Three-dimensional porous stent and preparation method and application thereof
A three-dimensional porous and porous technology, applied in medical science, prosthesis, additive processing, etc., to achieve precise controllability, good biocompatibility and biodegradability, and suitable pore size
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0075] A method for preparing a three-dimensional porous scaffold, comprising:
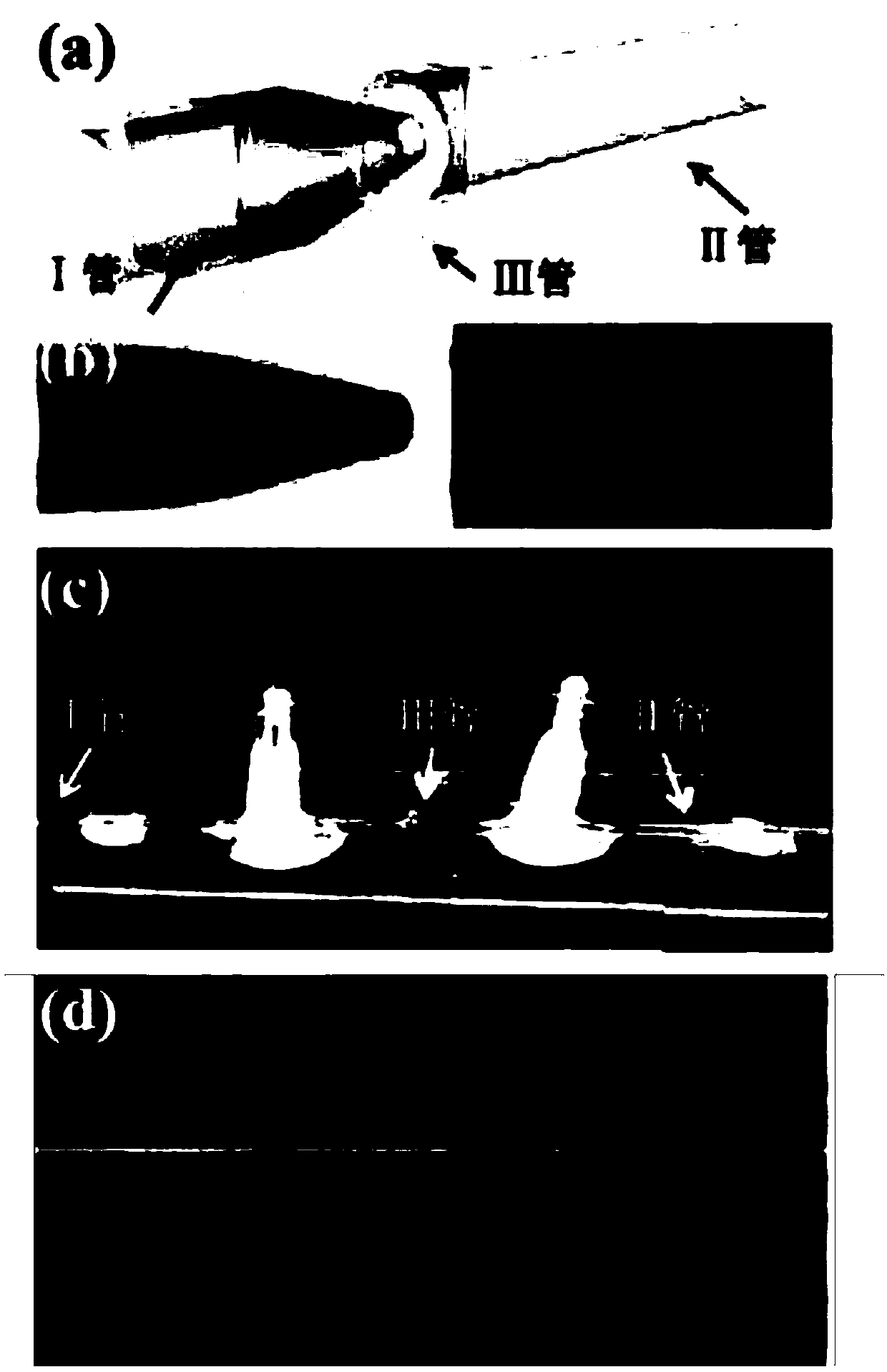
[0076] 1) Preparation steps of monodisperse emulsion droplets: using a microfluidic device, an external phase and an internal phase to prepare monodisperse emulsion droplets with a controllable particle size, and cleaning and collecting the monodisperse emulsion droplets;
[0077] Wherein, wherein, the external phase includes a composite composed of degradable natural biological materials and degradable synthetic polymer materials; the weight ratio of the degradable natural biological materials to the degradable synthetic polymer materials is 1:7.5 . The degradable natural biological material is sodium alginate. The artificially synthesized polymer material is polyethylene glycol diacrylate.
[0078] The internal phase is methyl silicone oil.
[0079] 2) The preparation steps of the emulsion droplet template: the collected monodisperse emulsion droplets are left to stand, the monodisperse emuls...
Embodiment 2
[0083] 1) Preparation steps of monodisperse emulsion droplets: using a microfluidic device, an external phase and an internal phase to prepare monodisperse emulsion droplets with a controllable particle size, and cleaning and collecting the monodisperse emulsion droplets;
[0084] Wherein, the outer phase 1 includes a composite composed of degradable natural biomaterials and degradable synthetic polymer materials; the weight ratio of the degradable natural biomaterials to the degradable synthetic biomaterials is 1:7.5. The degradable natural biological material is sodium alginate. The synthetic biomaterial is gelatin methacrylate (Gelma).
[0085] The internal phase is methyl silicone oil.
[0086] 2) The preparation steps of the emulsion droplet template: the collected monodisperse emulsion droplets are left to stand, the monodisperse emulsion droplets will self-assemble into a tightly packed structure, and finally form a uniform and neat emulsion droplet template; then the ...
Embodiment 3
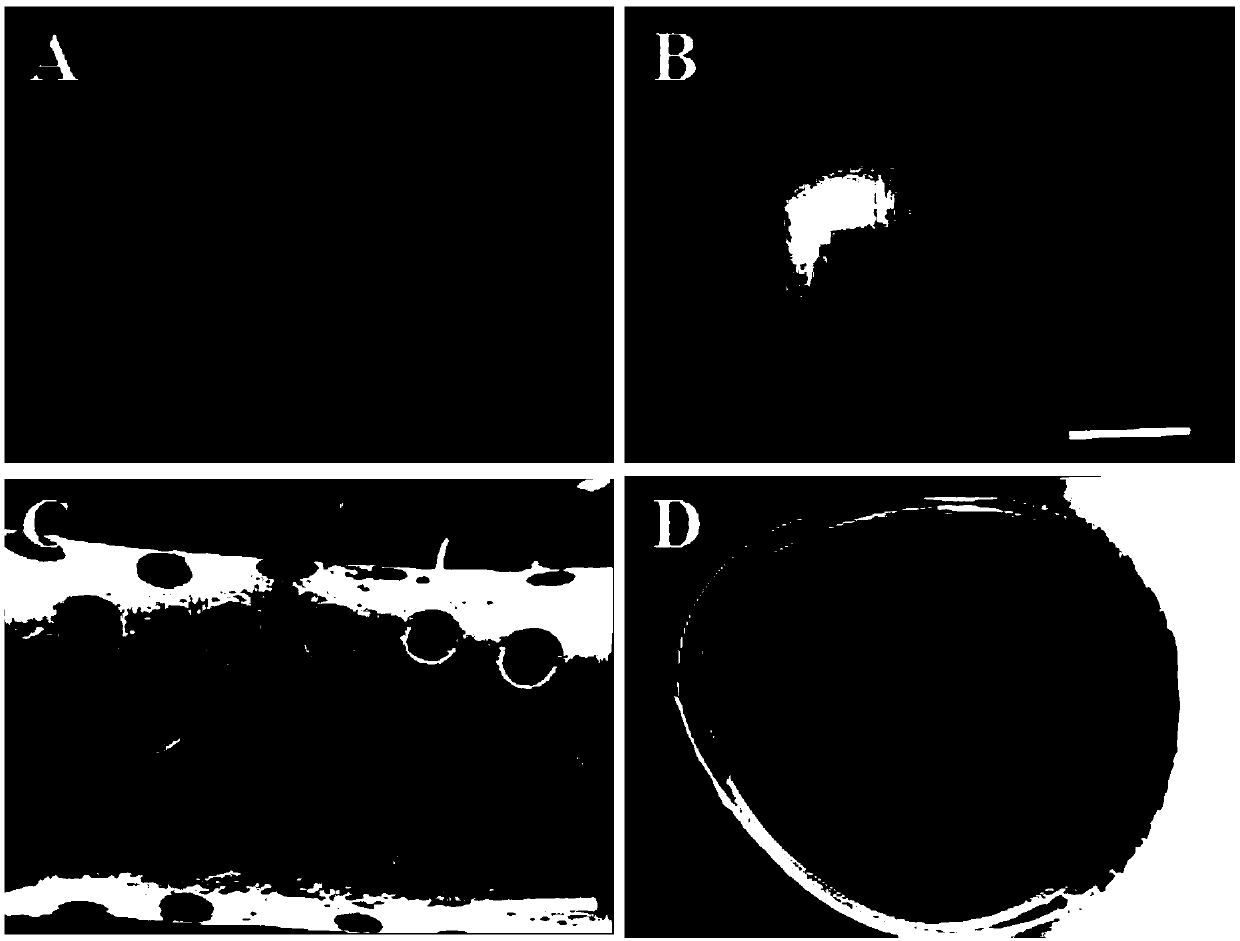
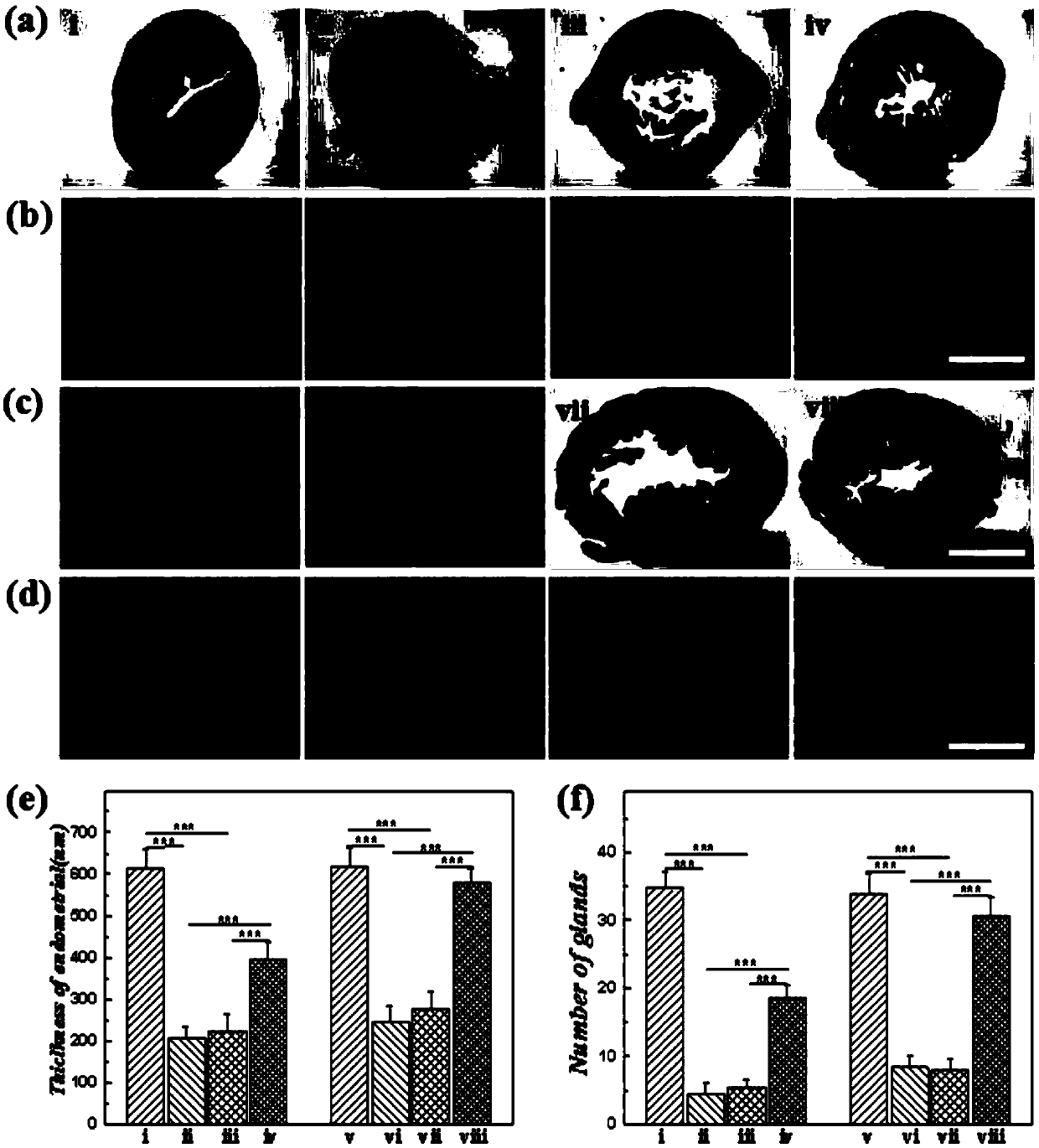
[0091] A method for preparing a drug-loaded three-dimensional porous scaffold: soak the three-dimensional porous scaffold described in Example 3 in a 75% alcohol solution overnight, then wash it repeatedly with sterile PBS (PH=7.4), and soak it in PBS for ultraviolet light Irradiate for 3h. Soak the porous scaffold in 100ug / mL bFGF solution to fully disperse the drug into the pores, take it out after 24 hours for later use, and obtain the drug-loaded three-dimensional porous scaffold.
[0092] Application of drug-loaded three-dimensional porous scaffold in intrauterine adhesion rat model:
[0093] (1) Establishment of intrauterine adhesion model rats: the rats were anesthetized with 350 mg / kg 10% chloral hydrate, the lower abdomen was shaved and fixed in the supine position on the operating board, disinfected with iodine, and a long slit was made in the middle of the lower abdomen. A longitudinal incision of about 2-3 cm was made to enter the abdominal cavity to expose the ut...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com