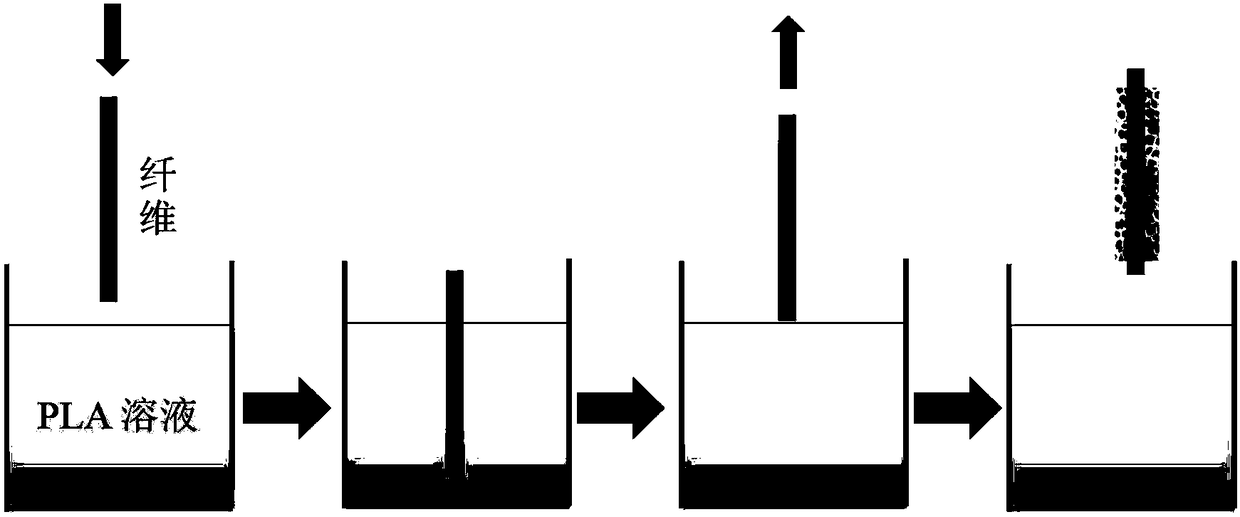
Preparation method of polylactic acid fiber composite surface porous film material
A technology of polylactic acid fiber and composite surface, which is applied in the direction of carbon fiber, fiber treatment, natural fiber, etc., can solve the problems of slow degradation rate of protease degradation liquid, unstable biological enzyme activity, unstable preparation effect, etc., achieving short time consumption, Strong stability and large specific surface area
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] 1) Weigh 5g of polylactic acid (PLA) with a number average molecular weight of 200,000 Daltons, stir and dissolve in 150mL of dichloromethane, and obtain a polylactic acid solution with a concentration of 2.5wt% at room temperature;
[0028] 2) Dip the carbon nanofiber (NCF) into the polylactic acid solution with a concentration of 2.5wt% in step 1), take it out after dipping for 50 seconds, and place it in a fume hood to dry naturally.
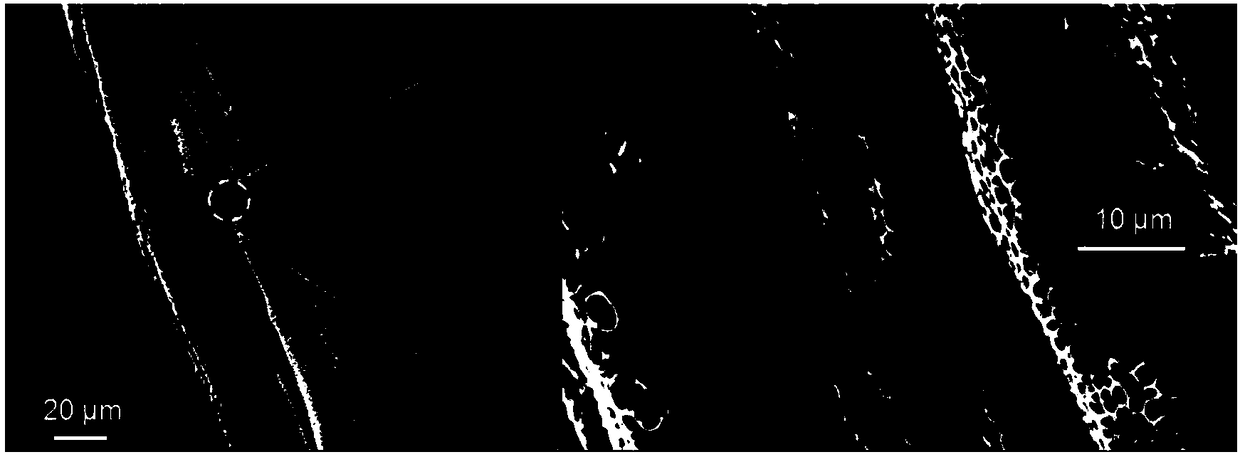
[0029] figure 1 It is a schematic diagram of the dip coating method of polylactic acid fiber composite surface porous membrane material, figure 2 SEM image of a typical polylactic acid porous membrane on the NCF surface of the polylactic acid fiber composite surface porous membrane material. From the SEM image, it can be seen that there are many polylactic acid membranes with nearly circular pores, and these pores are evenly distributed. Most of the pores are 1-31 μm in diameter and appear to be isolated from each other, usually at ...
Embodiment 2
[0033] 1) Weigh 5g of polylactic acid (PLA) with a number average molecular weight of 250,000 Daltons, dissolve it in 125mL of dichloromethane under stirring, and obtain a polylactic acid solution with a concentration gradient of 3.0wt% at room temperature;
[0034] 2) Dip the carbon nanofiber (NCF) into the polylactic acid solution with a concentration of 3.0wt% in step 1), take it out after 60 seconds, and place it in a fume hood to dry naturally.
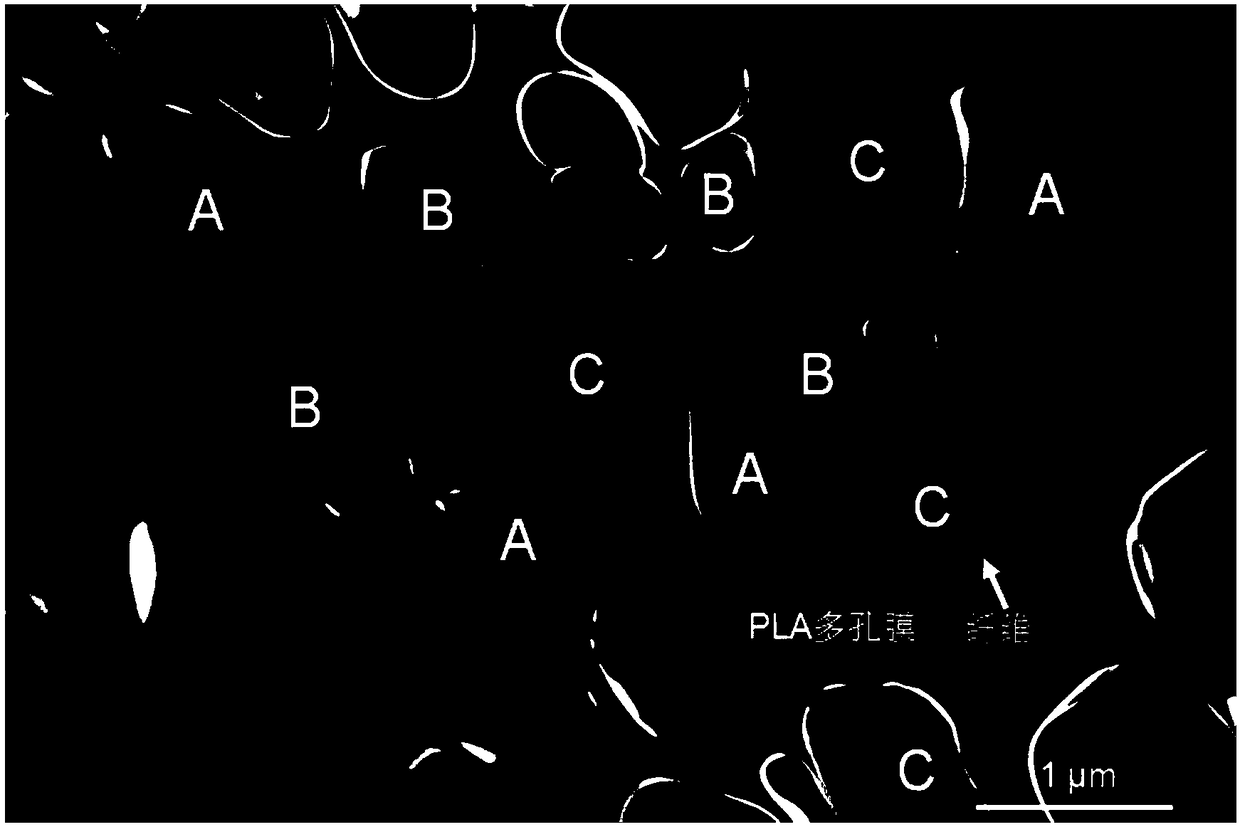
[0035] image 3 It is the SEM image of different pores in the polylactic acid fiber composite surface porous membrane material. As shown in the figure, there are other different pore arrangements on the surface of the NFC fiber, showing different pore morphology types: A is non-circular and deformed Pores; B are shallow pores indicating that they only contain polymer and air and the NCF fibers below the polymer pores cannot be seen; C is a "complete" porous structure, which means that the fibers below the polymer pores are still ...
Embodiment 3
[0037] 1) Weigh 5g of polylactic acid (PLA) with a number average molecular weight of 250,000 Daltons, dissolve it in 100mL of dichloromethane under stirring, and obtain a polylactic acid solution with a concentration gradient of 3.5wt% at room temperature;
[0038] 2) Immerse the carbon nanofiber (NCF) in the polylactic acid solution with a concentration of 3.5wt% in step 1), take it out after 60 seconds, and place it in a fume hood to dry naturally.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Number average molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com