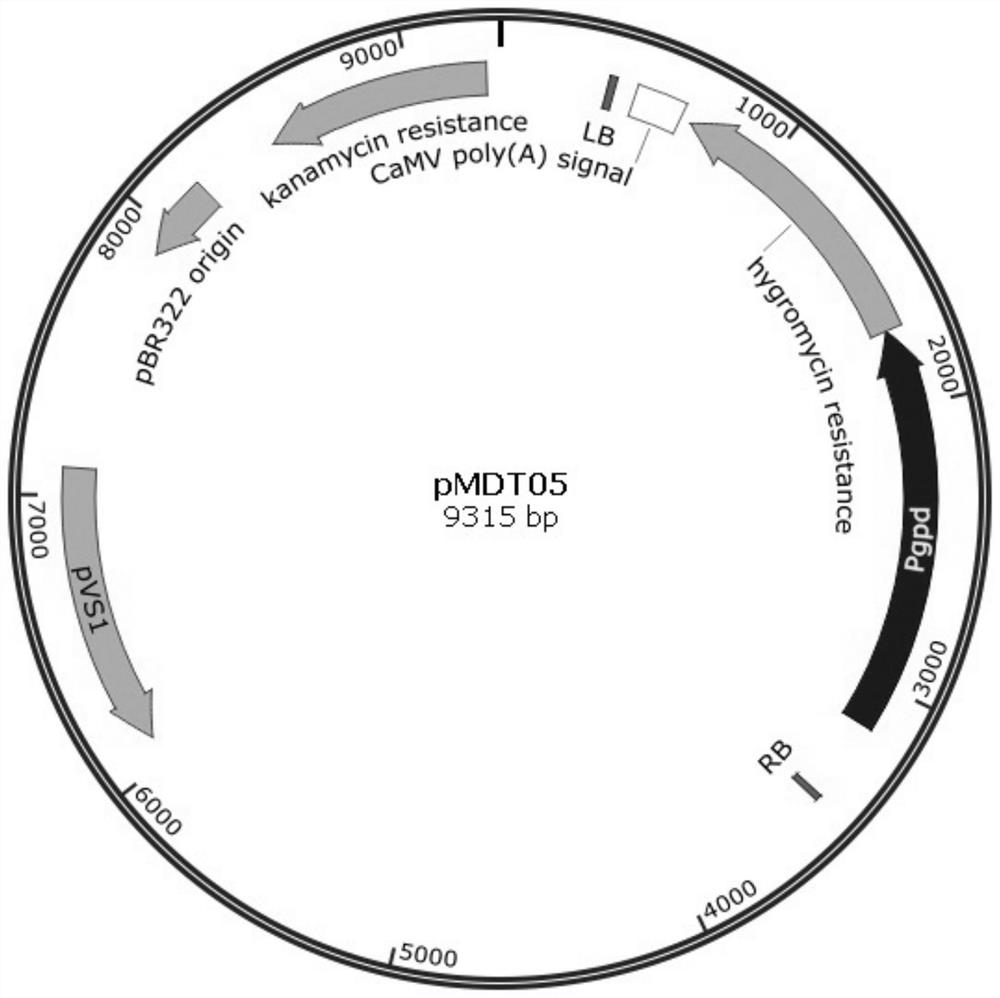
Genetically engineered bacteria expressing oxalate oxidase recombinantly and its construction method and application
A technology of oxalate oxidase and genetically engineered bacteria, applied in the field of genetic engineering, can solve the problems of low content, complicated extraction and purification process, and cumbersome procedures
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0042] Embodiment 1: artificially design and synthesize the optimized gene of oxalate oxidase
[0043] This embodiment provides an optimized gene of oxalate oxidase, which is used to encode an oxalate oxidase, and the amino acid sequence of the oxalate oxidase is shown in SEQ ID NO.1. Wherein, the signal peptide sequence of the oxalate oxidase is the 1-17 amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO.1, which is derived from Trichoderma reesei Rut-C30 strain; the mature peptide sequence of the oxalate oxidase is SEQ ID NO.1 The shown 18-458 amino acid sequence is derived from Ceriporiopsis subvermispora.
[0044] Furthermore, the nucleotide sequence of the optimized gene of oxalate oxidase provided in this example is shown in SEQ ID NO.2. The process of artificially designing and synthesizing the optimized gene of the oxalate oxidase is as follows:
[0045]The oxalate oxidase gene derived from Cereus paracereus was optimized according to the codon preference of Trichoderma reesei (...
Embodiment 2
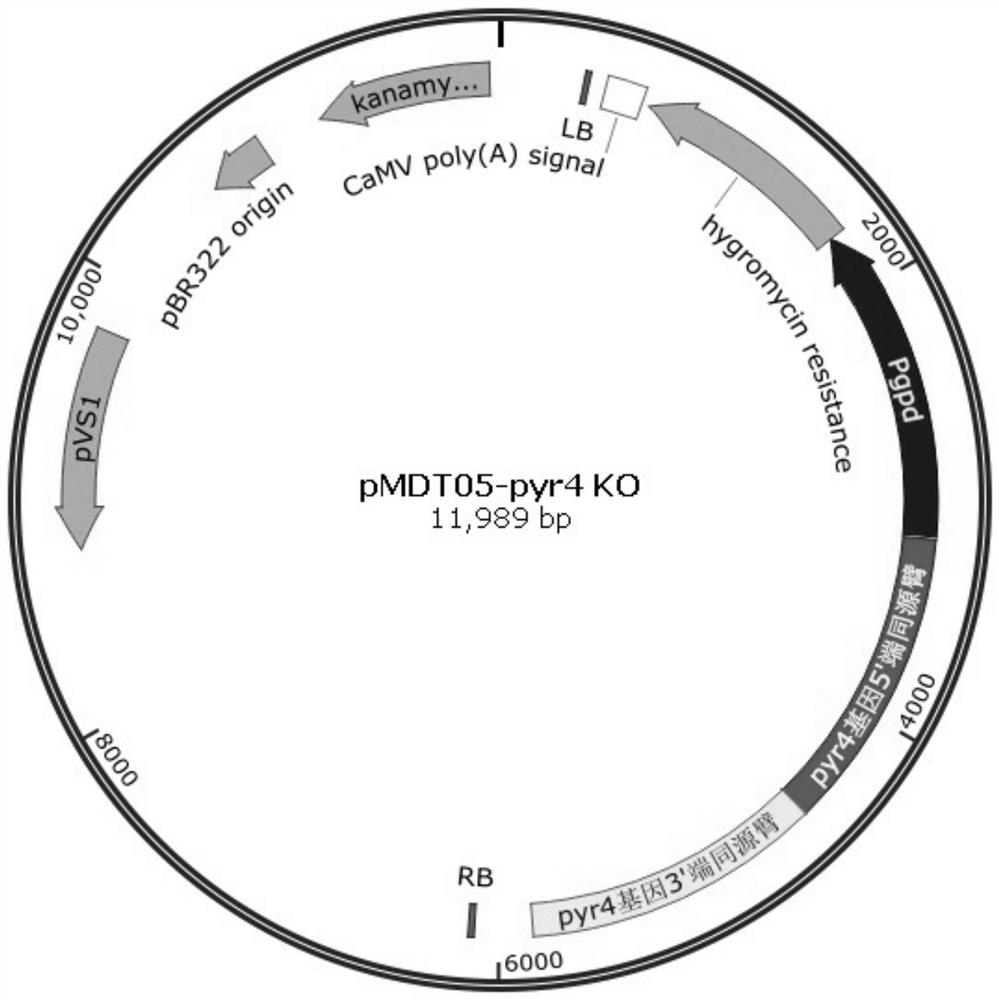
[0046] Embodiment 2: Construction of the pyr4 gene deletion mutant strain Rut-C30(pyr4-) of Trichoderma reesei Rut-C30
[0047] 201. Extraction of Genomic DNA from Trichoderma reesei Rut-C30
[0048] Inoculate the fresh spores of Trichoderma reesei Rut-C30 into the liquid medium for overnight culture, collect the mycelium by filtration, wash twice with sterile water, grind the mycelium with liquid nitrogen, take an appropriate amount of mycelium powder into a 1.5ml centrifuge tube, Use the Ezup column type fungal genomic DNA extraction kit (purchased from Shanghai Shenggong) to isolate genomic DNA, the method is as follows: add 200ul of BufferDigestion (digestion buffer) and 2ul of β-mercaptoethanol, then add 20ul of Proteinase K (protease K) solution, shake and mix. Water bath at 56°C for 1 h until the cells were completely lysed. After the water bath, 20 ul of RNase A (ribonuclease A) with a concentration of 10 mg / ml was added, and left at room temperature for 2 to 5 minut...
Embodiment 3
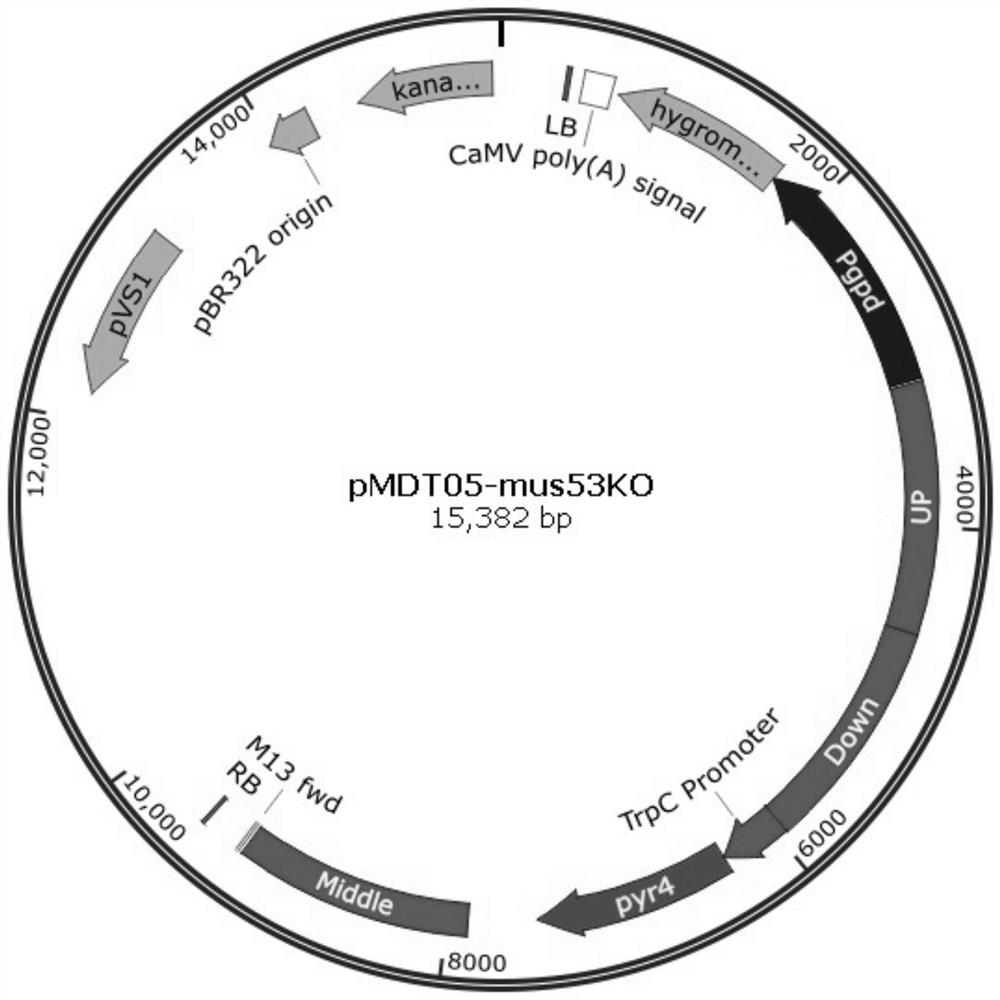
[0075] Embodiment 3: knockout the mus53 gene in Trichoderma reesei Rut-C30 (pyr4-) bacterial strain
[0076] According to public literature reports (Matthias G. Steiger, APPLIED AND ENVIRONMENTALMICROBIOLOGY, Jan. 2011, p.114–121) the mus53 gene (homologous to the human Lig4 gene) is required for the function of non-homologous end-joining (NHEJ), which Functional disruption can bring about 100% homologous recombination efficiency. In this example, the mus53 gene in the Trichoderma reesei Rut-C30 (pyr4-) strain was knocked out, laying the foundation for the subsequent site-specific integration knock-in example.
[0077] 301. Construction of Trichoderma reesei mus53 gene knockout vector pMDT05-mus53KO
[0078] Referring to the Trichoderma reesei mus53 gene (Protein Id: 58509) information provided in the open literature (MatthiasG.Steiger, APPLIED AND ENVIRONMENTAL MICROBIOLOGY, Jan.2011, p.114–121), search for the mus53 gene in the Trichoderma reesei genome database Locus sequ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com