Optical detector of Van der Waals heterojunction based on two-dimensional indium selenide and black phosphorus and manufacturing thereof
A photodetector and indium selenide technology, applied in the field of photodetection, can solve the problems of low light absorption and luminescence efficiency, large dark current, limitation, etc., and achieve the effects of improving detection sensitivity, reducing response time, and reducing noise
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
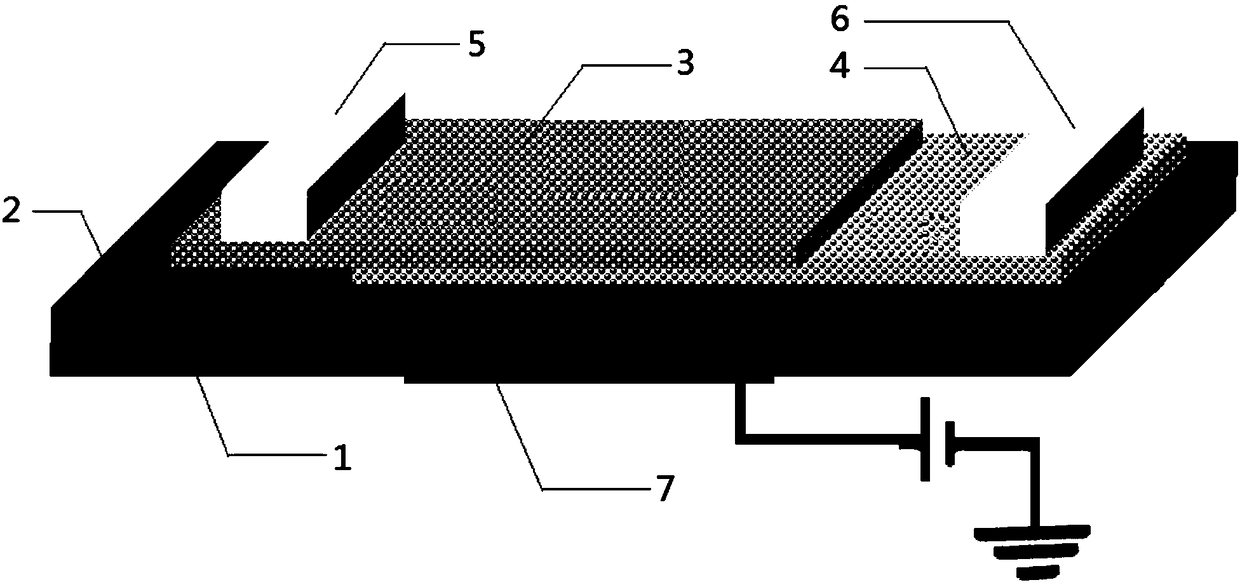
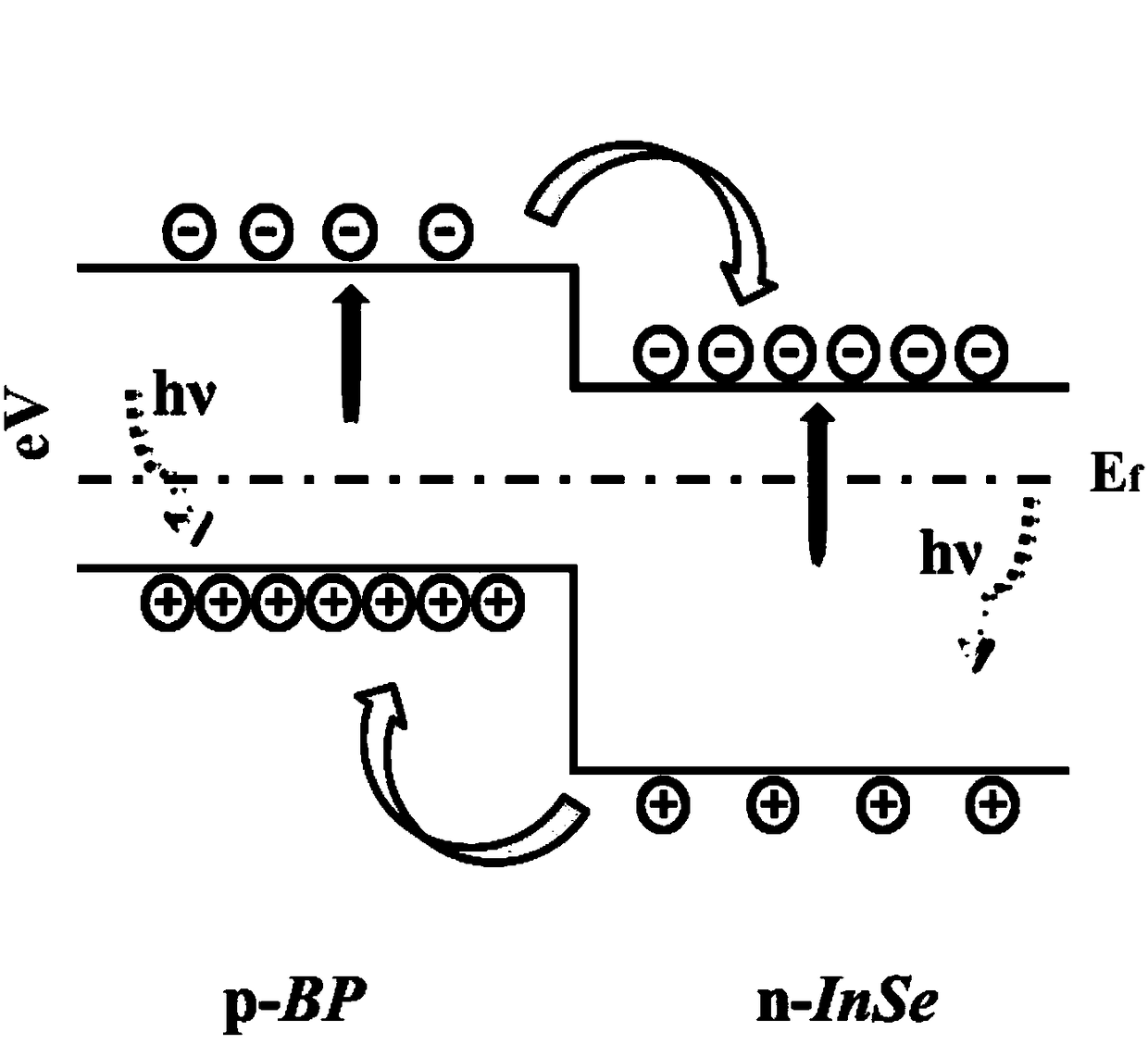
[0045] Such as figure 1 As shown, a photodetector based on a van der Waals heterojunction of two-dimensional indium selenide and black phosphorus, comprising a silicon substrate 1 and a silicon dioxide oxide layer 2 disposed on the silicon substrate 1, said The silicon dioxide oxide layer 2 is provided with a p-type black phosphorus layer 4, the p-type black phosphorus layer 4 is provided with an n-type indium selenide layer 3, and the p-type black phosphorus layer 4 and n-type selenium The indium layer 3 forms a van der Waals p-n heterojunction;
[0046] A drain electrode is arranged on the n-type indium selenide layer 3, a source electrode 6 is arranged on the p-type black phosphorus layer 4, and a side opposite to the silicon dioxide oxide layer 2 is arranged on the silicon substrate 1 There is a gate electrode 7 .
[0047] The thickness of the p-type black phosphorus layer 4 described in this embodiment is 10 nm, which is about 18 layers;
[0048] The thickness of the ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com