Composite electrolyte structure and lithium metal battery including the same
A composite electrolyte and structure technology, applied in the direction of non-aqueous electrolyte batteries, lithium batteries, solid electrolytes, etc., can solve the problems of reduced life and stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0322] Example 1: Fabrication of Lithium Metal Batteries
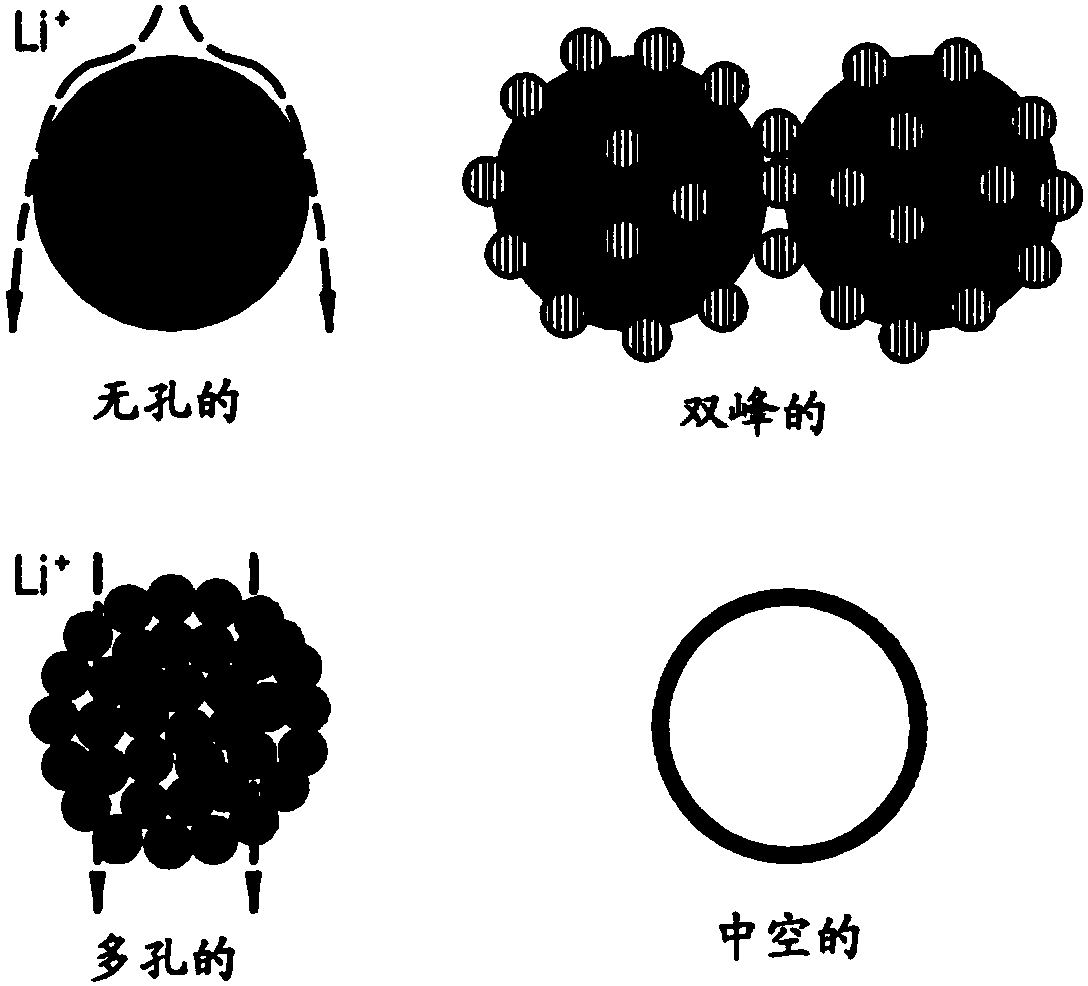
[0323] Poly(styrene-b-divinylbenzene) block copolymer microspheres (having an average particle size of about 3 μm, EPR-PSD-3, available from EPRUI Nanoparticles & Microspheres Co., Ltd.) were added to anhydrous tetrahydrofuran to A mixture comprising 5% by weight of block copolymer was obtained.
[0324]The block copolymer in the mixture comprising the block copolymer comprises polystyrene blocks and polydivinylbenzene blocks in a mixing ratio of about 9:1 by weight, and poly(styrene-b-divinyl Benzene) block copolymers have a weight average molecular weight of about 100,000 Daltons.
[0325] Lithium bis(fluorosulfonyl)imide (LiFSI, LiN(SO 2 f) 2 ) is added to a mixture comprising a block copolymer to obtain a protective layer-forming composition. The amount of LiFSI was about 30 parts by weight based on 100 parts by weight of the poly(styrene-b-divinylbenzene) copolymer.
[0326] The protective layer-forming com...
Embodiment 2
[0335] Example 2: Fabrication of Lithium Metal Batteries
[0336] A lithium metal battery was fabricated in the same manner as in Example 1, except that a ceramic conductor and a positive electrode electrolyte were included between the positive electrode and the solid electrolyte, and LiNi was used 0.6 Co 0.2 Mn 0.2 O 2 instead of Li[Ni 0.898 Co 0.087 Al 0.015 ]O 2 Except for the manufacture of positive electrodes. The lithium metal battery has a structure in which a lithium negative electrode, a solid electrolyte (first electrolyte), a second electrolyte, a positive electrode electrolyte, and a positive electrode are sequentially stacked on each other in this described order.
[0337] The second electrolyte used comprising a ceramic conductor was a ceramic solid electrolyte (Li 1.5 Al 0.5 Ti 1.5 (PO 4 ) 3 (Lithium Titanium Aluminophosphate; LATP), with a thickness of about 200 μm, available from Ohara glass).
[0338] The positive electrolyte was prepared by mi...
Embodiment 3
[0340] Example 3: Fabrication of Lithium Metal Batteries
[0341] Manufactured in the same manner as in Example 2 as Figure 7A The lithium metal battery shown in , except that no protective layer is formed on the lithium metal negative electrode. like Figure 7A As shown in , the lithium metal battery has a structure in which a first electrolyte 73 including microspheres 76, a second electrolyte 72 including LATP, a positive electrode electrolyte 71 and a positive electrode 80 are sequentially stacked on a lithium metal negative electrode 70.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| tensile modulus | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| aperture size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com