Collecting method of mesenchymal stem cells
A technology of mesenchymal stem cells and stem cells, applied in the collection of mesenchymal stem cells and the collection of mesenchymal stem cells separated from microcarriers, can solve the problem of reducing the expression of the surface marker CD105 of mesenchymal stem cells and the collection rate of mesenchymal stem cells. High, low cell viability and other problems, to achieve the effect of short processing time, less damage, high cell viability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0030] Inoculate bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells P3 generation cells into 125mL microcarrier culture flasks containing 100mL medium, maintain a stirring rate of 30rpm, and store in 5% CO 2 , and cultured in a cell incubator at 37°C and 95% humidity for 5 days.
[0031] Take out the microcarrier culture bottle, let it stand for 5min, suck off the upper medium, wash it twice with 50mL PBS containing EDTA, add EDTA-trypsin twice the volume of the microcarrier, take out the stirring hammer in the microcarrier bottle, and put The microcarrier culture flask was placed on a constant temperature shaker at 37°C, shaken at 150rpm for 8min, then 200rpm for 10s, and then 50mL of medium was added to stop digestion.
[0032] Filter the cell and microcarrier mixture with a 70 μm cell mesh, collect the cell filtrate, centrifuge at 200 g for 5 min, collect the precipitate, and resuspend the cells with the medium.
[0033] After the resuspended cells were stained with trypan blue at...
Embodiment 2
[0038] The cell quantity and cell viability assay that embodiment 2 collects
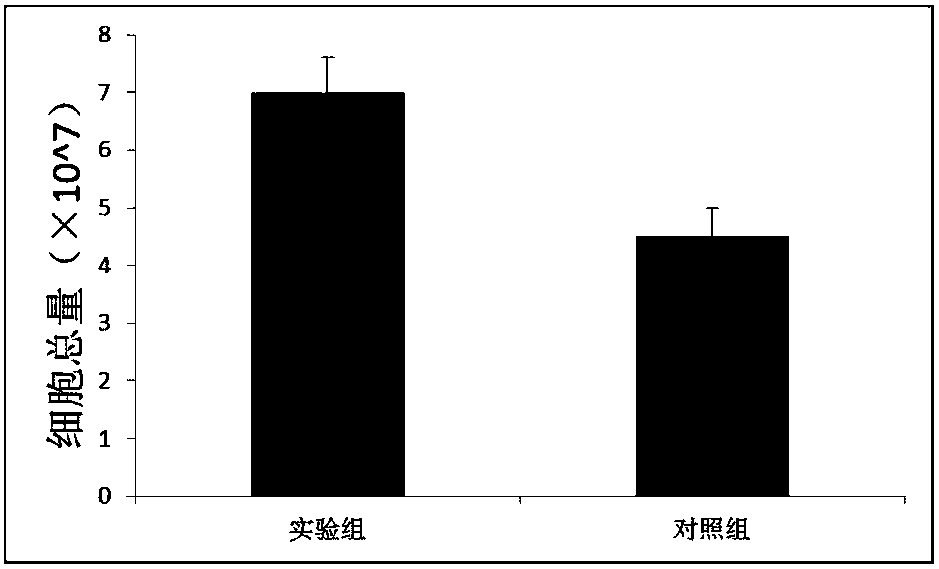
[0039] The resuspended cells of Example 1 and Comparative Example 1 were stained with trypan blue at a ratio of 1:1, respectively, and placed in an automatic cell counter to count the number of collected cells and cell viability. The results are shown in figure 1 and figure 2 .
[0040] The results showed that the number and viability of the mesenchymal stem cells collected in Example 1 were higher than those in Comparative Example 1.
Embodiment 3
[0041] Example 3 Detection of surface markers of mesenchymal stem cells collected by flow cytometry
[0042] The mesenchymal stem cells collected in Example 1 and Comparative Example 1 were subjected to flow cytometric detection. Add 1×10 per tube 6For the number of cells, wash once with staining buffer, and centrifuge at 1000rpm for 5 min; discard the supernatant, blow and mix the cells with staining buffer; add 2 μL each of CD73, CD90, CD105, CD34, CD45 and HLA-DR antibodies, and set up a tube as Blank control; react in the dark for 15-20min at 4°C; wash once with staining buffer, centrifuge at 1000rpm for 5min; discard the supernatant of directly labeled cells, add 500μL of loading buffer in the dark, mix well, and filter through a 200-mesh sieve Cell samples were filtered through a mesh, and cell surface antigens were detected by flow cytometry. The test result of embodiment 1 group sees image 3 , the test results of the comparative example group 1 are shown in Figur...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com