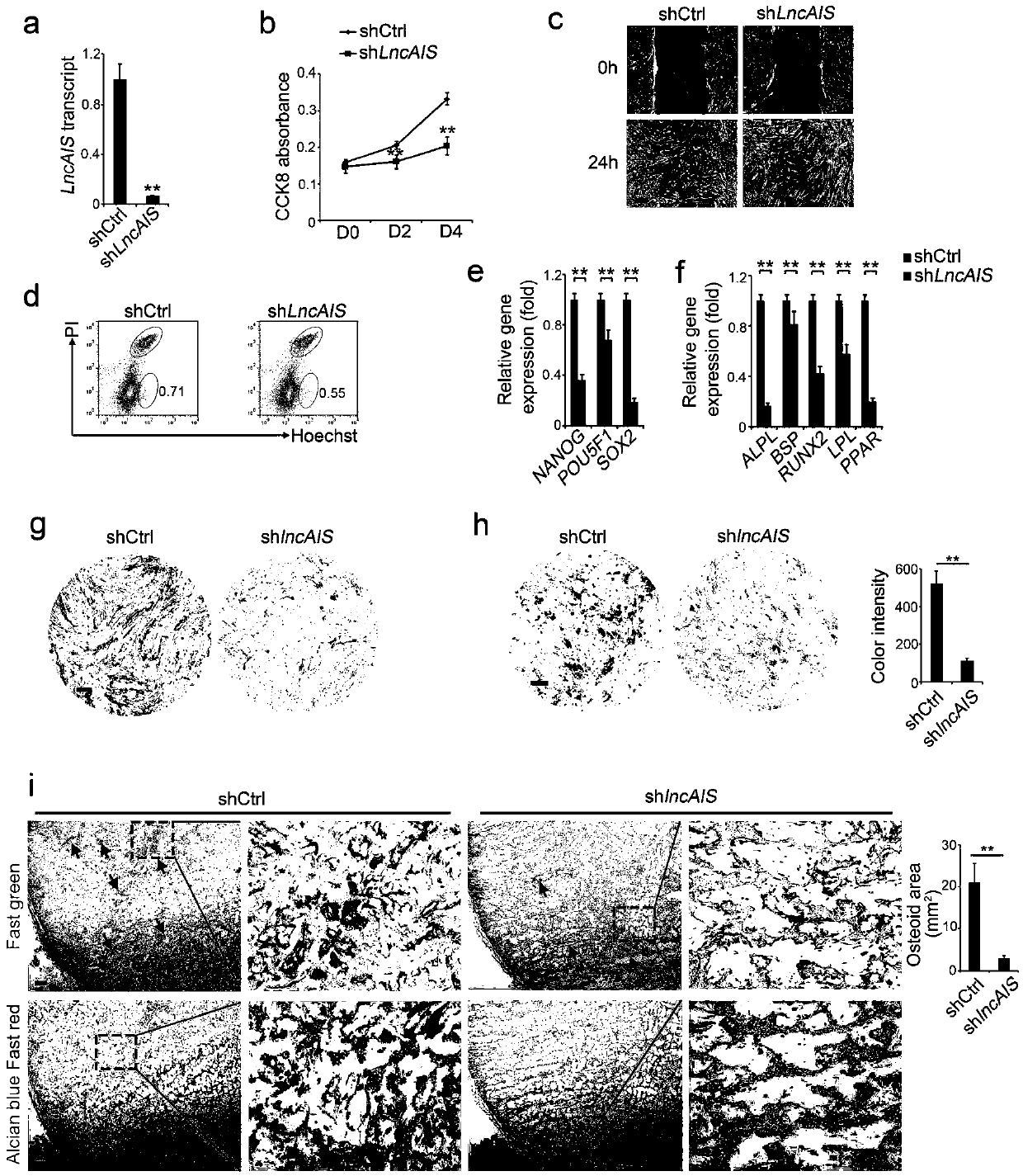
[0136] Example 2: LncAIS knockdown inhibits osteogenic differentiation and bone formation
[0137] In order to explore the physiological role of lncAIS in the pathogenesis of AIS, we used lentivirus-mediated short hairpin RNA (shRNA) to knock down lncAIS in healthy normal BM-MSC (the shLncAIS gene sequence used for lncAIS knockdown is shown in Table 2 above Shown in SEQ ID NO: 4-6), and confirm knockdown efficiency by real-time quantitative PCR, as figure 2 shown in a. BM-MSC was infected with lentivirus expressing shlnAIS and cultured in MSC medium for 3 days, and then the mRNA level of lncAIS was detected by real-time qPCR. The primer pairs used for cDNA amplification in qRT-PCR are listed in Table 5 above. The relative gene expression fold change was normalized to endogenous β-actin and counted as the mean±S.D. **, P <0.01. The data are from three independent experiments using BM-MSCs derived from 3 healthy donors.
[0138] The cell proliferation of shlnAIS BM-MSC and shCtr...
Embodiment 3
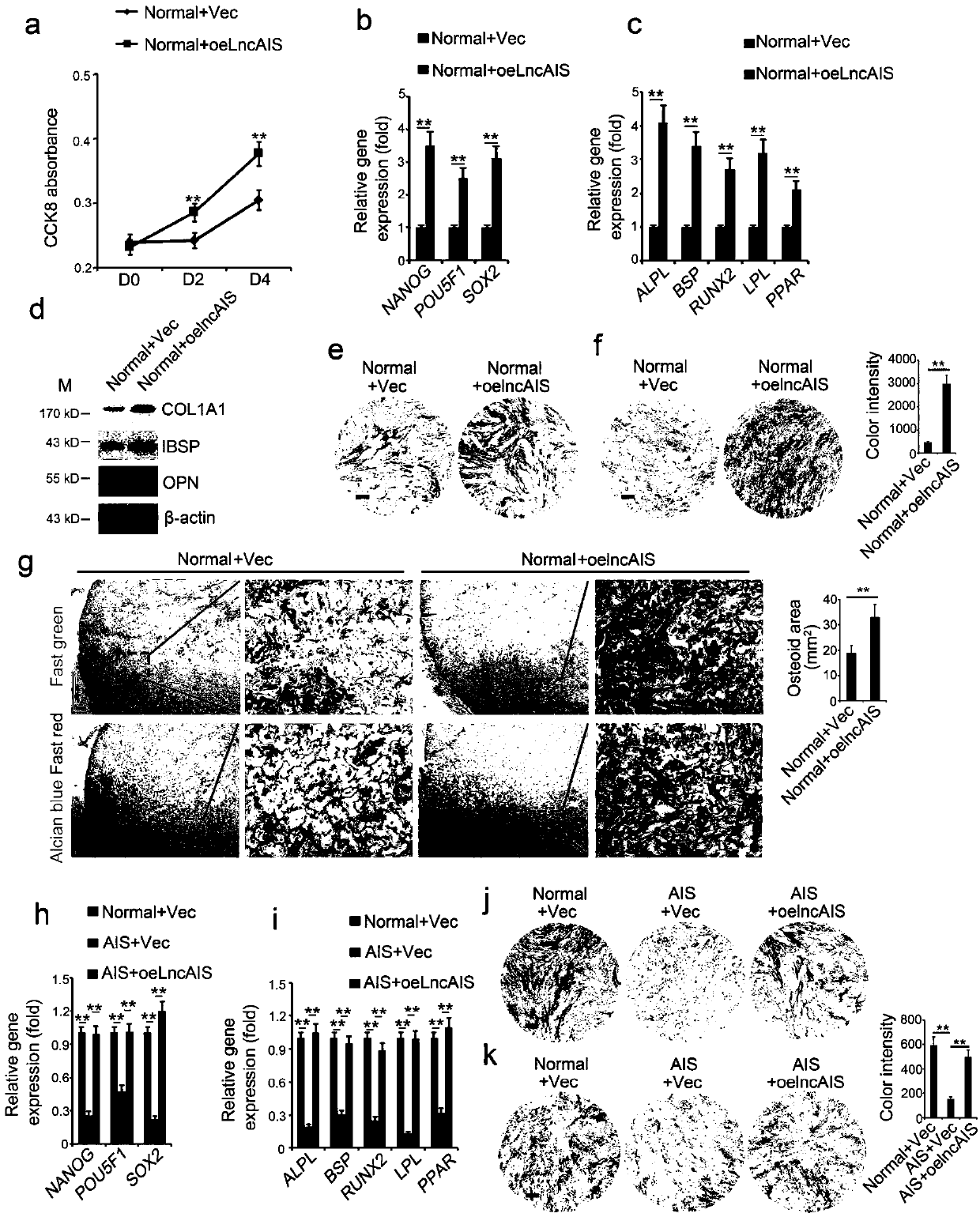
[0146] Example 3: Overexpression of LncAIS promotes osteogenic differentiation and bone formation
[0147] We overexpress lncAIS in normal BM-MSC by lentivirus, first construct the target sequence into pSicoR plasmid, and simultaneously use pMD2.G and psPAX2 vectors to package the virus, and then infect the target BM-MSC. Overexpression of LncAIS (oeLncAIS) significantly increases the cell proliferation of normal BM-MSC ( image 3 a). Consistently, lncAIS overexpression enhanced the expression levels of self-renewal related genes (NANOG, POU5F1, and SOX2) and osteogenic differentiation genes (ALPL, BSP, RUNX2, LPL, and PPAR) ( image 3 b, 3c). In addition, compared with vector-transfected BM-MSCs during adult differentiation, lncAIS overexpression also increased osteogenic marker genes such as osteopontin (OPN), COL1A1 and IBSP ( image 3 d) Protein levels. Therefore, staining by ALP ( image 3 e) and Von Kossa stain ( image 3 f) Overexpression of lncAIS enhances the osteogenic...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com