A double-clad ytterbium-doped optical fiber
A technology of ytterbium-doped fiber and double cladding, applied in cladding fiber, multi-layer core/cladding fiber, optics, etc., can solve the problem of high-power lasers that are difficult to work stably, difficult to break the helical light mode, and difficult to enter the fiber core To achieve the effect of improving stable working ability, improving transmission loss and thermal effect control
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
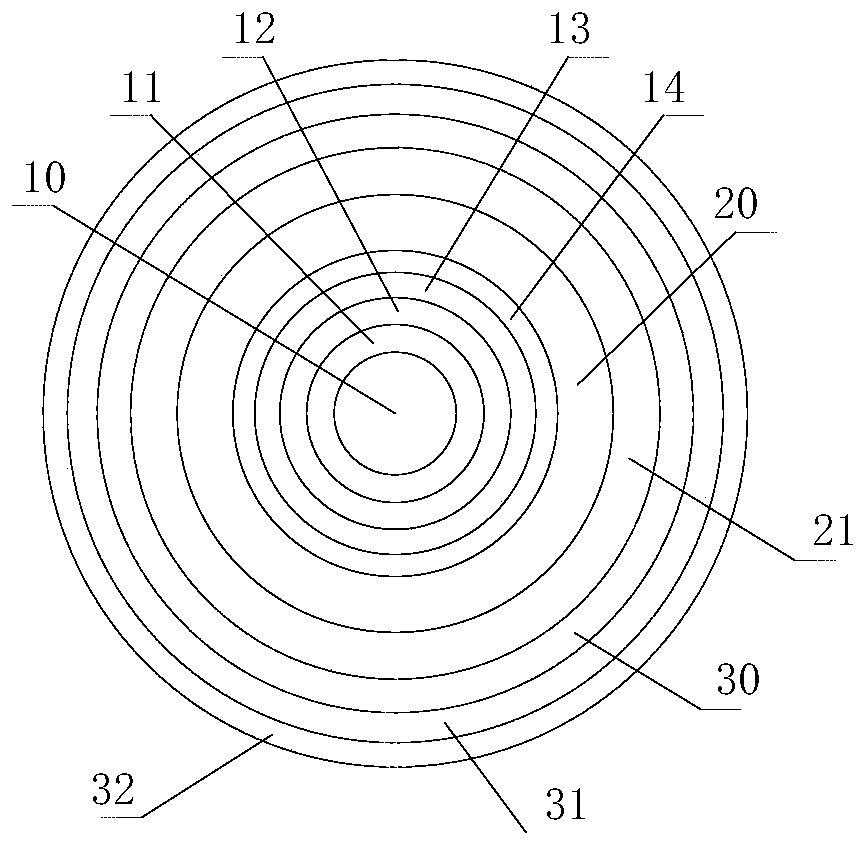
[0036] see figure 1 As shown, the embodiment of the present invention provides a double-clad ytterbium-doped optical fiber. The optical fiber includes a core, an inner cladding 20 and an outer cladding 21 from the inside to the outside, and the core includes a circular cladding from the inside to the outside. A central core region 10, and at least four annular doped core regions concentrically arranged with the central core region 10, the concentration of ytterbium ions in the central core region 10 and the four annular doped core regions are sequentially arranged from inside to outside increase, and both the inner cladding layer 20 and the outer cladding layer 21 are quartz cladding layers.
[0037] The double-clad ytterbium-doped fiber in the embodiment of the present invention is designed with multiple ring-shaped doped core regions and combined with the double-clad design to form a dual-guided laser power in the core region that combines refractive index guidance and gain ...
Embodiment 2
[0040] The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that the cross-sections of the inner cladding layer 20 and the outer cladding layer 21 are regular octagonal structures, that is, an octagonal double cladding structure, and the apex of the inner cladding layer 20 is located at The center line of the side length of the outer cladding 21 makes the inner cladding 20 and the outer cladding 21 orthogonal to each other, so as to break the cladding spiral light more effectively, thereby improving the pumping efficiency of the cladding.
Embodiment 3
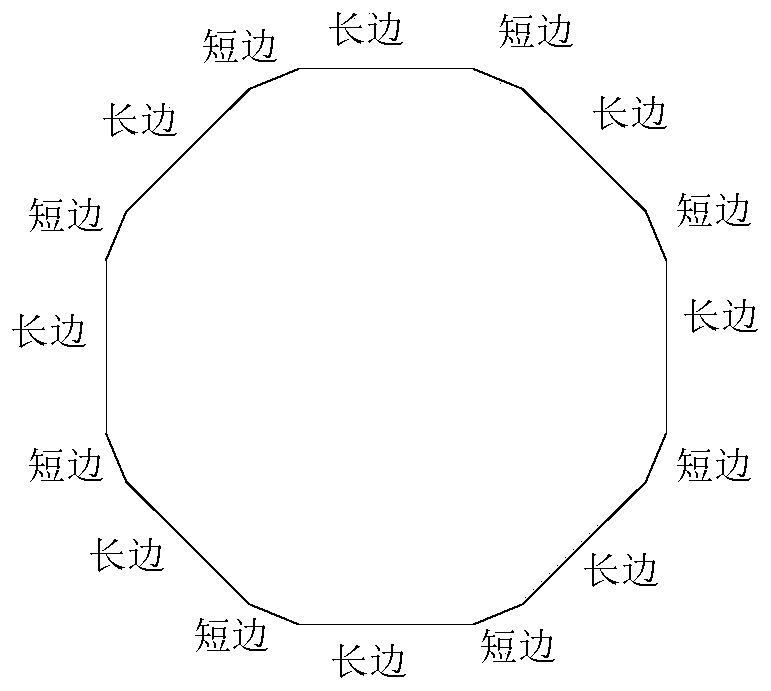
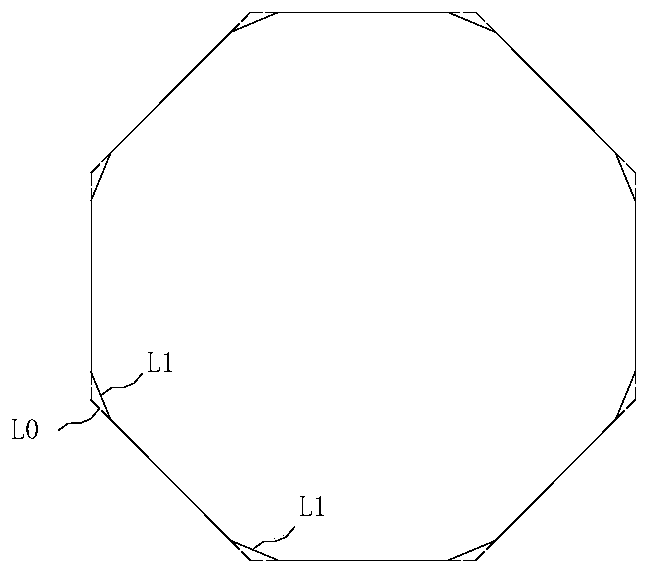
[0042] see figure 2 and image 3 As shown, the difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that the cross section of the inner cladding layer 20 is a regular octagonal structure, and the cross section of the outer cladding layer 21 is a centrally symmetrical hexagonal shape, and the hexagonal shape consists of Eight long sides and eight short sides are connected alternately, and the apex of the inner cladding 20 is located on the centerline of the long sides of the outer cladding 21 . During manufacture, the hexagon can be formed by cutting off eight corners on the basis of the regular octagonal structure, so as to solve the problem of abnormal flow of paint caused by the sharp octagonal structure, so that the manufactured ytterbium-doped optical fiber Coating consistency is higher.
[0043] The extension lines of eight described long sides intersect each other and form a regular octagon, the side length of the regular octagon is L0, and the short side length of ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Concentricity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Absorption coefficient | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com