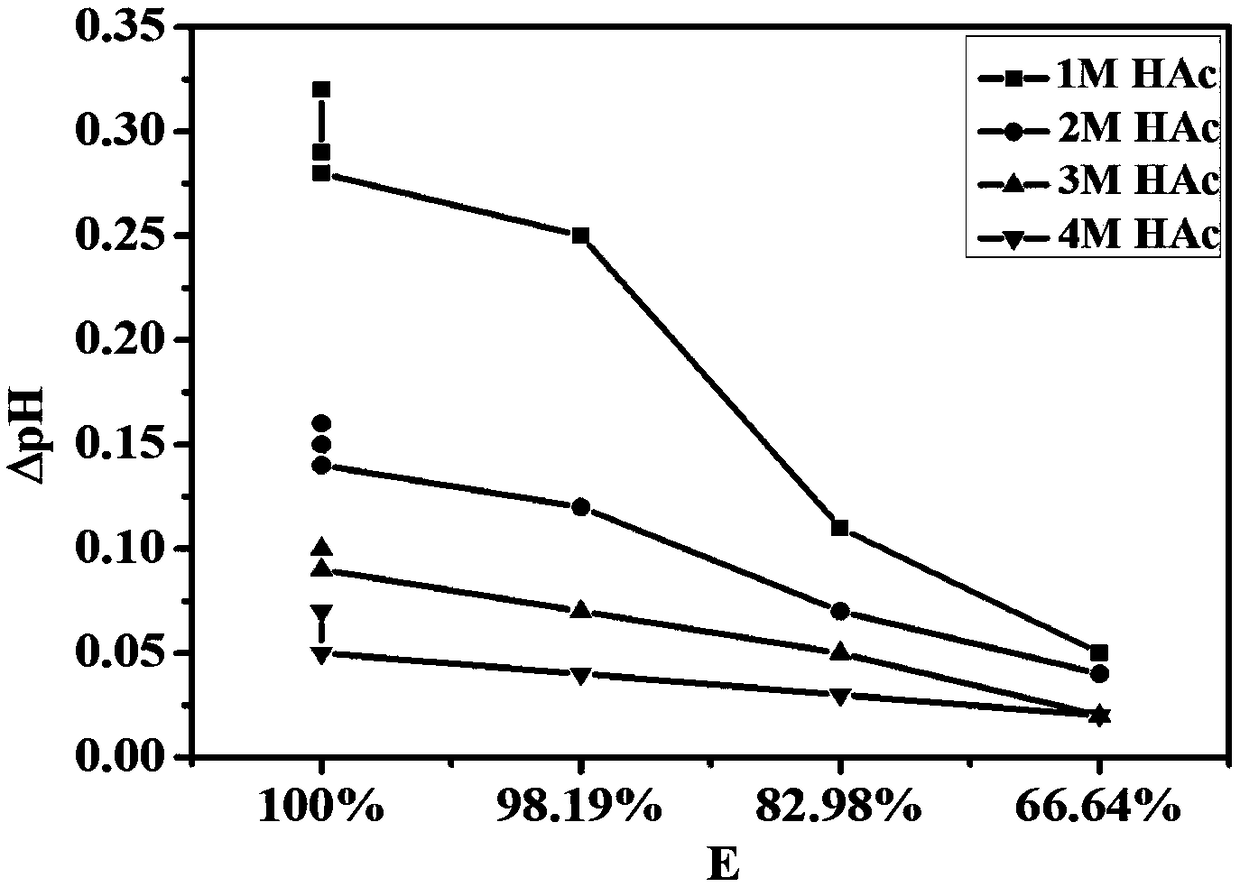
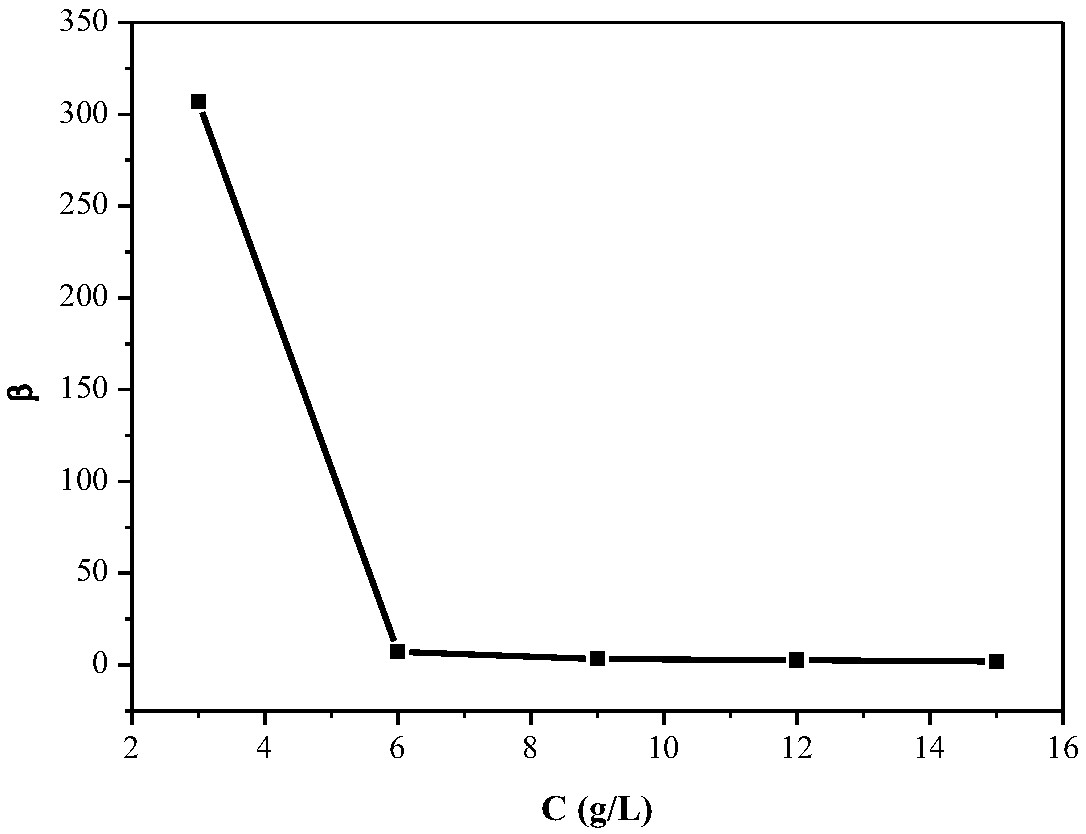
Method for controlling pH change in process of removing manganese through acidic extracting agent
An acidic extractant and extraction technology, which is applied in the field of metal separation and recovery, can solve the problems of cumbersome operation and the inability to predetermine the amount of acid and alkali, and achieve the effect of solving difficult pH adjustment, good pH constant, and simple operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] In this embodiment, a method for controlling pH changes in the process of manganese removal by an acidic extractant comprises the following steps:
[0028] (1) adding alkali to the acid solution with an acidity coefficient of 3-5 to obtain a buffer solution with a pH value of 4-4.5;
[0029] (2) adding the buffer solution described in step (1) to the manganese feed liquid to be adjusted to 4.0-5.0 in pH, so that the concentration of manganese ions is less than 6g / L, and adjusting the pH to 3.8-4.2 with acid or alkali, to obtain a mixed solution;
[0030] (3) carry out multistage extraction to the mixed solution described in step (2) with acidic extractant solution, to remove the manganese ion in the manganese feed liquid to be removed; The concentration of described acidic extractant solution is less than or equal to 0.4mol / L, Between the amount of the total substance of the acidic extractant in the used acidic extractant solution of the described multistage extraction...
Embodiment 2
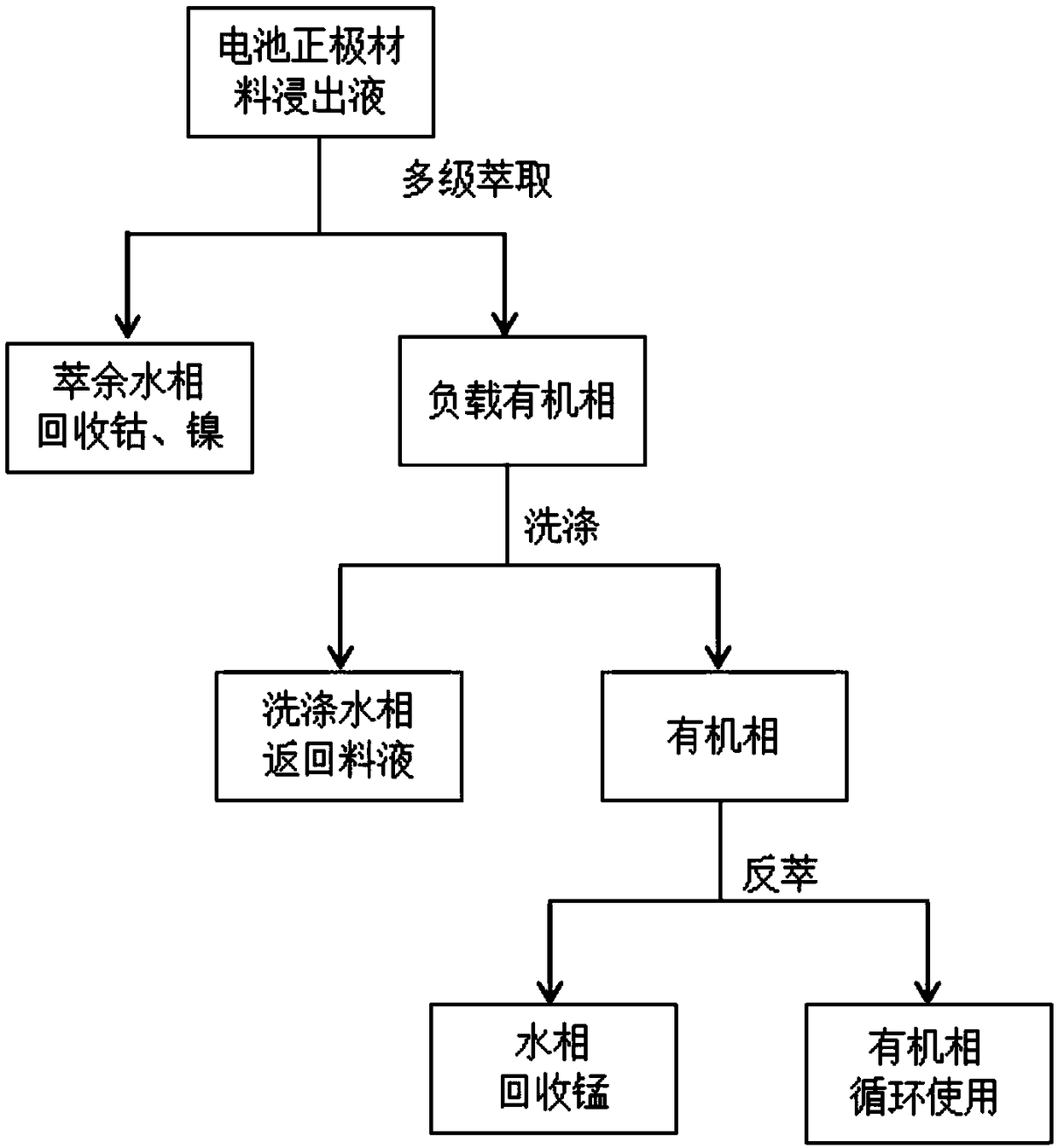
[0035] This embodiment is a method for removing manganese from a ternary positive electrode material of a 111-type lithium-ion battery, and the flow chart is as follows figure 2 shown, with the following steps:
[0036] 1. Leaching of cobalt, nickel and manganese in battery cathode materials
[0037] Weigh 10g waste lithium-ion battery cathode material powder, select H 2 SO 4 +H 2 o 2 As a leaching agent, it is leached under reflux by heating a magnetic stirrer at a constant temperature. h 2 SO 4 Concentration is 2.5mol / L, H 2 o 2 The concentration is 2.0mL / g, the leaching temperature is 85°C, the leaching time is 120min, and the liquid-solid ratio is 10:1. Adjust the pH of the leached feed solution to 4.0-5.0, filter the precipitate, and dilute to volume in a 250mL volumetric flask. As determined by atomic absorption spectrometry, the contents of each element in the leachate are: Co: 6.553g / L; Ni: 6.839g / L; Mn: 6.081g / L.
[0038] 2. Manganese removal by extraction...
Embodiment 3
[0050] This embodiment is a method for removing manganese from the positive electrode material of a high-cobalt lithium-ion battery, and the flow chart is as follows figure 2 shown, with the following steps:
[0051] 1. Leaching of cobalt, nickel and manganese in battery cathode materials
[0052] The leaching method and process are the same as in Example 2. The content of each element in the obtained leachate is respectively: Co: 14.60g / L; Ni: 3.86g / L; Mn: 2.212g / L.
[0053] 2. Manganese removal by extraction of leachate
[0054] Pipette 5.7mL of glacial acetic acid, add appropriate amount of distilled water to dilute, and adjust the pH of the solution to slightly greater than 4 with solid sodium hydroxide. Then add 25mL of the above-mentioned leached battery feed solution to it, and use a little sodium hydroxide solution and sulfuric acid solution to fine-tune the pH of the mixed solution to 4.0, and constant volume in a 100mL volumetric flask. Among them, the contents ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com