Silicon briquette machining method
A processing method and technology for silicon blocks, which are applied to the processing of silicon blocks and ingot polycrystalline processing, can solve the problems of large fluctuations in cutting quality, waste of silicon materials and steel wires, and increased costs, so as to solve the problems of diamond wear and fall off, The effect of comprehensive wire reduction and good processing quality
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
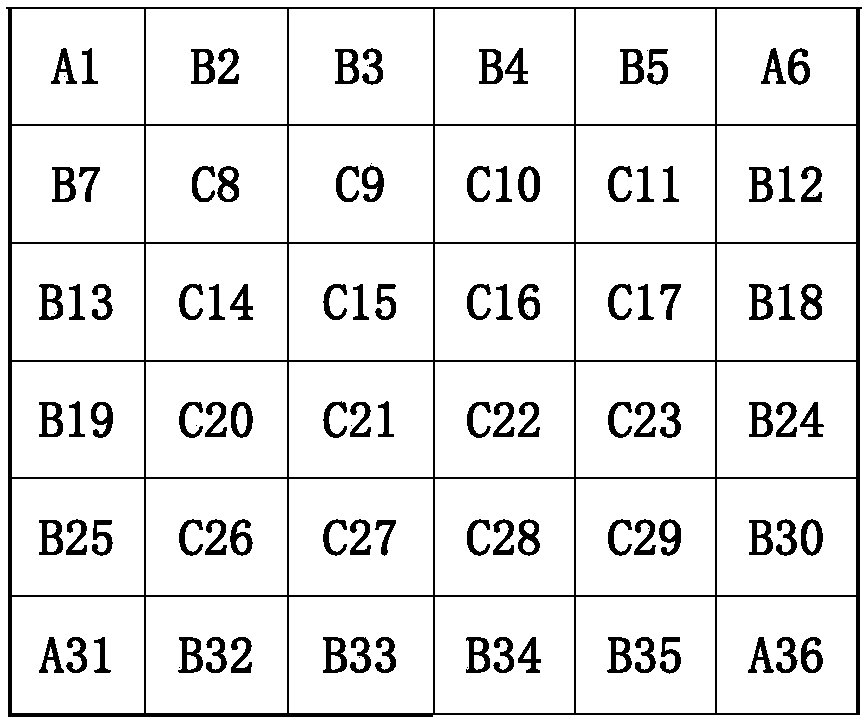
[0052] First, select the G6 ingot, and cut the polycrystalline ingot to obtain 36 silicon square rods of the same size (for a schematic diagram, see figure 1 , A, B and C series labels in the figure indicate that the contact surfaces with the crucible during ingot preparation are two surfaces, one surface and zero surface respectively).
[0053] A1
B2
B3
B4
B5
A6
B7
C8
C9
C10
C11
B12
B13
C14
C15
C16
C17
B18
B19
C20
C21
C22
C23
B24
B25
C26
C27
C28
C29
B30
A31
B32
B33
B34
B35
A36
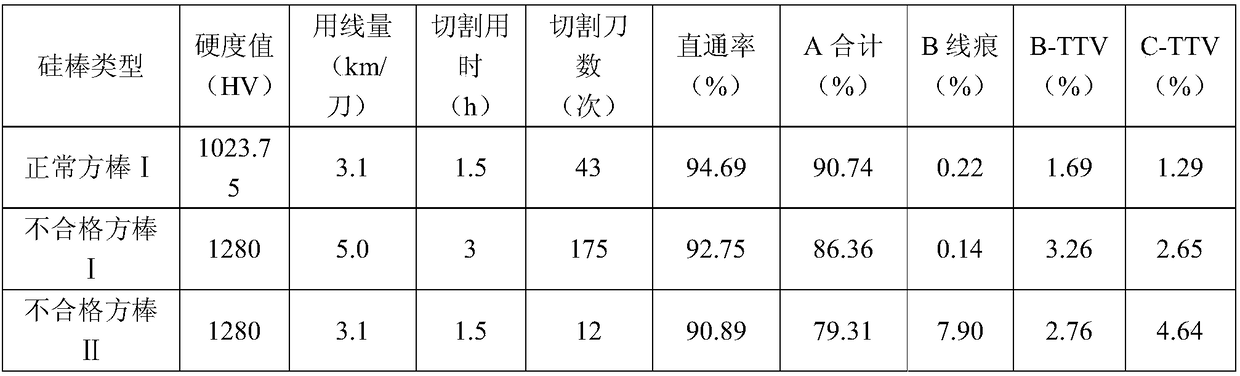
[0054] Secondly, the micro-Vickers hardness of the above 36 silicon rods was respectively tested using a Vickers micro-hardness tester.
[0055] Again, the square bars are classified according to the test values of the above 36 square bars (see Table 2 for details).
[0056] Then, formulate the corresponding cutting process according to the hardness classification (s...
Embodiment 2
[0069] Except for the following content, other content is identical with embodiment 1:
[0070] After the cutting is completed, the steps of mechanical energy degumming, cleaning and sorting are carried out to complete the processing of polycrystalline diamond wire slices.
[0071] This embodiment also has excellent effects similar to those of Embodiment 1, and the obtained slices are of high quality and have less overall wire consumption.
Embodiment 3
[0073] The hardness of the G6 ingot is detected by conventional methods in the prior art, and then a corresponding cutting process is specified according to the hardness value to perform diamond wire slicing.
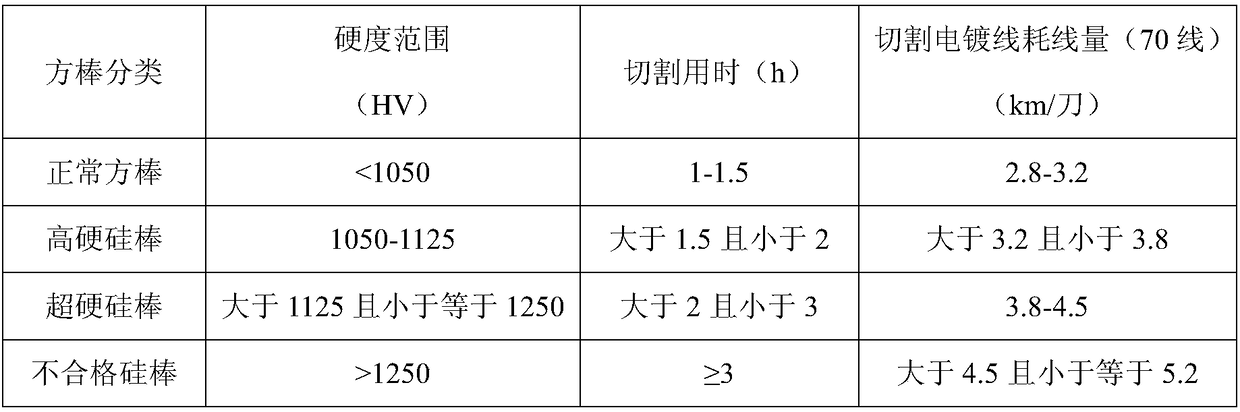
[0074] The relationship between cutting process and ingot hardness is as follows:
[0075] If the hardness of the ingot is less than 1050HV, the cutting time is 1h-1.5h, and the consumption of diamond wire for cutting is 2.8km / knife-3.2km / knife;
[0076] If the hardness of the ingot is 1050HV-1125HV, the cutting time is greater than 1.5h and less than 2h, and the consumption of diamond wire for cutting is greater than 3.2km / knife and less than 3.8km / knife;
[0077] If the hardness of the ingot is greater than 1125HV and less than or equal to 1250HV, the cutting time is 2h-3h, and the consumption of diamond wire for cutting is 3.8km / knife-4.5km / knife;
[0078] If the hardness of the ingot is >1250HV, the cutting time is >3h, and the consumption of diamond wire for cutti...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Hardness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Hardness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Hardness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com