In-plane quasi-isotropic structure-stealthy composite material and preparation method thereof
A quasi-isotropic, composite material technology, applied in the field of composite materials, can solve the problems of easy delamination, anisotropy of electromagnetic properties, poor impact resistance, etc., to reduce reflection, solve easy delamination, and achieve isotropy Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0051] A method for preparing an in-plane quasi-isotropic structure-stealth composite material of the present invention specifically comprises the following steps:
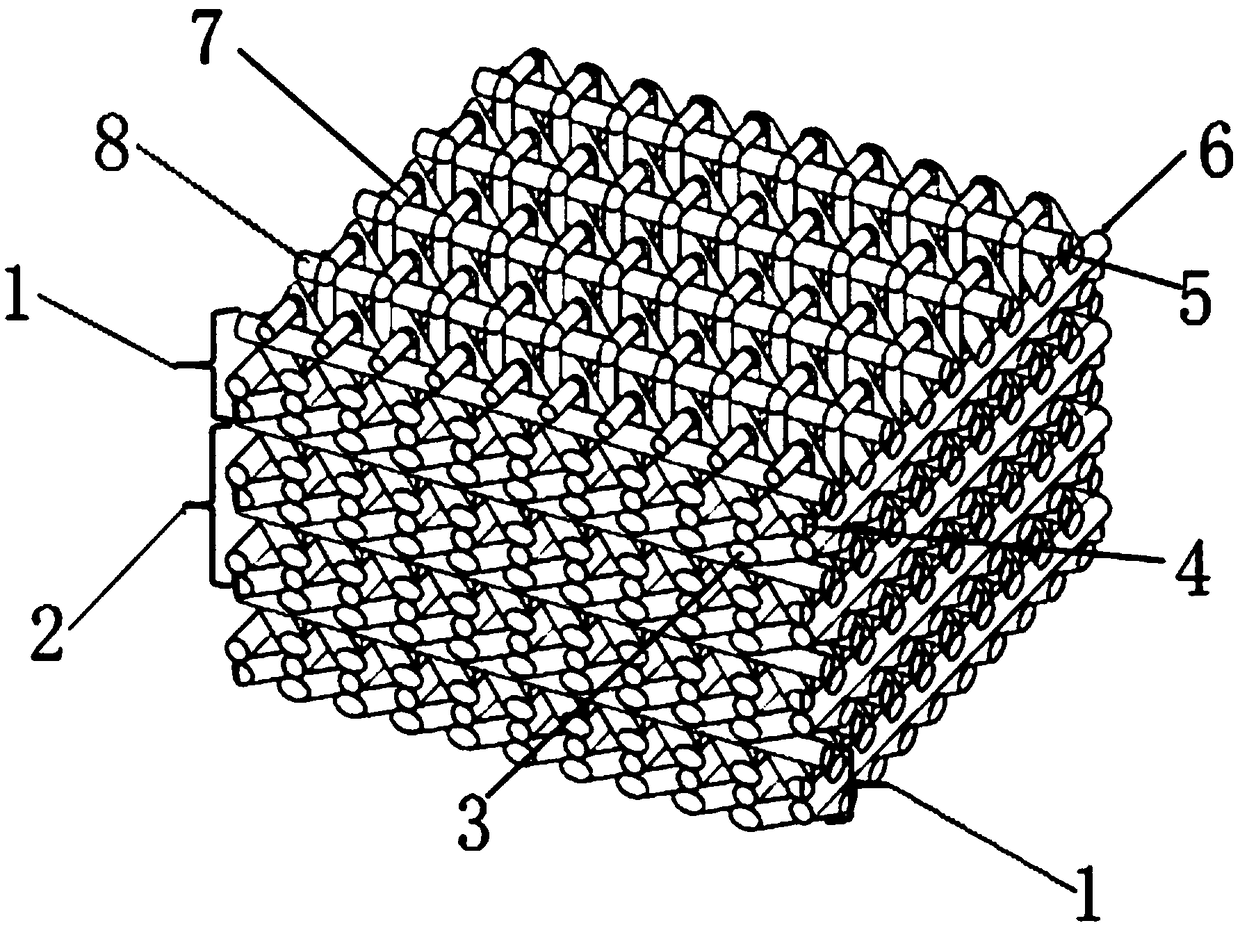
[0052] Step 1: Weaving of reinforcement
[0053] Hang the cut wave-absorbing fiber and wave-transmitting fiber on the hook of the yarn carrier of the determinant three-dimensional three-dimensional knitting machine according to the size, shape and arrangement of the fiber layers of the fabric, and then complete each step in the order of the weaving steps until a whole After the cycle is over, the weaving steps are repeated continuously until the required specifications of the reinforcement are reached;
[0054] Step 2: Model the Augment
[0055] Put the reinforcement braided in step 1 into an oven and dry at 100°C to 110°C for 2h to 4h, take it out after drying, and cut the dried reinforcement to Appropriate size, clean the mold and apply a release agent on the surface of the mold, after drying, put the cut rein...
Embodiment 1
[0074] A method for preparing an in-plane quasi-isotropic structure-stealth composite material, specifically comprising the following steps:
[0075] Step 1: Weaving of reinforcement
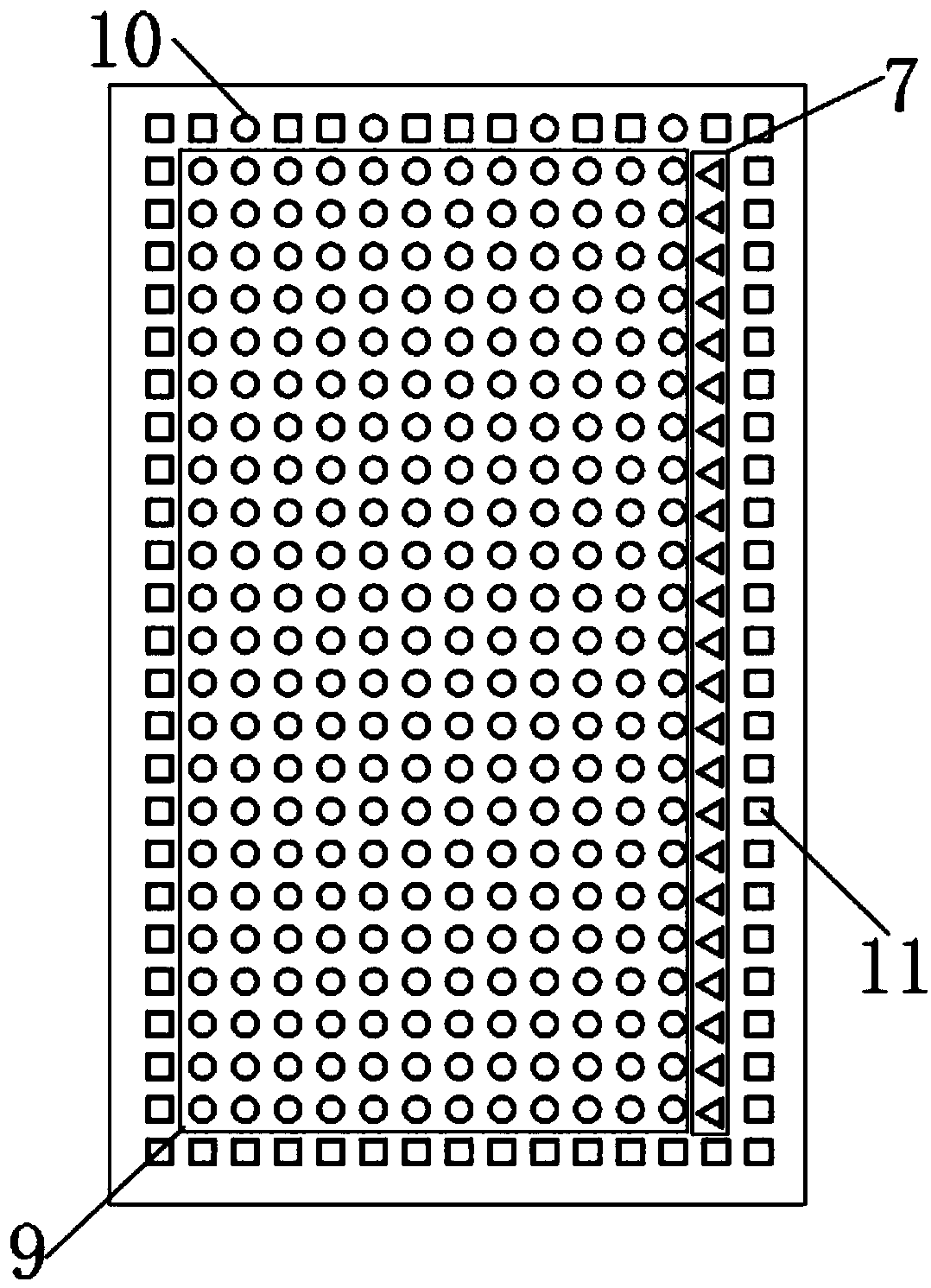
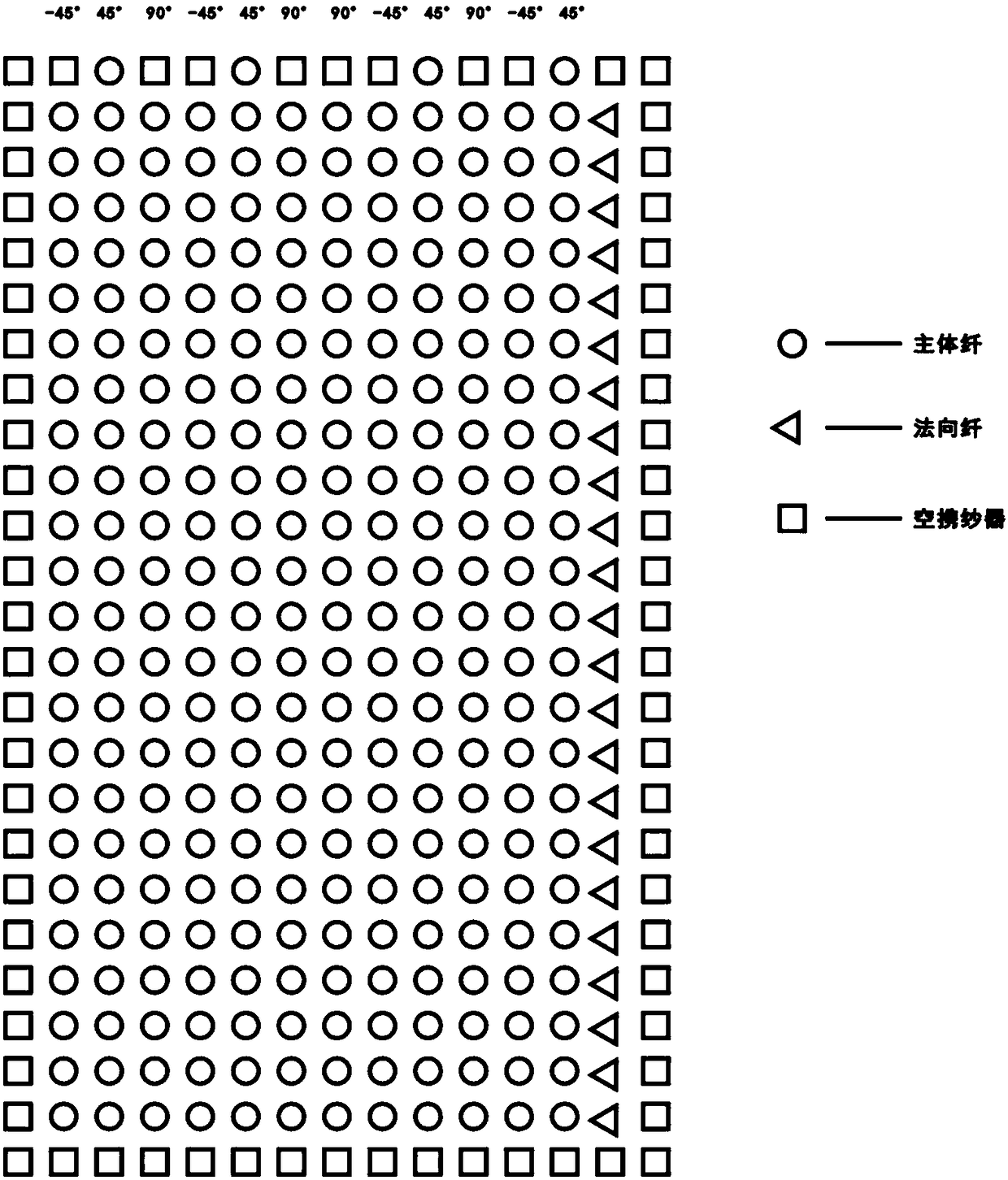
[0076] In this example, the wave-absorbing fiber is selected from Japan’s Toray T800-12k carbon fiber with excellent electromagnetic wave absorption performance and mechanical properties, and the wave-transmitting fiber is selected from the S fiber that is commonly used in China and has better strength, modulus, dielectric constant and high temperature resistance than E glass fiber. glass fiber. Among them, the glass fibers in the directions of 0°, 90°, and 45° in the wave-transmitting layer are 800tex, and the normal direction fibers are 400tex glass fibers. The size of the reinforcement is 250mm*185mm, the fibers in the 90° direction are 6 fibers / cm, the fibers in the 0° direction are 2 fibers / cm, and the arrangement order and ratio of the fibers are {G 1 -45° G 2 0° G 3 45° G 4 90° C...
Embodiment 2
[0094] A method for preparing an in-plane quasi-isotropic structure-stealth composite material, specifically comprising the following steps:
[0095] Step 1: Weaving of reinforcement
[0096] In this example, the wave-absorbing fiber is selected from Japan’s Toray T800-12k carbon fiber with excellent electromagnetic wave absorption performance and mechanical properties, and the wave-transmitting fiber is selected from the S fiber that is commonly used in China and has better strength, modulus, dielectric constant and high temperature resistance than E glass fiber. glass fiber. Among them, the glass fibers in the directions of 0°, 90°, and 45° in the wave-transmitting layer are 800tex, and the normal direction fibers are 400tex glass fibers. The size of the reinforcement is 250mm*185mm, the fibers in the 90° direction are 6 fibers / cm, the fibers in the 0° direction are 2 fibers / cm, and the arrangement order and ratio of the fibers are {G 1 -45° G 2 0° G 3 45° G 4 90° C...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com