Inverter low voltage riding-through control method for weak network far-end severe voltage failure
A low voltage ride through and voltage fault technology, applied in the field of electrical information, can solve the problems of little research, inverter instability, inapplicability, etc., to improve the stability and dynamic control performance, and solve the effect of overshoot
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment
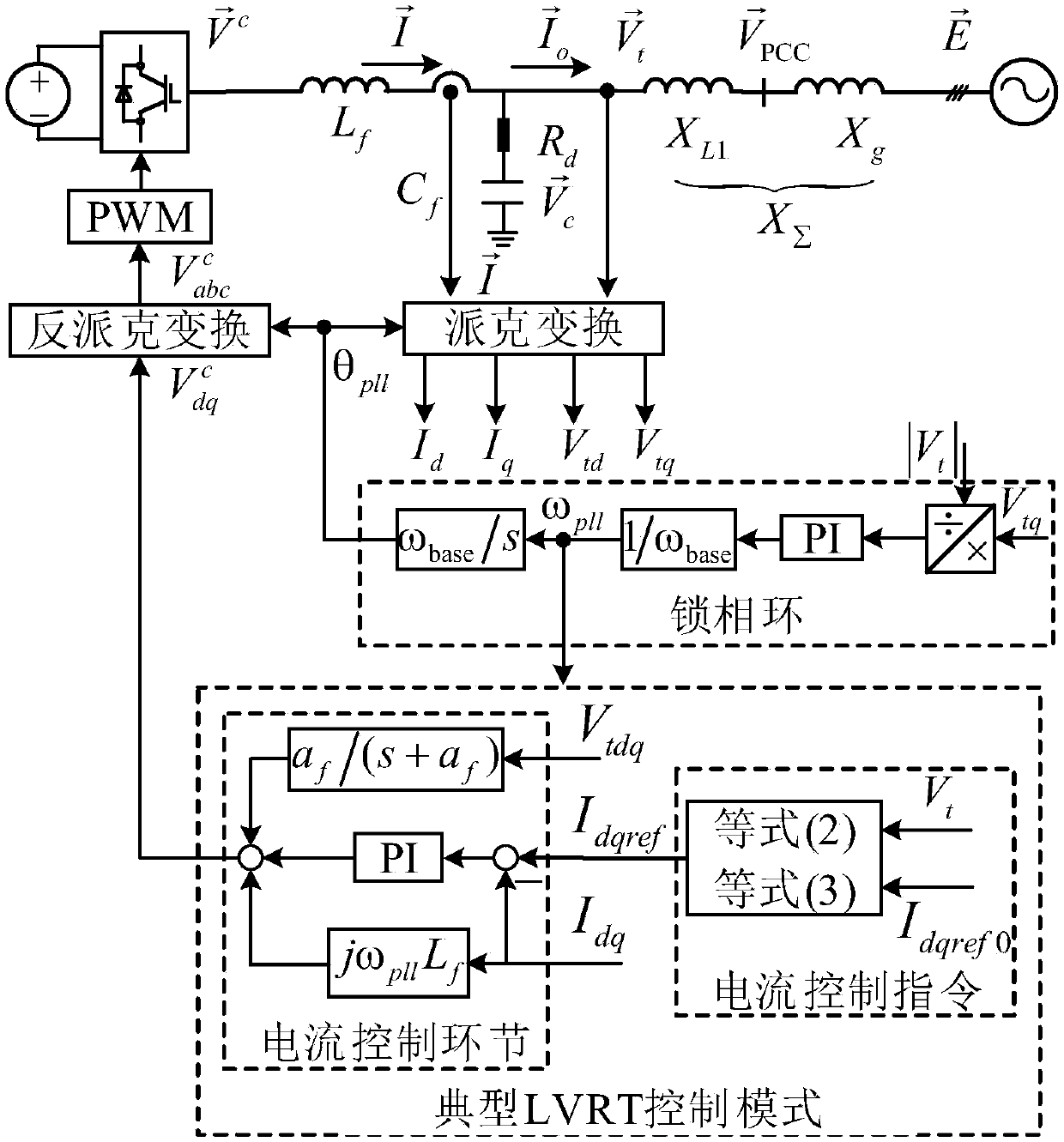
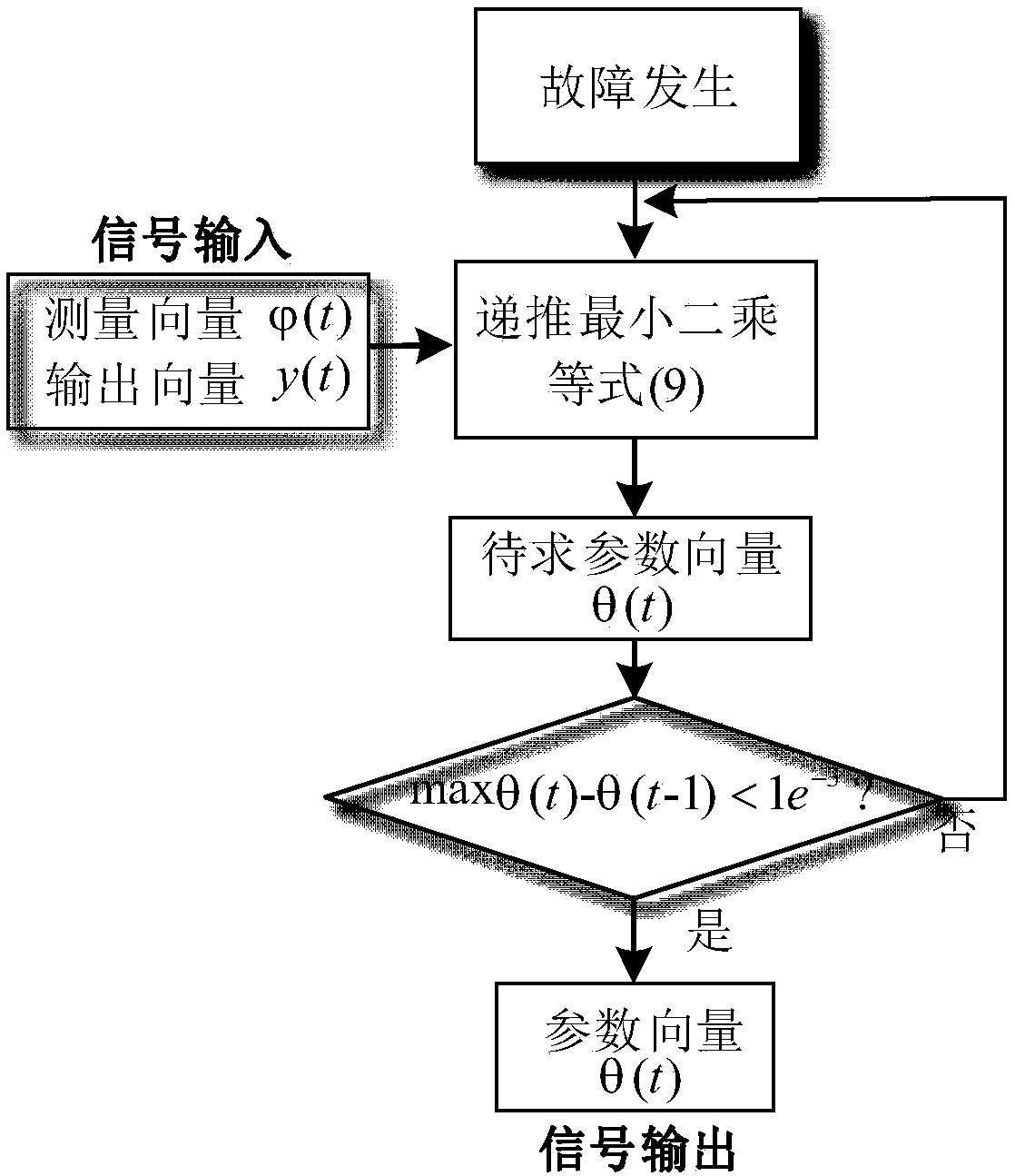
[0094] In order to verify the effectiveness of the proposed control strategy, in the MATLAB / Simulink environment figure 1 The system shown is simulated. The normal control mode of the inverter is "active power / AC voltage" control mode, and the system runs stably at P e = 0.6pu and V t = 1pu, t = 3s when the far-end voltage drop fault occurs. The main parameters are detailed in Table 3.
[0095] Figure 4 Given the line impedance X ∑ =0.8pu, the gain coefficient is k=4, and the voltage drop degree is E=0.2pu, the inverter terminal voltage waveform response curve. Depend on Figure 4 It can be seen that the inverter terminal voltage oscillates up and down around 0.9pu, causing the inverter control mode to switch back and forth between the pre-fault control mode and the typical low-voltage control mode, and the inverter becomes unstable.
[0096] Figure 5 Given the inverter equipped with the low voltage ride through control method proposed by the present invention, the l...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com