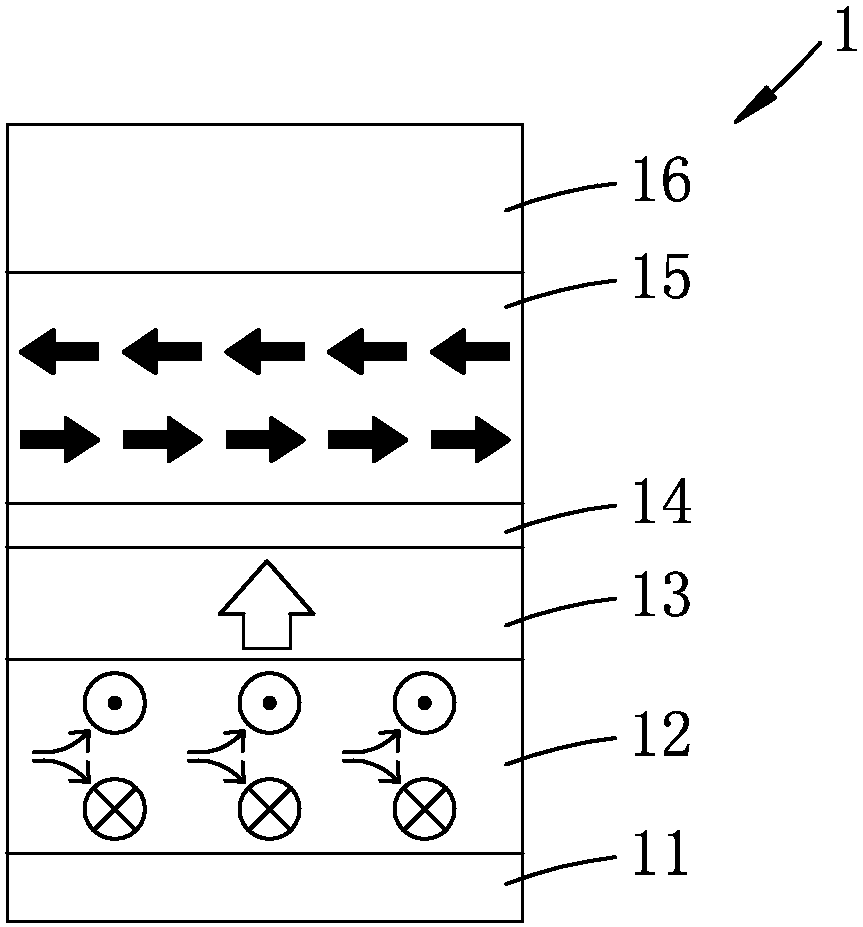
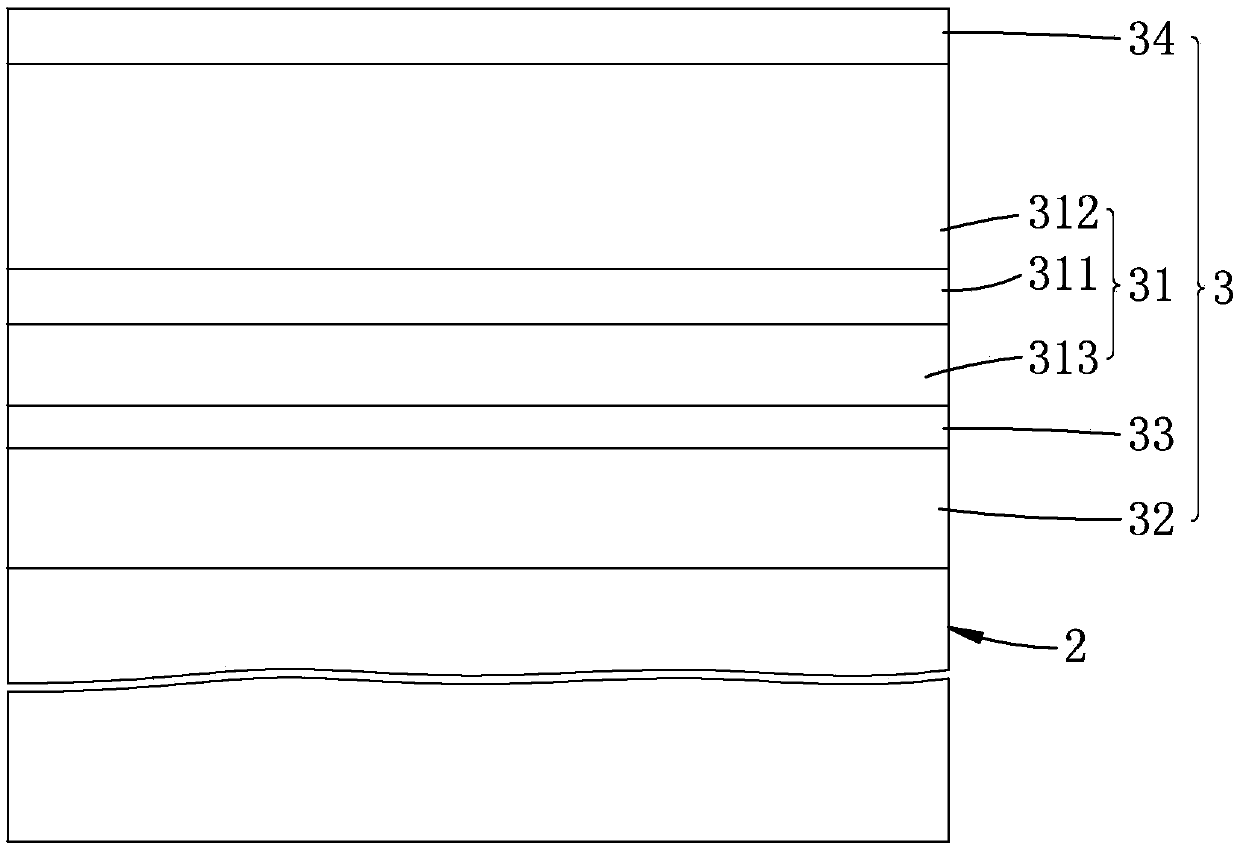
Thermally stable spin-orbit torsion magnetic random access memory
A technology of spin-orbit and thermal stability, applied in static memory, digital memory information, information storage, etc., can solve problems such as insufficient thermal stability, and achieve the effect of solving insufficient thermal stability and simplifying the MRAM manufacturing process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific example 1
[0061] A specific example 1 (E1) of the thermally stable spin-orbit torsion RAM of the present invention is substantially the same as the comparative example 1 (CE1), the difference being that the specific example 1 ( E1) is an Ir with a thickness of 8nm 20 mn 80 The alloy film is used as a second metal film of a magnetic free layer of the specific example 1 (E1); that is, a multilayer film formed on a silicon wafer of the specific example 1 (E1) is Ta(2.5 nm) / Pt(2nm) / Co(1.17nm) / Ir 20 mn 80 (8nm) / Pt(4nm) / Ta(2.5nm); and the magnetic free layer is Pt(2nm) / Co(1.17nm) / Ir 20 mn 80 (8nm).
specific example 2
[0063] A specific example 2 (E2) of the thermally stable spin-orbit torsion RAM of the present invention is substantially the same as the comparative example 1 (CE1), and the difference is that the specific example 2 ( E2) is an Ir with a thickness of 10nm 20 mn 80 The alloy film is used as a second metal film of a magnetic free layer of the specific example 2 (E2); that is, a multilayer film formed on a silicon wafer of the specific example 2 (E2) is Ta(2.5 nm) / Pt(2nm) / Co(1.17nm) / Ir 20 mn 80 (10nm) / Pt(4nm) / Ta(2.5nm); and the magnetic free layer is Pt(2nm) / Co(1.17nm) / Ir 20 mn 80 (10nm).
specific example 3
[0067] A specific example 3 (E3) of the thermally stable spin-orbit torsion RAM of the present invention is substantially the same as the comparative example 2 (CE2), and the difference is that the specific example 3 ( E3) is an Ir with a thickness of 8nm 20 mn 80 The alloy film is used as a second metal film of a magnetic free layer of the specific example 3 (E3); that is, a multilayer film formed on a silicon wafer of the specific example 3 (E3) is Ta (2.5 nm) / Pt(2nm) / Co(0.88nm) / Ir 20 mn 80 (8nm) / Pt(4nm) / Ta(2.5nm); and the magnetic free layer is Pt(2nm) / Co(0.88nm) / Ir 20 mn 80 (8nm).
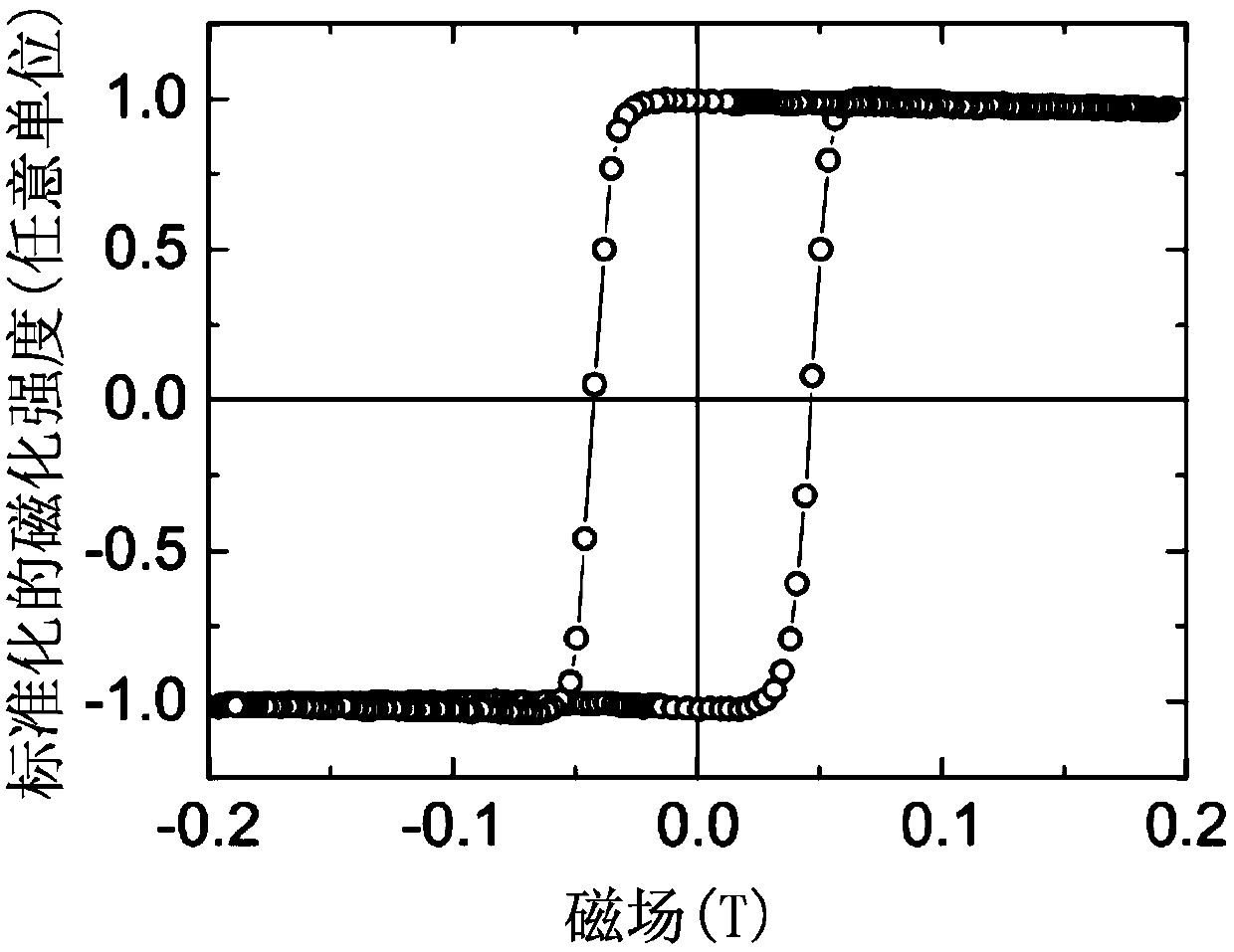
[0068] see again Figure 4 and Figure 5 , what needs to be further supplemented here is that when the present invention writes the comparative examples (CE1-CE2) and the specific examples (E1-E3) to analyze their magnetic properties, it uses a focusing vertical magneto-optical gram The focused polar magneto-optical Kerr effect system (focused polar magneto-optical Kerr effect system; h...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com