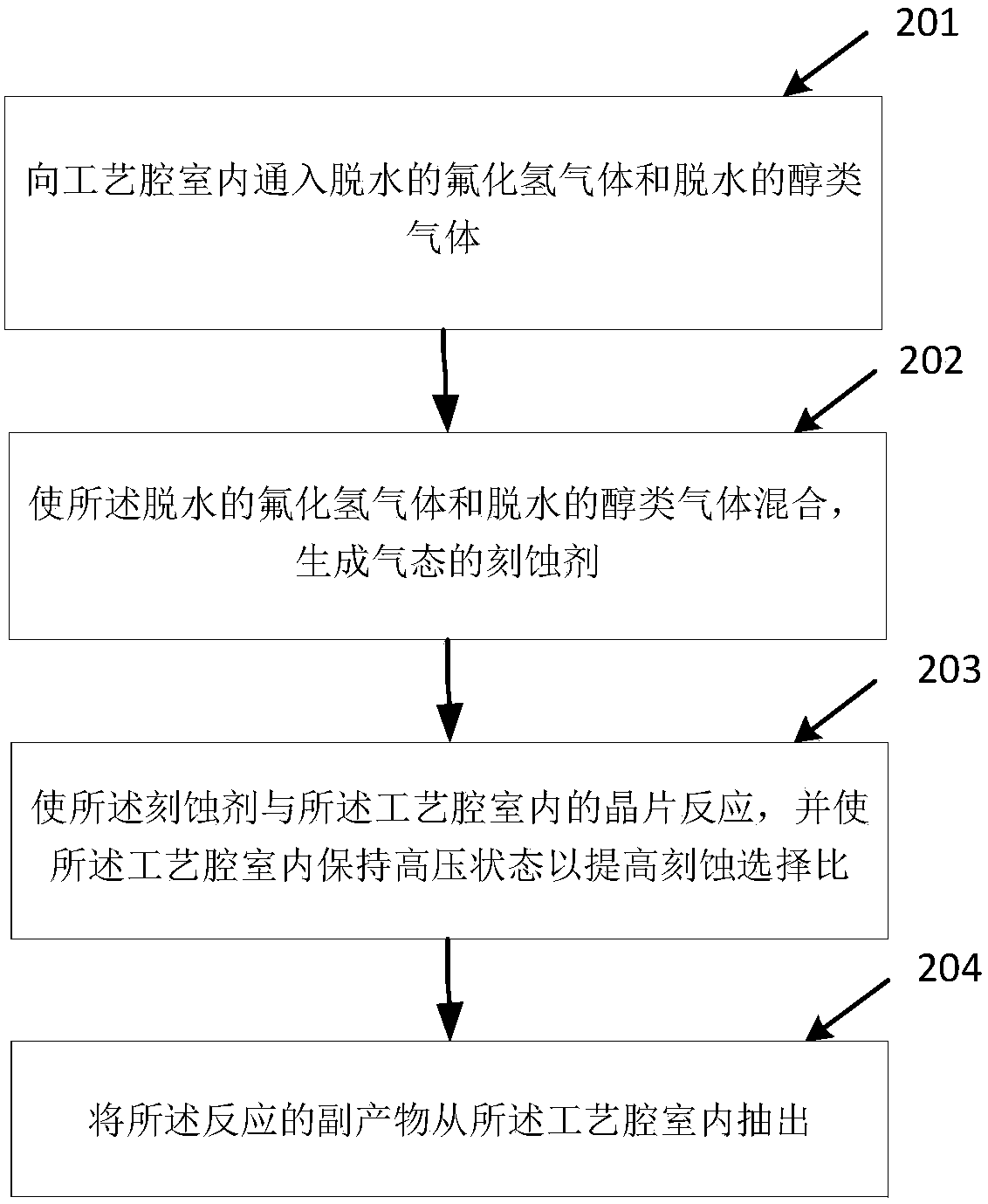
Method and manufacturing process for removing silicon dioxide from wafer
A technology of silicon dioxide and wafers, which is applied in semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturing, transistors, electrical components, etc., can solve the problems of shrinking isolation layer size, affecting device performance, and low etching selection, so as to reduce substrate damage and reaction The process is simple and the effect of less particles
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0054] Example 1: HARP fill shallow trench insulation layer profile adjustment (STI HAPR deposition gap fill profile modified):
[0055] Figure 4a , 4b and 4c respectively show schematic diagrams of HARP filled shallow trench insulating layer profile adjustment according to the prior art, wherein, Figure 4a For devices after STI (Shallow Trench Isolation) etching, Figure 4b For devices during STI HARP deposition, Figure 4c A device that produces voids after STI HARP deposition; Figure 5a , 5b , 5c and 5d respectively show schematic diagrams of the effect of the method for removing silicon dioxide on the wafer according to the present invention in the process of adjusting the profile of the shallow trench insulating layer filled with HARP, wherein, Figure 5a For devices after STI (Shallow Trench Isolation) etching, Figure 5b For devices during STI HARP deposition, Figure 5c For adopting the method for removing the silicon dioxide on the wafer of the present i...
example 2
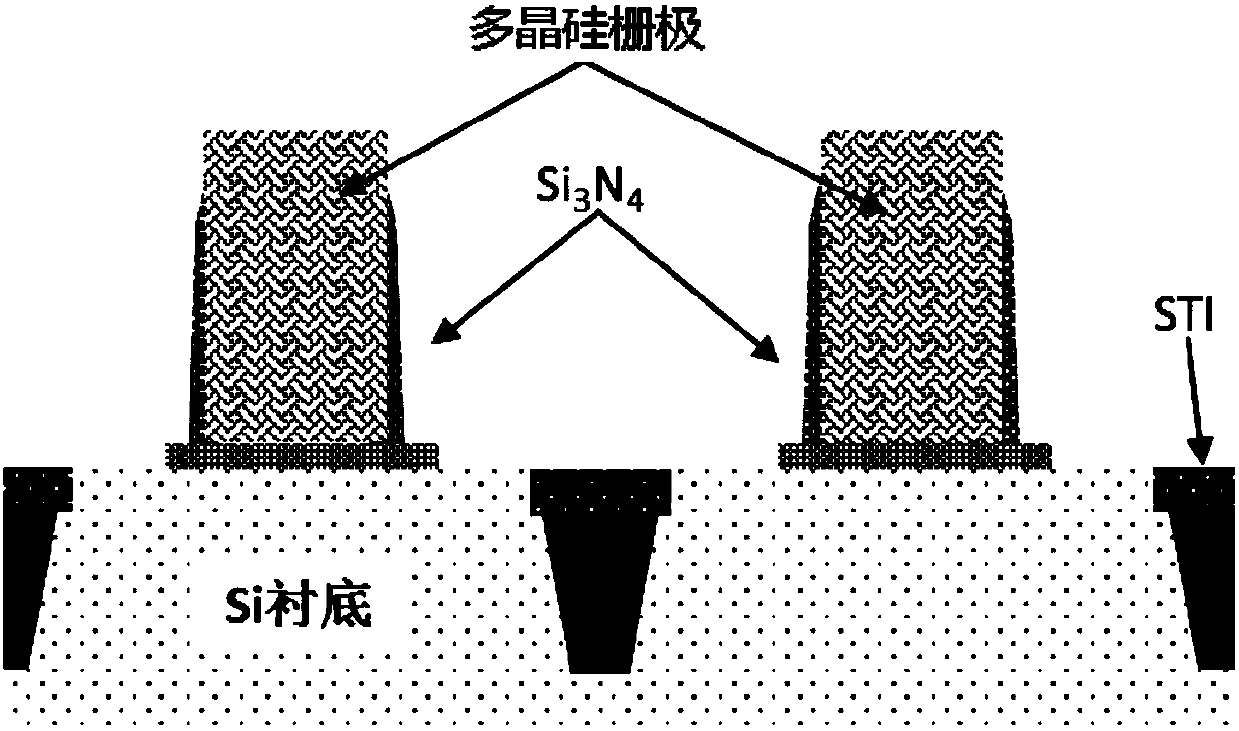
[0058] Example 2: STI Si 3 N 4 Natural oxide layer removal:
[0059] Figure 6a and 6b Schematic diagrams of a device with a natural oxide layer and a device after removing the natural oxide layer according to the method of the present invention are respectively shown.
[0060] In this example, the processing steps are the same as Example 1. Such as Figure 6a As shown, the integrated circuit manufacturing process uses Si 3 N 4 As the hard mask (Hard Mask) layer of STI, use H when removing 3 PO 4 Wet removal, after the wafer is placed in the air for a period of time on the Si 3 N 4 The surface of the layer will naturally oxidize a layer of dense SiO 2 layer, while H 3 PO 4 to SiO 2 The removal rate is very slow, so when removing Si 3 N 4 Before removing this layer of natural oxide layer. In addition, the step height of STI (referring to the height of STI above the substrate surface) will affect the electrical performance of the device. This height can neith...
example 3
[0061] Example 3: IC Pad oxide remove:
[0062] Figure 7a and 7b Schematic diagrams of a device with a pad oxide layer and a device after removing the pad oxide layer according to the method of the present invention are respectively shown.
[0063] In this example, the processing steps are the same as Example 1. Such as Figure 7a As shown, the pad oxide layer (Pad oxide) is used as the hard mask layer Si of STI 3 N 4 The buffer layer is thermally oxidized a layer of SiO on the surface of the substrate using a furnace tube method. 2 Layer, the thickness of the 28nm process is about 50A (different thicknesses are selected according to different processes), and it needs to be removed before the subsequent process is manufactured. In addition, STIHARP is SiO deposited by CVD 2 , low density, poor compactness, high etching rate. Etching SiO in prior art 2 The selection ratio of HARP is low, it is not easy to control the step height of STI, and at the same time, a depre...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com