Phosphate additive for rich-lithium manganese-based positive electrode, preparation method of phosphate additive, and positive electrode
A lithium-rich manganese-based, phosphate-based technology, applied in battery electrodes, non-aqueous electrolyte battery electrodes, electrical components, etc., to achieve the effect of improving cycle performance and rate performance, and beneficial to electrochemical performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
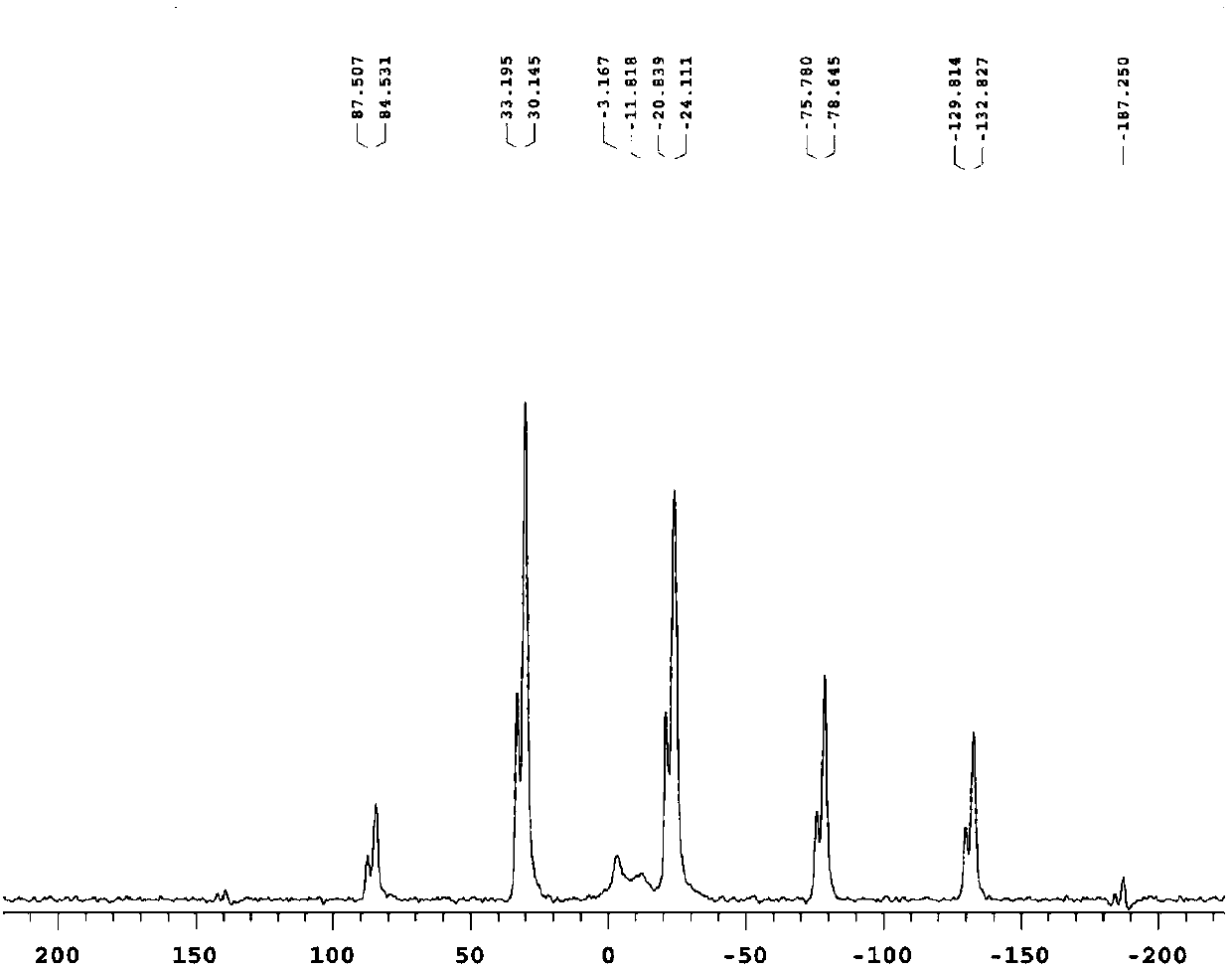
[0044] (1) Add 2.76g of lithium hydroxide (LiOH) into a sample bottle with a capacity of 50mL, and add 20mL of deionized water and a Teflon stir bar of suitable length; seal the sample bottle and place it on a heatable magnetic stirrer On, set the temperature at 60°C and rotate at 300 rpm to dissolve lithium hydroxide into a saturated aqueous solution of lithium hydroxide; add 3 g of sodium trimetaphosphate to a saturated aqueous solution of lithium hydroxide to obtain a mixture;
[0045](2) Seal the sample bottle containing the mixture and place it on a heatable magnetic stirrer to continue stirring at a constant temperature of 60° C. for 10 h to obtain a solution containing suspended matter, and then centrifuge the solution containing suspended matter at a speed of 4500 rpm, First wash with deionized water for 3 times, then wash with ethanol for 3 times, then vacuum-dry at 80°C for 12 hours to obtain a white powder containing part of crystal water, then put the white powder i...
Embodiment 2~5
[0053] Adopt the method identical with embodiment 1, its difference is only that LTMP and PVP adopt the mass shown in table 1 to add.
[0054] Table 1 Addition amount of LTMP and PVP / g
[0055]
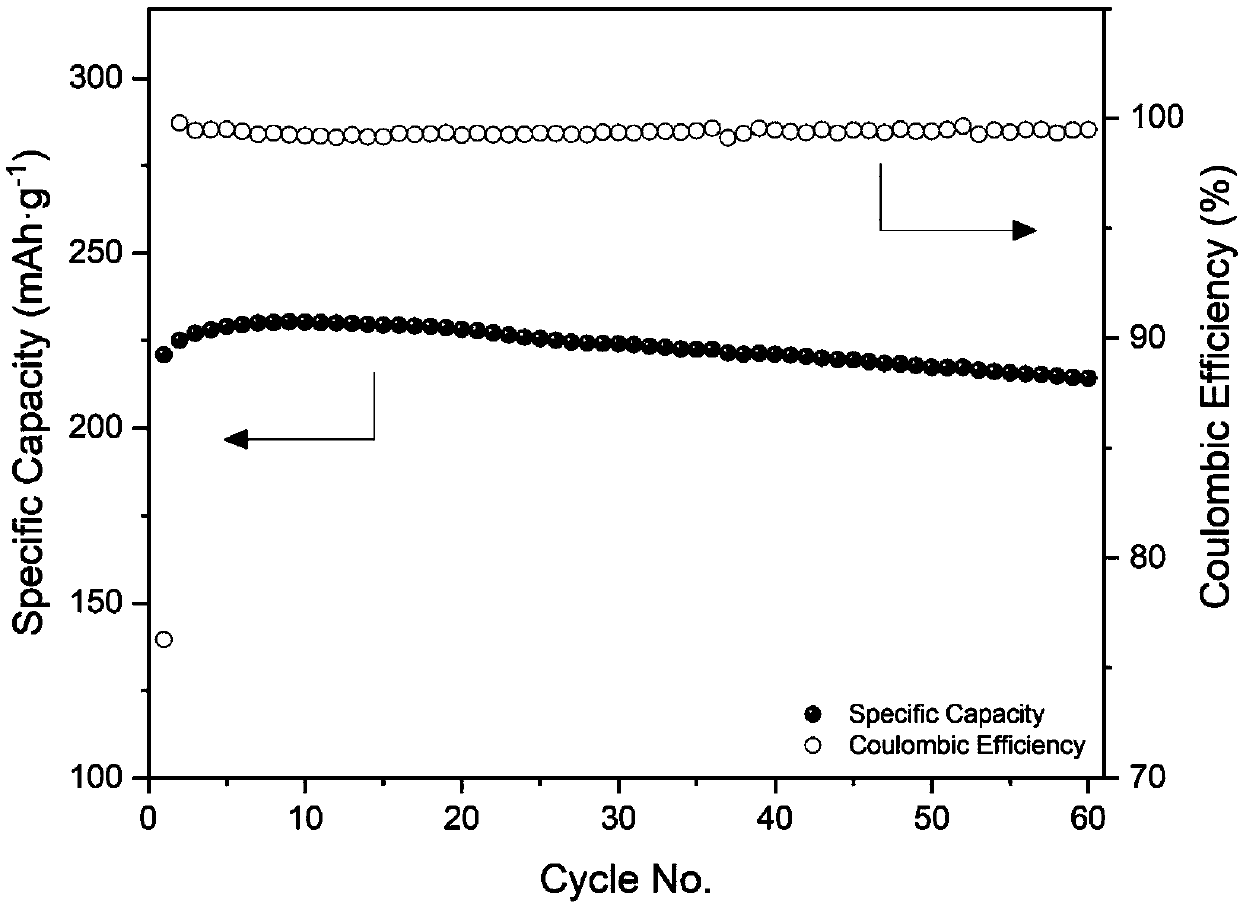
[0056] The performance of the lithium-rich manganese-based positive electrode sheet half-cells prepared in Examples 2-5 after a cycle of 60 cycles was measured, and the results are shown in Table 2.
[0057] Table 2. Discharge mass specific capacity of lithium-rich manganese-based positive electrode sheet in the 60th cycle cycle obtained in Examples 2-5
[0058] Example number
[0059] The SEM figure and image 3 Similar; The surface SEM figure of the obtained lithium-rich manganese-based positive pole sheet is the same as Figure 4 similar.
Embodiment 6~8
[0061] Using the same method as in Example 1, only using different lithium-rich manganese-based materials, see Table 3 for details
[0062] Table 3 Composition of lithium-rich manganese-based materials with different components
[0063] Example number
[0064] The performance of the lithium-rich manganese-based positive electrode sheet half-cell prepared in Examples 6-10 after a cycle of 60 cycles was measured, and the results are shown in Table 4.
[0065] Table 4 Discharge mass specific capacity of lithium-rich manganese-based positive electrode sheet in the 60th cycle cycle obtained in Examples 6-10
[0066] Example number
[0067] The SEM figure and image 3 Similar; The surface SEM figure of the obtained lithium-rich manganese-based positive pole sheet is the same as Figure 4 similar.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| quality score | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com