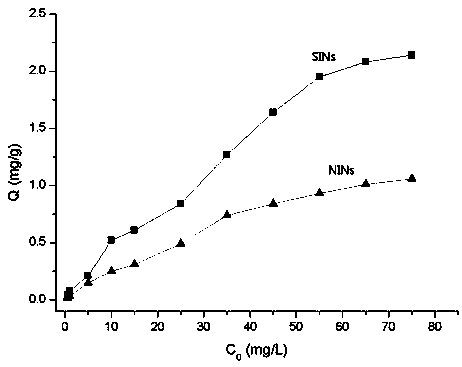
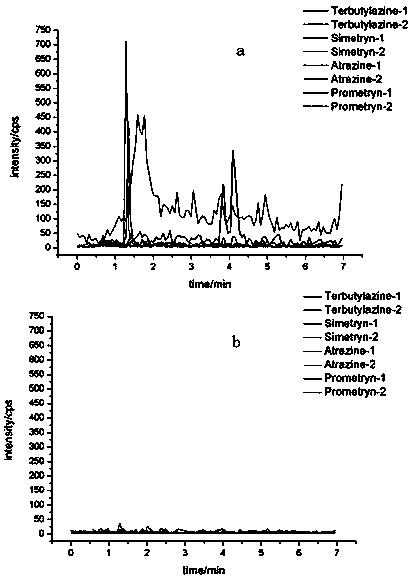
Method for detecting triazine herbicide residues in agricultural products through molecular imprinting and dispersive solid-phase extraction
A technology of molecular imprinting and dispersing solid phase, applied in chemical instruments and methods, material separation, analysis of materials, etc., can solve problems such as low purification efficiency, reduce matrix effects, improve accuracy and precision, and overcome the difficulty in controlling flow rate. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] Example 1: This molecular imprinting-dispersive solid-phase extraction method for detecting triazine herbicide residues in agricultural products, the specific content is as follows:
[0028] Add 50.66mg of siclofen, 0.081mL of methacrylic acid, and 40mL of acetonitrile into a 100mL borosilicate glass bottle, sonicate for 3 minutes, put it in a refrigerator at 4°C, and let it stand for 12 hours to seal and self-assemble to obtain a template-monomer complex; Add 30mg of azobisisobutyronitrile, 0.597mL of ethylene glycol dimethacrylate, pass into high-purity N 2 15min, then heat-initiated precipitation polymerization in a 60°C water bath at a speed of 60rpm for 48h; after the reaction, centrifuge at 10,000rpm to obtain polymer particles, and then use a Soxhlet extraction device to mix methanol-acetic acid (9:1, v / v) Wash the template molecules in the polymer particles with the eluent, replace the eluent every 8 hours, and elute for 16 hours until the template molecules c...
Embodiment 2
[0035] Embodiment 2: The method of this molecular imprinting-dispersed solid phase extraction to detect triazine herbicide residues in agricultural products, the specific contents are as follows:
[0036] (1) Add 63.33 mg of xicaojing, 0.127 mL of acrylic acid, and 50 mL of methanol into a 100 mL borosilicate glass bottle, ultrasonicate for 3 min, put it in a -5°C refrigerator, and let stand for 12 h to seal and self-assemble to obtain a template-monomer complex; 35 mg of azobisisobutyronitrile, 0.746 mL of trimethylolpropane trimethacrylate were added to it, and high-purity N was added. 2 15min, then thermally induced precipitation polymerization at 50°C water bath and rotating speed of 100rpm for 20h; after the reaction, centrifuged at 10000rpm to obtain polymer particles, and then used a Soxhlet extraction device to extract methanol-acetic acid mixed solution (20:1, v / v) Wash the template molecules in the polymer particles with the eluent, replace the eluent every 8 hours...
Embodiment 3
[0041] Embodiment 3: The method of this molecular imprinting-dispersed solid phase extraction to detect triazine herbicide residues in agricultural products, the specific contents are as follows:
[0042] Add 53.92 mg atrazine, 0.101 mL trifluoromethacrylic acid, 50 mL dichloromethane to a 100 mL borosilicate glass bottle, ultrasonicate for 5 min, put it in a 10°C refrigerator for 12 hours, seal and self-assemble to obtain a template-monomer complex ; Add 30mg azobisisobutyronitrile, 0.746mL ethylene glycol dimethacrylate to it, feed high-purity N 2 15min, then thermally induced precipitation polymerization reaction at 70°C water bath and rotating speed of 120rpm for 15h, after the reaction, centrifuged at 12000pm to obtain polymer particles; ) is the eluent to wash the polymer particles; the eluent is replaced every 8 hours, and atrazine cannot be detected from the supernatant by HPLC after elution; after elution, the polymer is washed with methanol and acetone in turn The ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com