Cabbage type rape high oleic acid QTL and molecular marker closely linked thereto
A technology of Brassica napus and molecular markers, which is applied to the determination/inspection of microorganisms, DNA/RNA fragments, recombinant DNA technology, etc., can solve problems such as unclear genetic basis, improve accuracy and selection efficiency, and solve genetic resources. The effect of a single, accelerated improvement process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
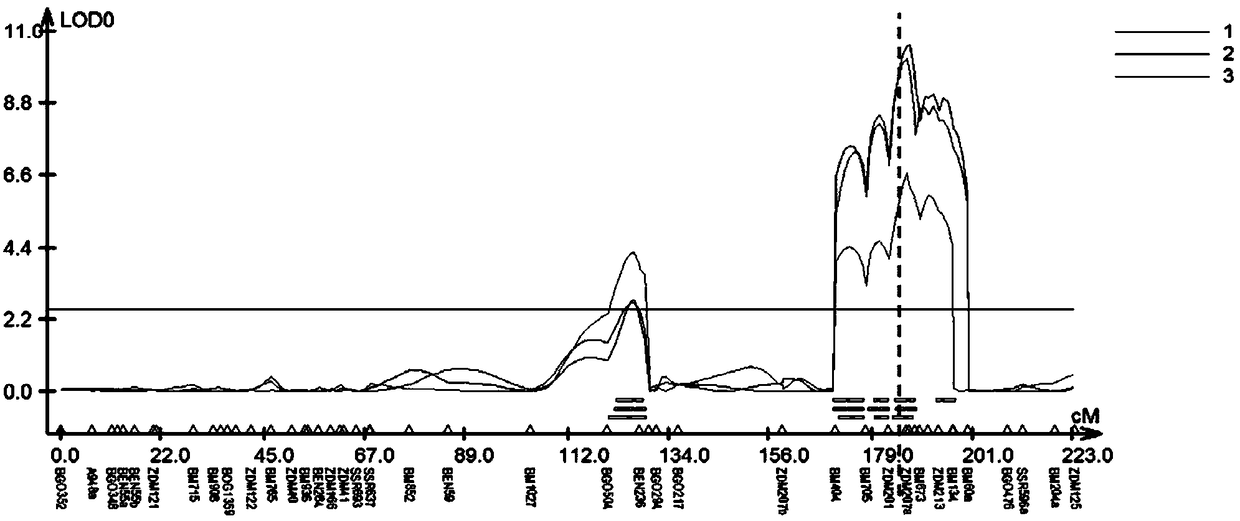
[0032] Example 1: Using the DH population to locate novel QTLs for oleic acid
[0033] 1. Construction and field experiment of DH localization population of Brassica napus
[0034] The Brassica napus strain ZP1 (with oleic acid content of 67.68%, Brassica napus ZP1, Brassica napusL.ZP1) was delivered to China. Wuhan. Wuhan University Chinese Type Culture Collection Center on November 10, 2017 for preservation, and the deposit number is CCTCC NO: P201722) was used as the female parent, and the Brassica napus strain A254 was used as the male parent (the content of oleic acid was 72.296%, patent number ZL 2009102734352; publication number CN101824472A) to obtain F1, and F1 was planted. Culture (refer to the literature for microspore culture method, Yu Fengqun, etc., Research on some culture factors to improve the seedling rate of Brassica napus microspore embryoid, Journal of Crops, 1997, 23(2): 165-168) obtained from 150 strains Lines composed of double haploid (referred to as ...
Embodiment 2
[0041] Example 2: Validation of a novel QTL for oleic acid using the F2 population
[0042] 1. F2 group construction
[0043] In order to further confirm the above results, the applicant selected the two parents ZP1 without A5 locus as the female parent and the conventional variety Huashuang 5 (a new national cabbage rape variety approved by the National Crop Variety Approval Committee of the Ministry of Agriculture of China in 2004). (Certification number: Guoshenyou 2004006), which has been widely promoted and planted in China), F1 was obtained by crossbreeding, and F2 population was obtained through F1 selfing, and the effect and stability of OLEA9 were verified by F2 population. In a subpopulation of F2 containing 170 individuals, the distribution of oleic acid content was bimodal, and analysis of this marker near the peak indicated significant phenotypic differences among the three different genotypes.
[0044] 2. Parental resequencing of F2 population and development of...
Embodiment 3
[0047] Example 3: Application of QTL site-specific marker for oleic acid content of Brassica napus A9 chromosome
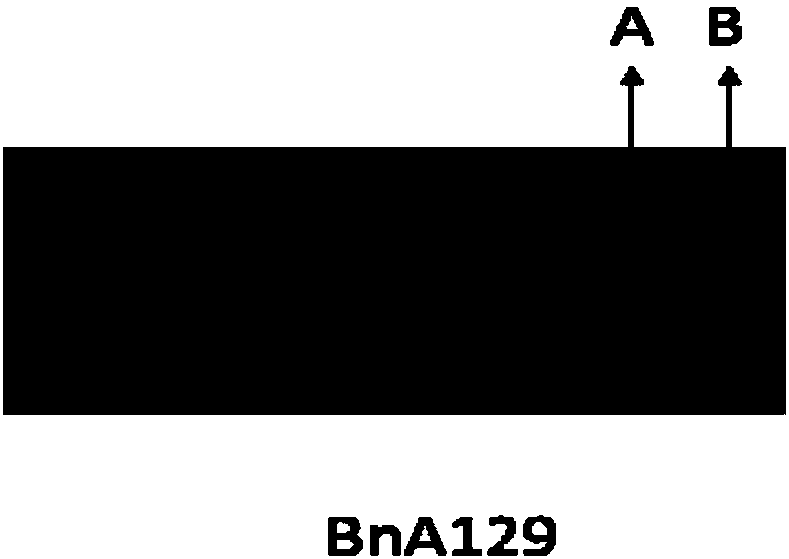
[0048] The marker BnA129 (see Table 2 for nucleotide sequence) near the peak was selected from the developed InDel markers for effect testing. The marker primer amplified the target fragment of 100 bp in the genomic DNA of the high oleic acid parent ZP1, and amplified the target fragment of 109 bp in the genomic DNA of the low oleic acid content parent Huashuang 5 (see figure 2 ), there is a 9bp InDel difference between the two, so the amplified fragment can be used as a co-dominant molecular marker for the trait of high oleic acid content in Brassica napus.
[0049] The genotypes of 170 F2 plants were analyzed by BnA129, of which 42 plants were A genotype with the same pattern as the parent ZP1, carrying the A9 chromosome high oleic acid locus allele, and the average oleic acid content was 67.47±1.76%; 51 individual plants were B genotype and had the same bandi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com