User mobility supporting method distinguishing content in content centric networking (CCN)
A user mobility and mobility technology, applied in the network field, can solve the problems of wasting network bandwidth resources, unable to know user mobility status, and delay-sensitive real-time service impact.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
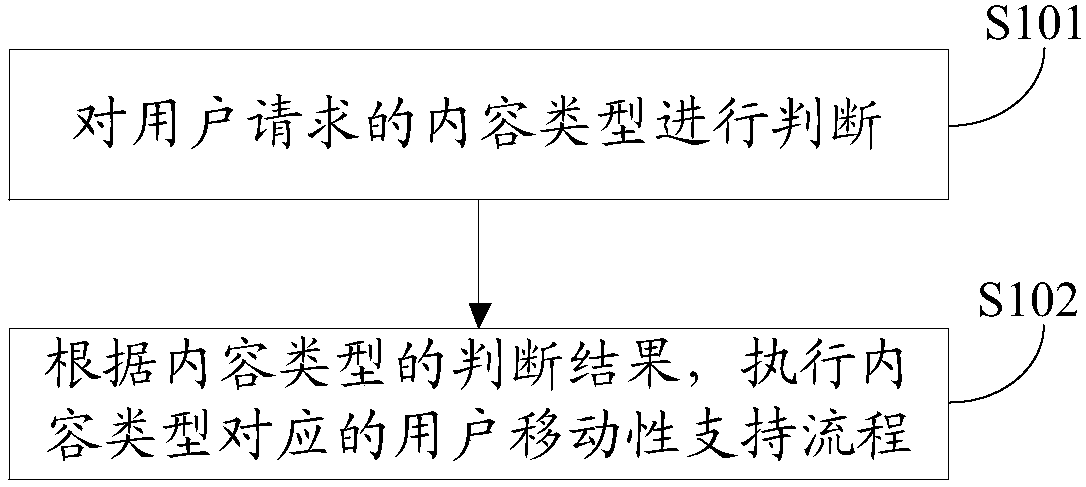
[0131] In the first embodiment of the present invention, a user mobility support method for distinguishing content in a CCN network, such as figure 1 shown, including the following specific steps:
[0132] Step S101, judging the content type requested by the user;
[0133] Content types include: fast forwarding type, guaranteed forwarding type and best effort type;
[0134] Step S102, according to the determination result of the content type, execute the user mobility support process corresponding to the content type;
[0135] Wherein, step S102 specifically includes:
[0136] If the content type is determined to be the fast forwarding type, execute the fast forwarding type user mobility support process;
[0137] If the content type is determined to be the guaranteed forwarding type, perform the guaranteed forwarding type user mobility support process;
[0138] If the content type is determined to be the best-effort type, perform the best-effort type user mobility support ...
no. 2 example
[0178] The second embodiment of the present invention, this embodiment introduces a user mobility support data structure device for distinguishing content, including the following components:
[0179] Content Store, Pending Interest Table, and Forwarding Information Base.
[0180] Wherein, the content storage is used to cache the data messages of the route nodes; any entry in the content storage is a cache entry; the content storage includes: the third content name, the data message and the first survival time.
[0181] The pending interest table is used to record the status of interest messages received by nodes but not yet consumed. Any entry in the pending interest table is a pending interest table item; the pending interest table includes: fourth content name, list and second survival time; wherein, the list includes: entry, mobile state flag and content type.
[0182] Wherein, if the mobile state flag bit is 0, the user requesting content corresponding to the content nam...
no. 3 example
[0186] In the third embodiment of the present invention, a method for processing user mobility support interest messages with different contents includes the following specific steps.
[0187] Step S301, judging the message subtype of the interest message received by the node.
[0188] Message subtypes of Interest messages include: normal forwarding, mobile retransmission, mobile support request, and active cache request.
[0189] Nodes include but are not limited to: users, content sources, users' original access routers, and user's new access routers.
[0190] Step S302, performing at least one matching judgment on the interest message according to the judgment result of step S301 and the set matching principle.
[0191] Specifically, step S302 includes:
[0192] Step S3021: If the message subtype of the interest message is determined to be normal forwarding or mobile retransmission, then determine whether the first content name of the interest message matches the cache en...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com