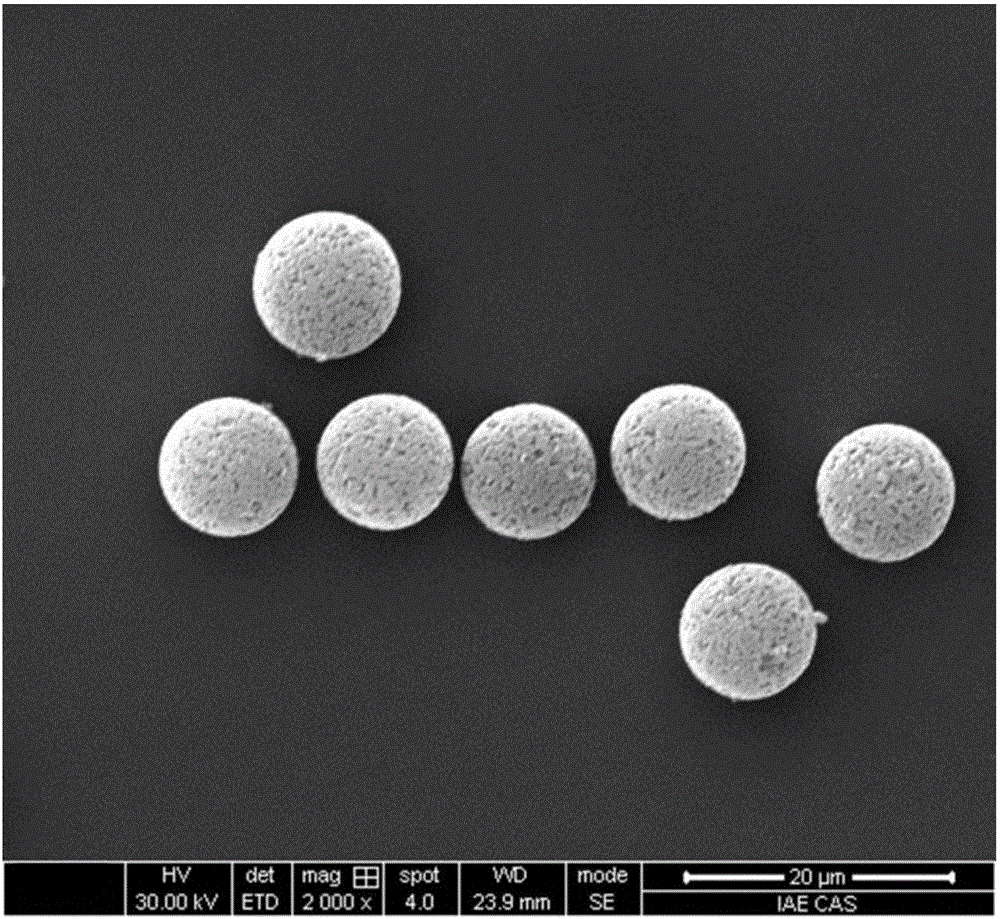
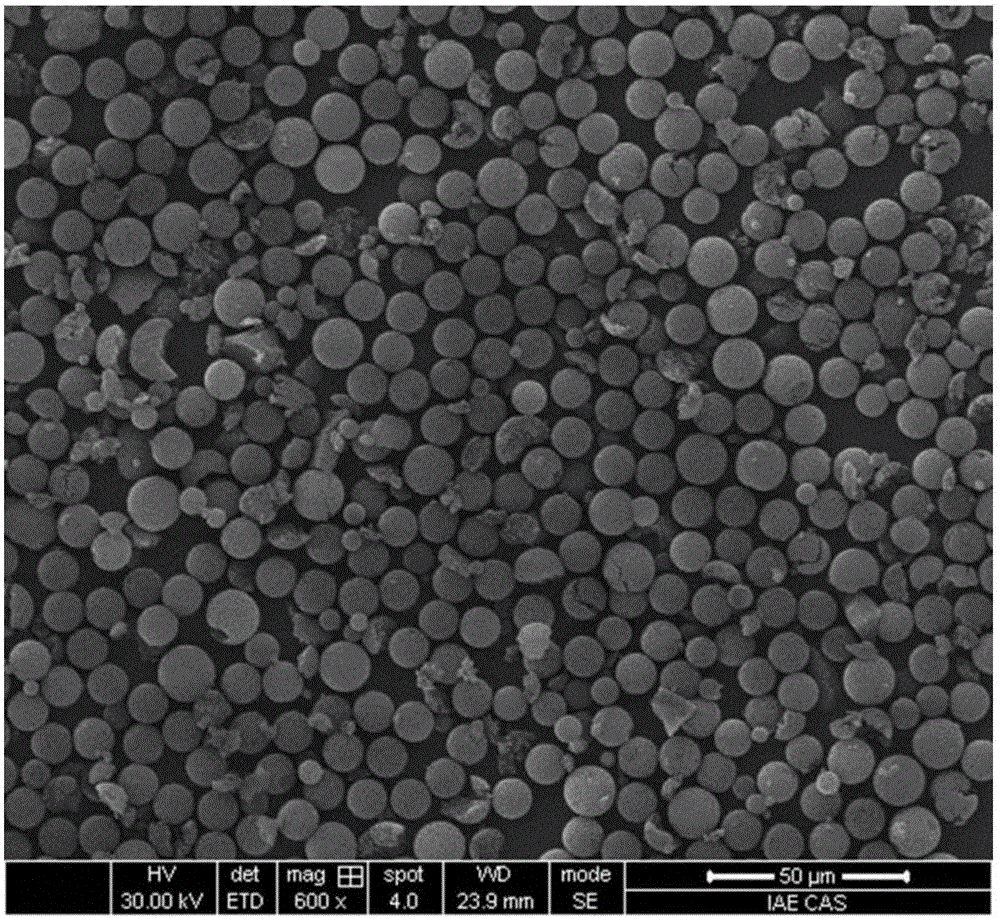
Molecular imprinting fluorescent microsphere array detection card and application thereof
A technology of molecularly imprinted microspheres and fluorescent microspheres, applied in the fields of material science and chemical analysis and detection, can solve the problems of cumbersome post-processing, and achieve the effects of shortening adsorption time, good biocompatibility, and large surface area.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
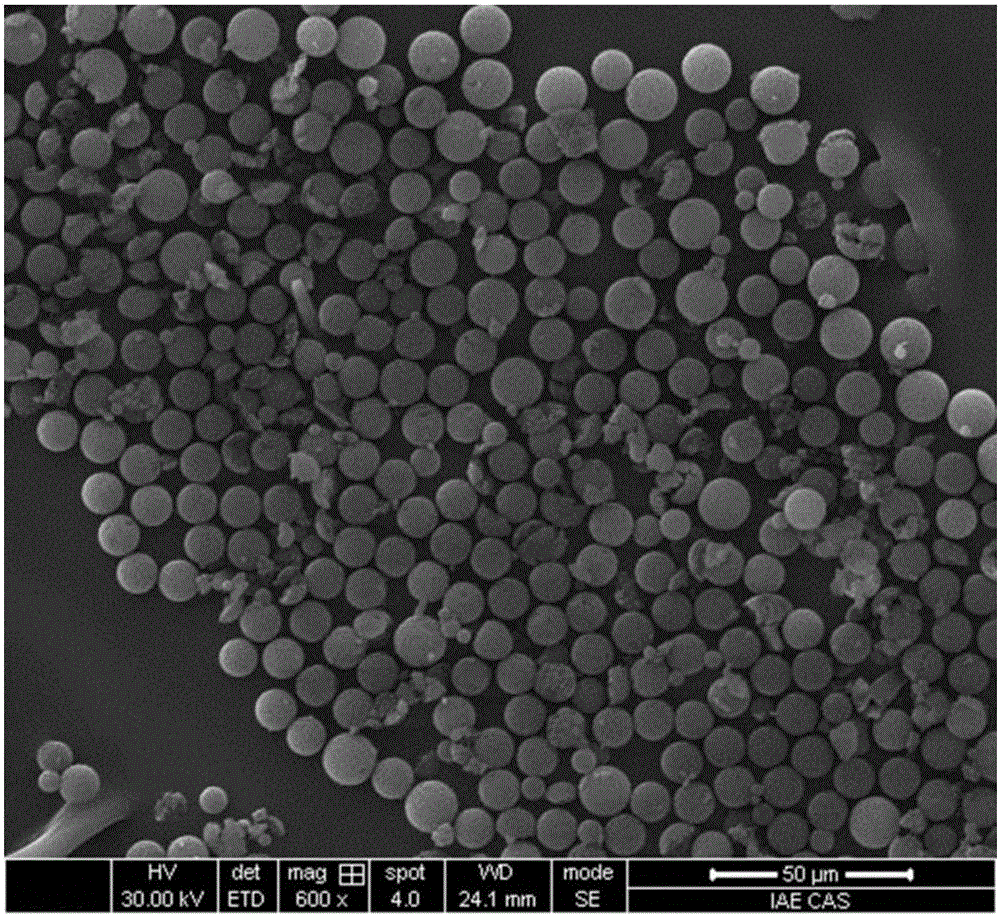
[0031] Example 1 (1) Preparation of Acephate Molecularly Imprinted Microspheres (MIPs)
[0032] Weigh 0.02g sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS), add 0.24mL dibutyl phthalate (DBP), 0.497g·mL -1 Polystyrene microspheres (Ps) microspheres 0.085mL, 10mL H 2 O, room temperature 25 ℃ 125rpm stirring swelling 15h, until the oil droplets disappeared. Add 0.1642g azobisisobutyronitrile (AIBN), 2.5mL toluene, 10mL4.8% polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) aqueous solution, 12.5mL H to the reaction system 2 O, stirring and swelling at room temperature 125rpm for 2h. Then add 0.1832g acephate, 0.344g methacrylic acid (MAA), 2.5mL ethylene glycol dimethacrylate (EDMA), 10mL4.8% PVA aqueous solution, 12.5mL H 2 O, stirring and swelling at room temperature for 2h. Finally, at 50°C, pass N 2protection, stirring at 180rpm for 24h, and the obtained particles were washed with methanol, hot water and tetrahydrofuran. After the reaction was completed, the obtained acephate molecularly imprinted microspheres (MI...
Embodiment 2
[0039] (1) Preparation of Acephate MIPs
[0040] Weigh 0.02g SDS, add 0.24mL DBP, 0.497g·mL -1 Ps microspheres 0.085mL, 10mL H 2 O, room temperature 25 ℃ 125rpm stirring swelling 15h, until the oil droplets disappeared. Add 0.1642g AIBN, 2.5mL toluene, 10mL4.8% PVA aqueous solution, 12.5mL H to the reaction system 2 O, stirring and swelling at room temperature 125rpm for 2h. In the reaction system, add 0.1832g acephate, 0.344g MAA, 2.5mL EDMA, 10mL4.8% PVA aqueous solution, 12.5mL H 2 O, stirring and swelling at room temperature for 2h. Finally, at 50°C, pass N 2 protection, stirring at 180rpm for 24h, and the obtained particles were washed with methanol, hot water and tetrahydrofuran. After the completion of the reaction, the obtained MIPs were centrifuged to remove the supernatant, and then methanol: acetic acid = 9:1 (v / v) was used as a solvent, and Soxhlet extraction was performed at 95° C. for 12 hours. The template molecules were removed in total. The polymer was ...
Embodiment 3
[0047] (1) Preparation of Acephate MIPs
[0048] Weigh 0.02g SDS, add 0.24mL DBP, 0.497g·mL -1 Ps microspheres 0.085mL, 10mL H 2 O, stirred and swelled at room temperature at 125 rpm for 15 hours until the oil droplets disappeared. Add 0.1642g AIBN, 2.5mL toluene, 10mL4.8% PVA aqueous solution, 12.5mL H to the reaction system 2 O, stirring and swelling at room temperature 125rpm for 2h. In the reaction system, add 0.1832g acephate, 0.344g MAA, 2.5mL EDMA, 10mL4.8% PVA aqueous solution, 12.5mL H 2 O, stirring and swelling at room temperature for 2h. Finally, at 50°C, pass N 2 protection, stirring at 180rpm for 24h, and the obtained particles were washed with methanol, hot water and tetrahydrofuran. After the completion of the reaction, the obtained MIPs were centrifuged to remove the supernatant, and then methanol: acetic acid = 9:1 (v / v) was used as a solvent, and Soxhlet extraction was performed at 95° C. for 12 hours. The template molecules were removed in total. The ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| emission peak | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com