Rapid estimation method for determining synthesis proportion and chelation rate of microelement compound amino acid/small-peptide chelate through combination of spectrophotometric method and XRD (X-ray diffraction)
A compound amino acid and trace element technology, used in chemical, chemical, biochemical application fields, can solve the problems of long experiment time, small injection volume, large dilution multiple, etc., to ensure the chelation rate, strong applicability and fast method. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0026] Example 1 Preparation of copper chelate based on alfalfa protein enzymatic hydrolyzate.
[0027] 1 Determination of the appropriate reaction ratio of alfalfa protein hydrolyzate and copper chloride
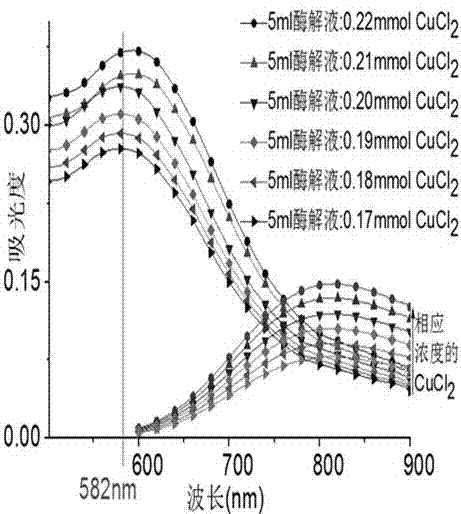
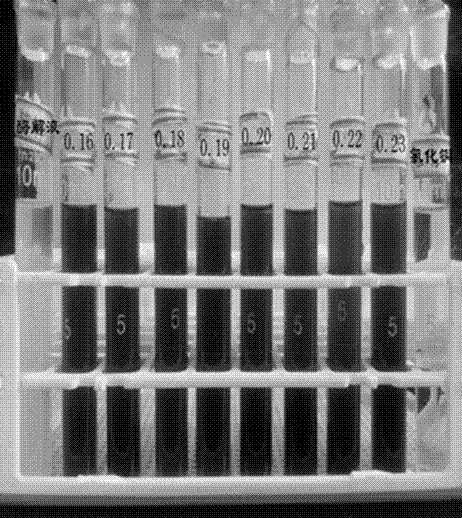
[0028] From figure 1 The visual colorimetry of the product shows that when 0.17-0.22 mmol copper chloride is added to 5 mL of alfalfa protein enzymatic hydrolyzate, the solution is dark blue, indicating that copper chelates are formed, but it is impossible to distinguish whether copper ions are excessive; figure 2 It can be seen that when 5mL proteolysis solution reacts with different amounts of copper chloride, there is a maximum absorption peak at 582nm, and when the amount of copper chloride is 0.20 mmol, the absorbance is the largest, and when the amount of copper chloride is 0.21 mmol, the chelate The absorption peak of the compound shifted red, indicating that copper chloride was excessive. Therefore, the ingredient ratio was preliminarily determined to be 5mL alfa...
Embodiment 2
[0031] Example 2 Preparation of copper chelate based on alfalfa protein acid hydrolyzate.
[0032] 1 Determination of the appropriate reaction ratio of alfalfa protein acid hydrolyzate and copper chloride
[0033] From Figure 5 The visual colorimetry of the product shows that when the amount of copper chloride added is 0.20-0.25 mmol, the solution is green, indicating that copper chelates are generated, but it is impossible to distinguish whether copper ions are excessive; Figure 6 It can be seen that when 5mL protein acid hydrolyzate reacts with different amounts of copper chloride, there is a maximum absorption peak at 615 nm, and when the copper chloride is 0.24 mmol, the absorbance is the maximum. When the amount of copper chloride continued to increase to 0.25 mmol, the absorption peak shifted red, indicating that the amount of copper chloride was excessive. Therefore, the ingredient ratio was preliminarily determined to be 5mL acid hydrolyzed protein solution: 0.24 ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com